22 Oct Acute Kidney Injury Reduction after Implementation of an ICU Visual Clinical Decision Support ToolA3

Acute Kidney Injury Reduction after Implementation of an ICU Visual Clinical Decision Support ToolA3
Background
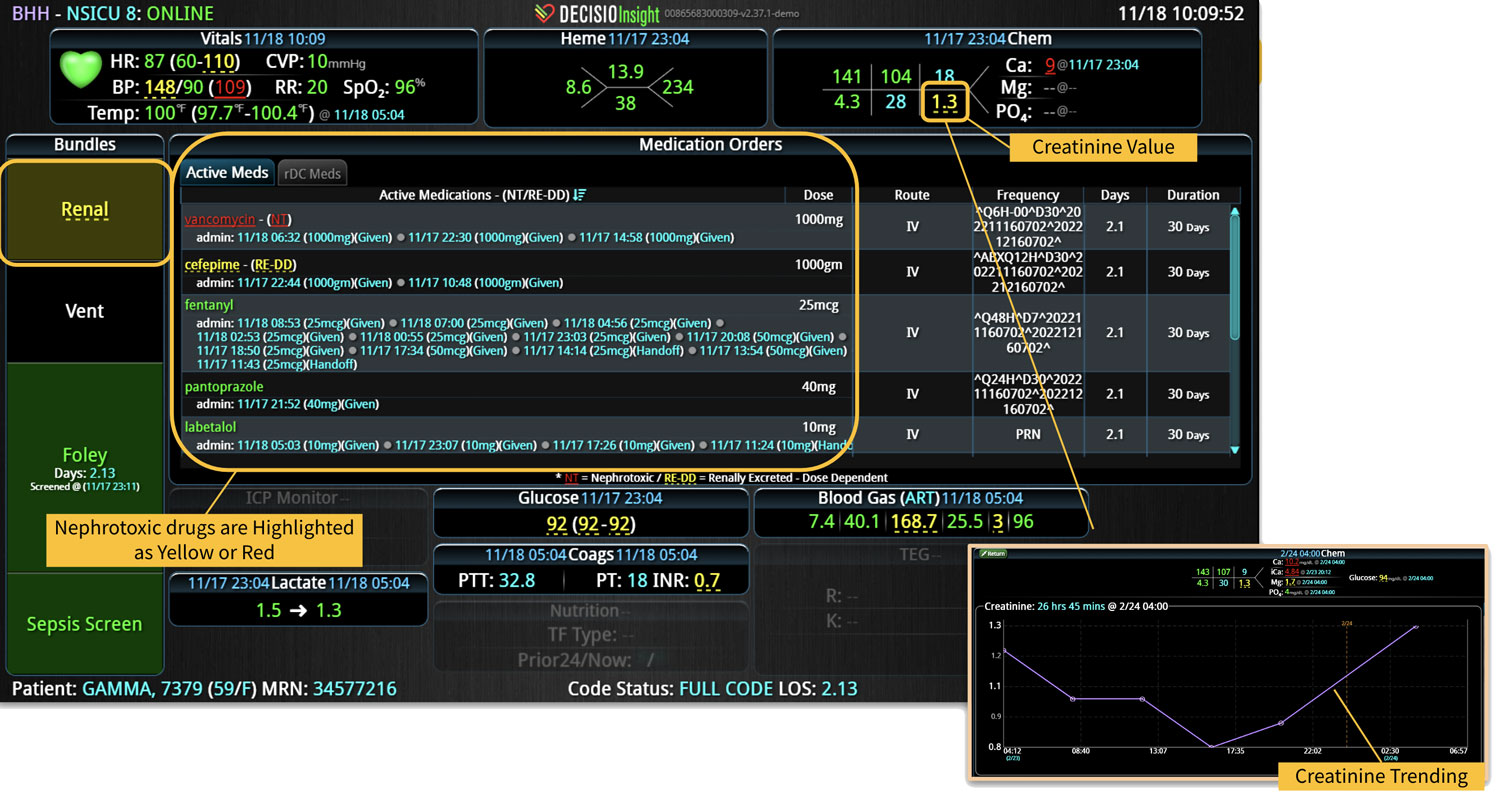
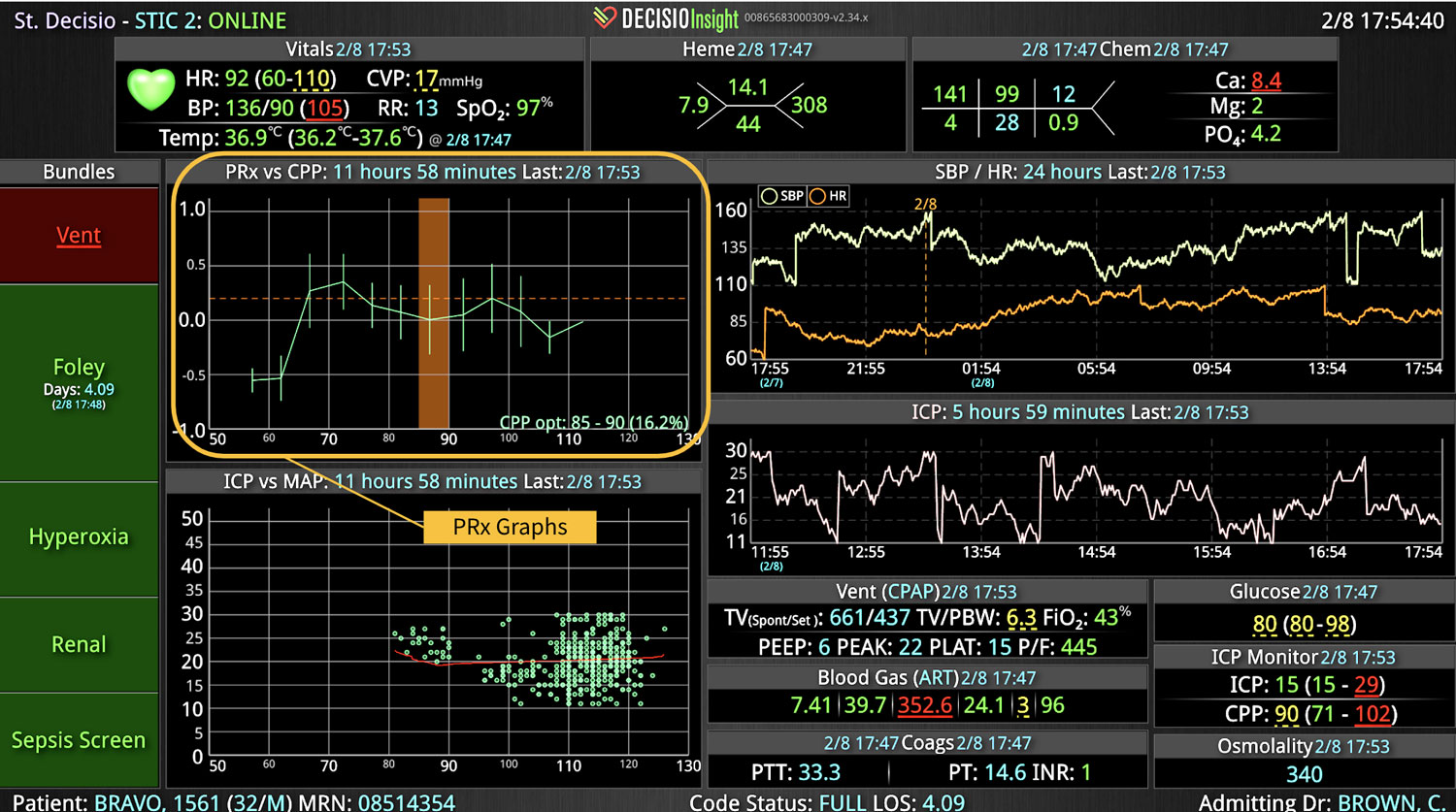
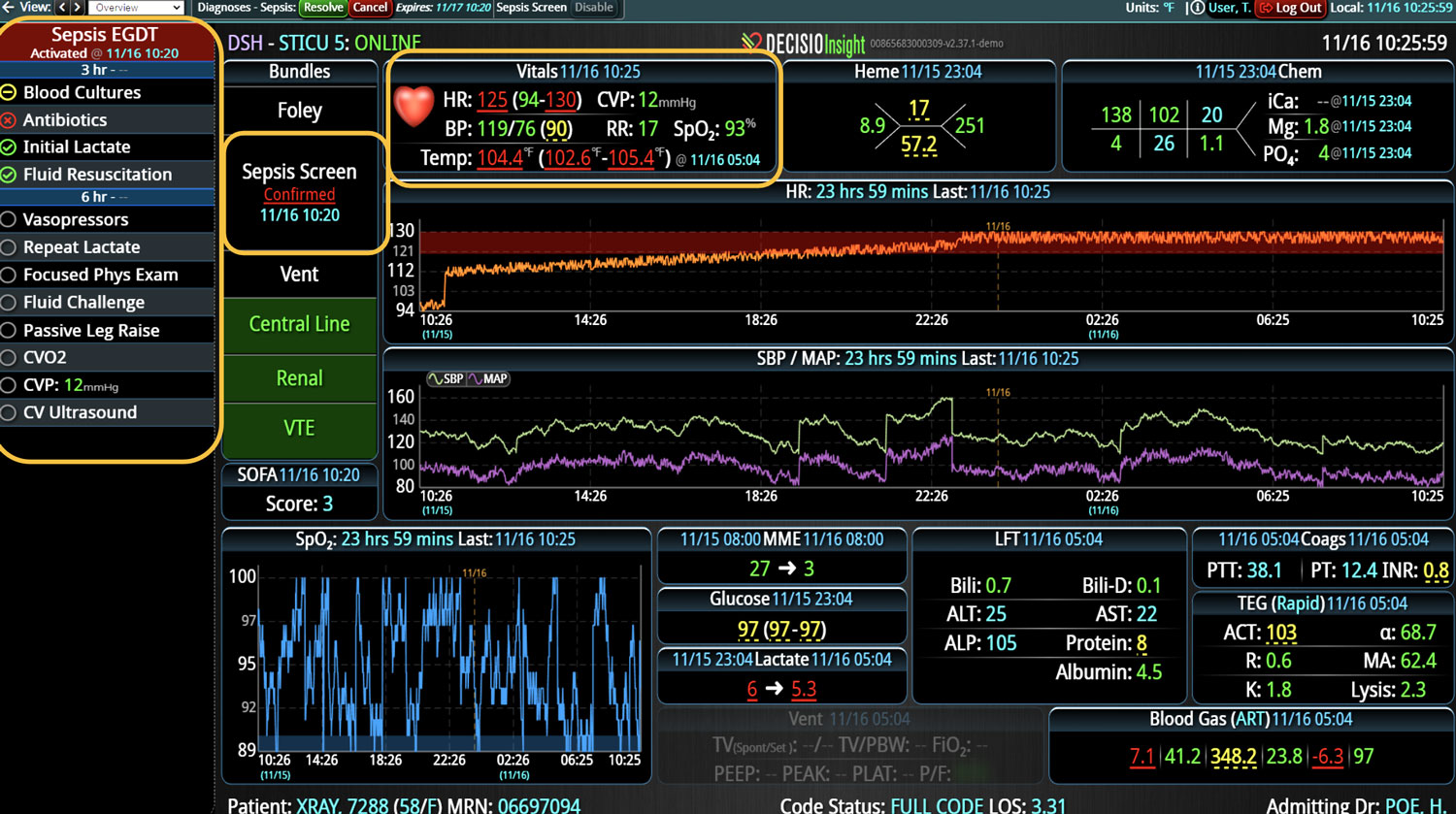
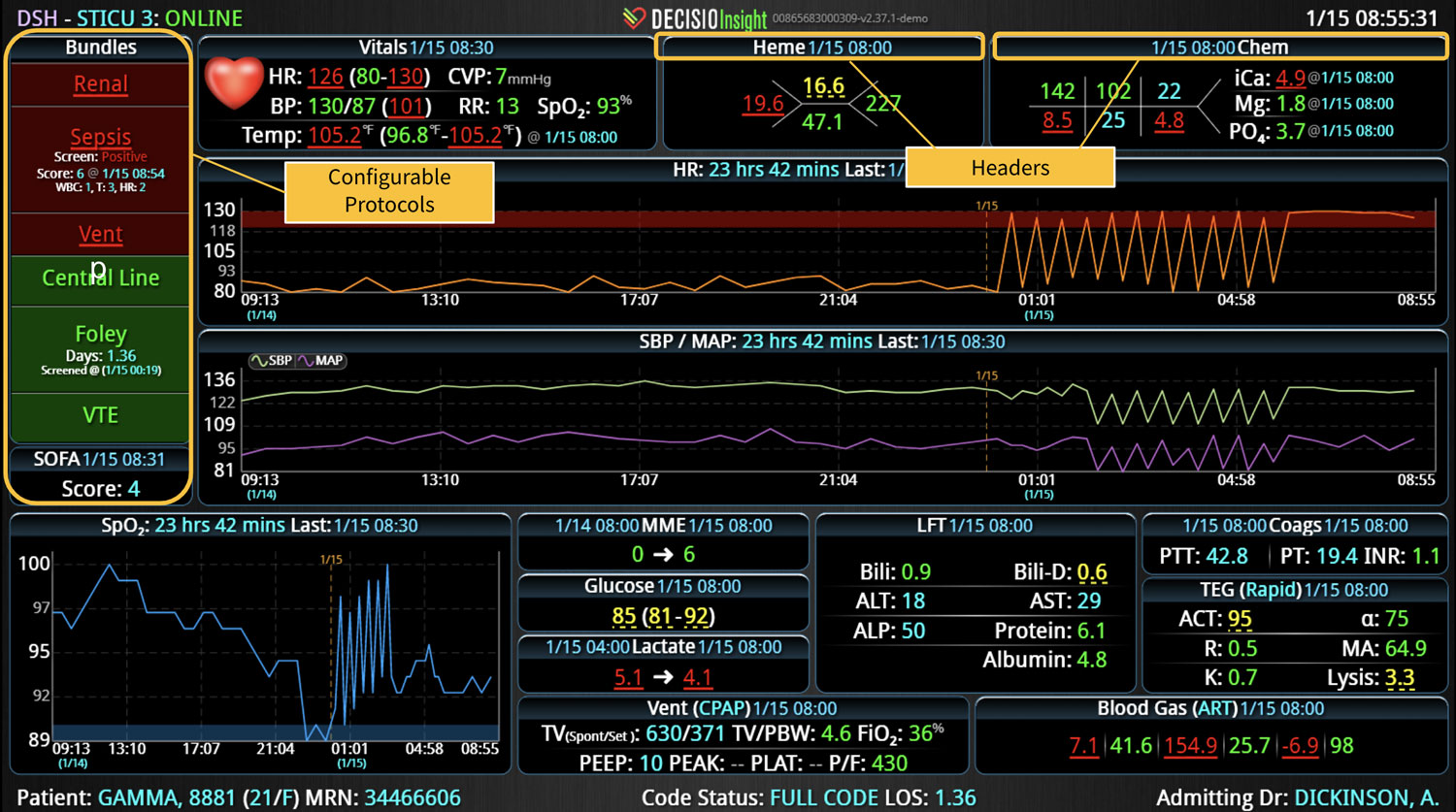
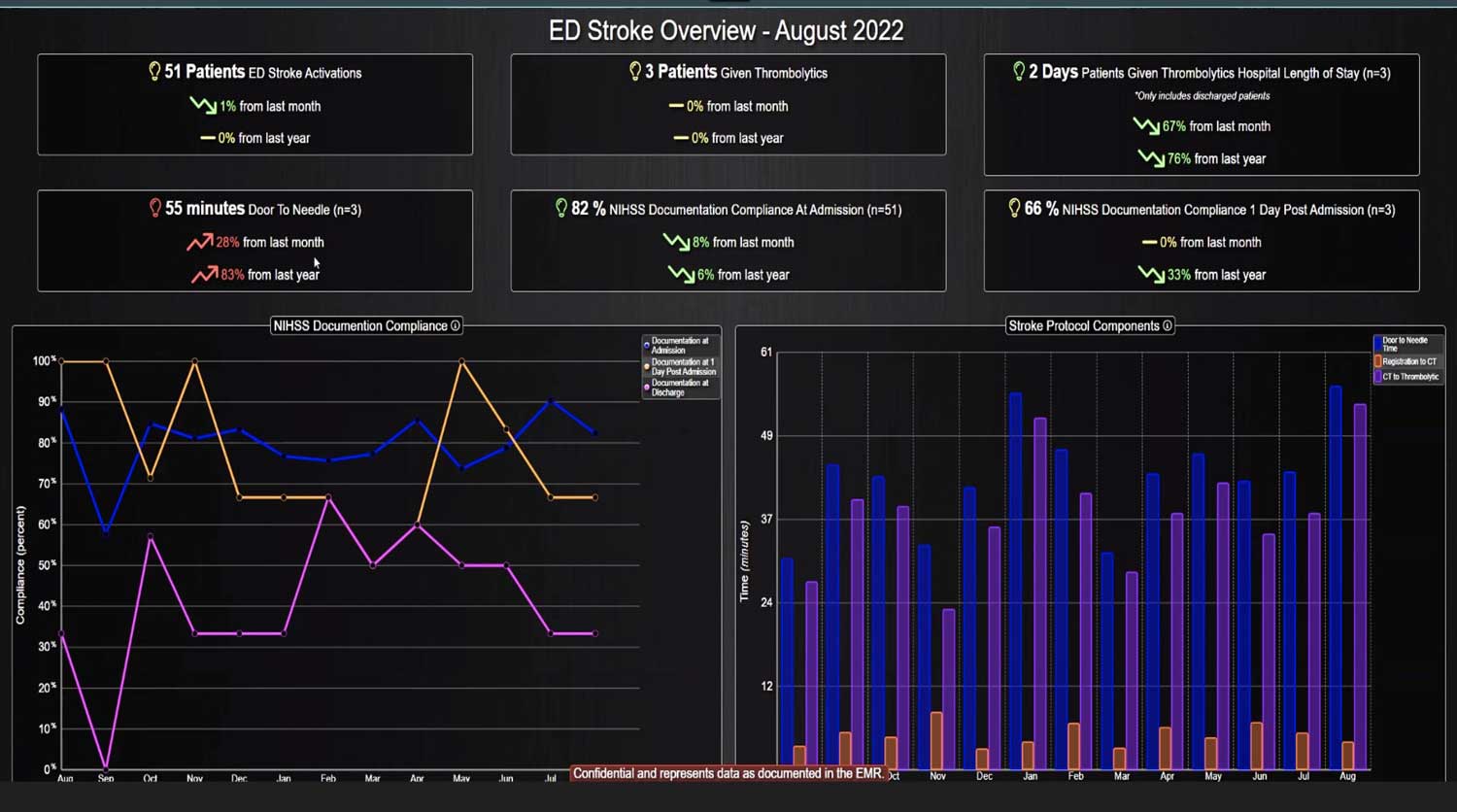
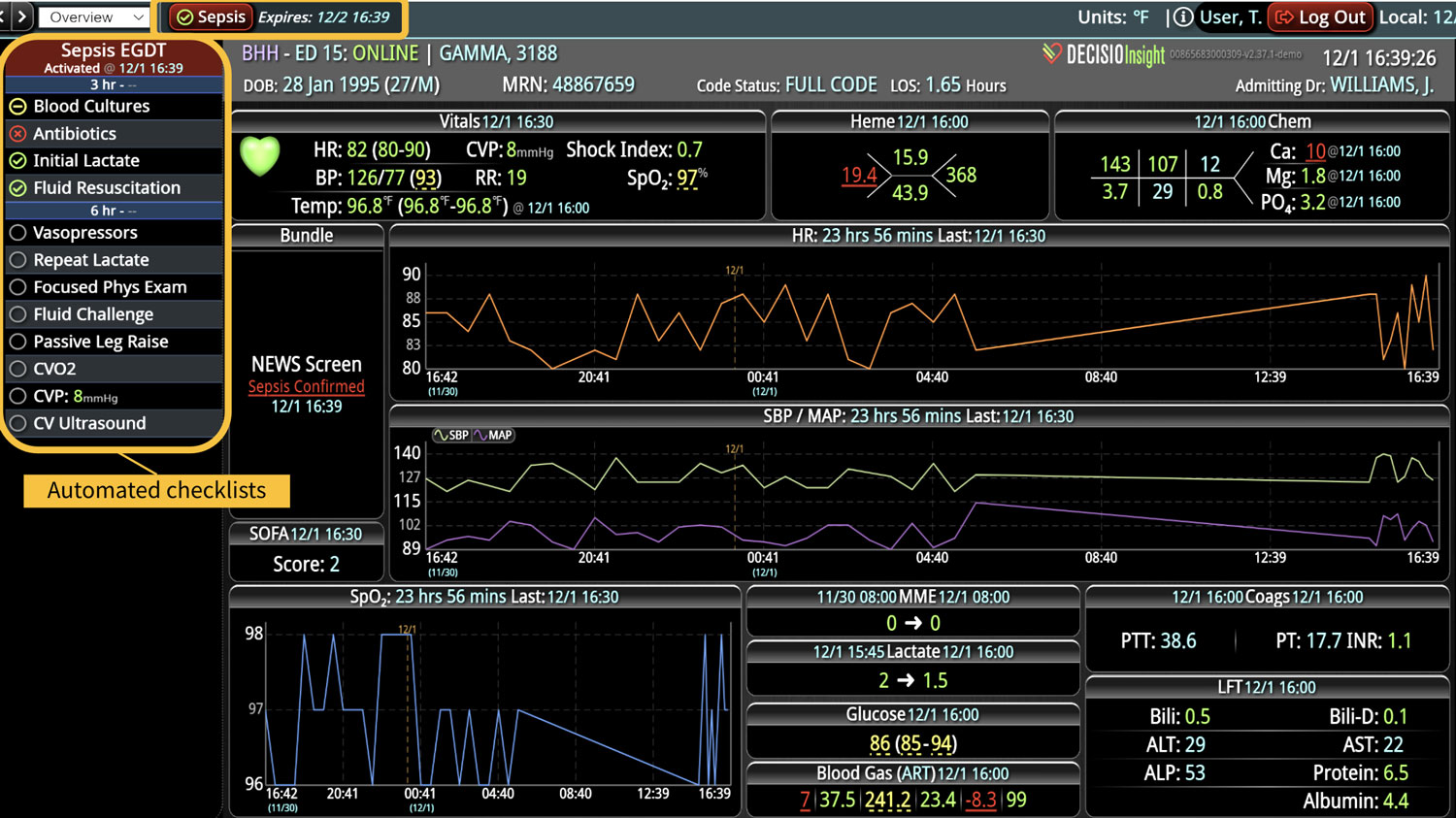
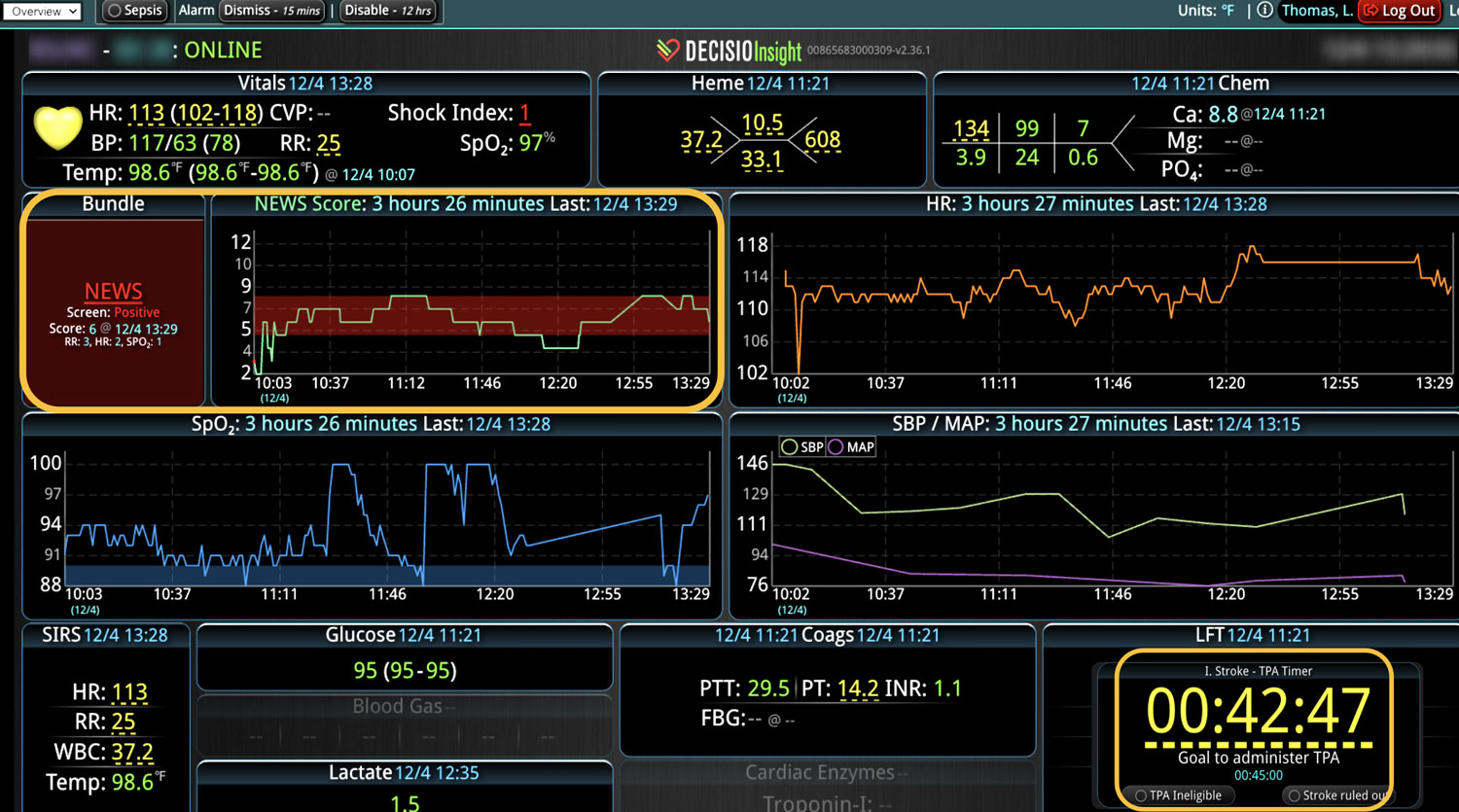
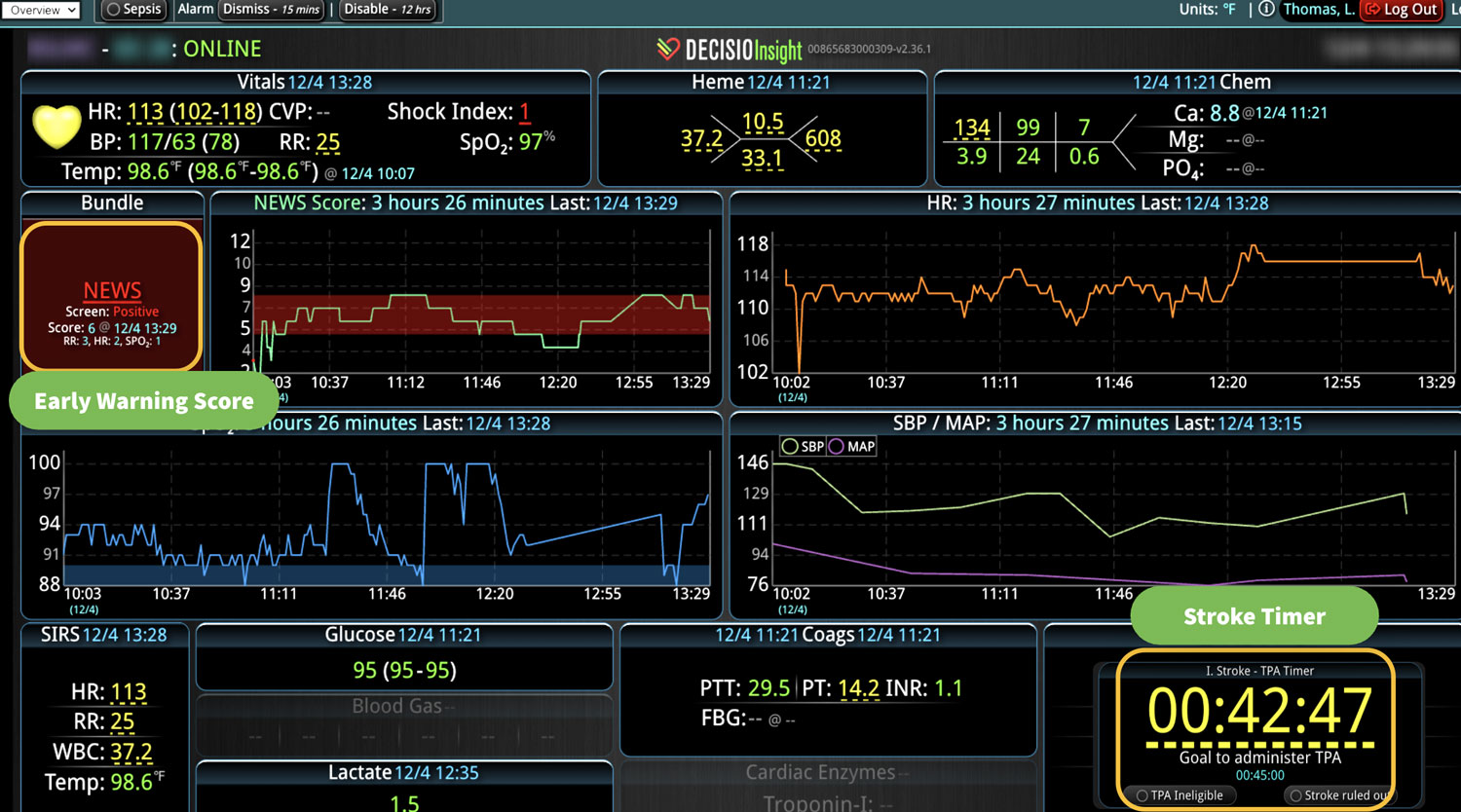
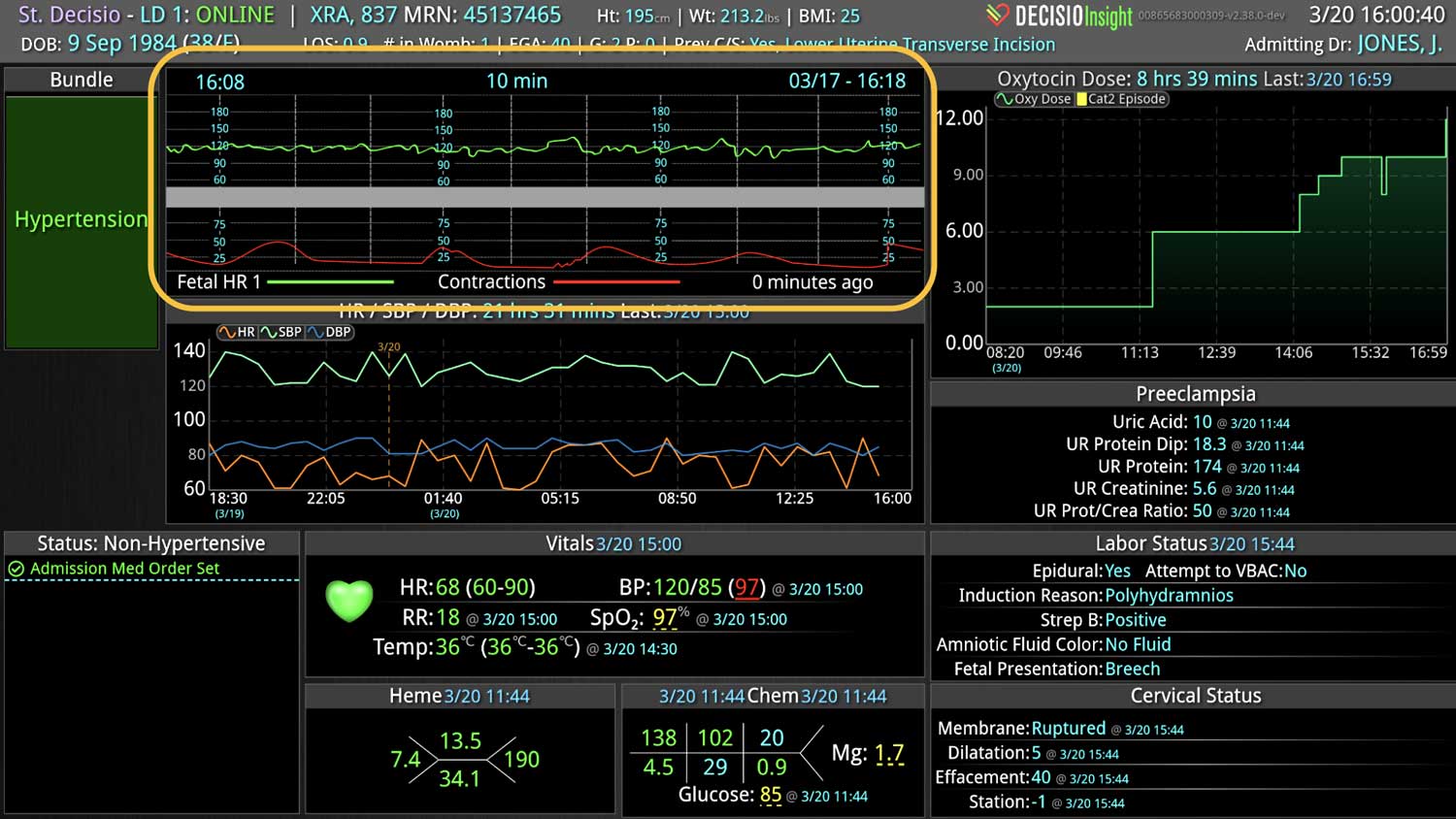
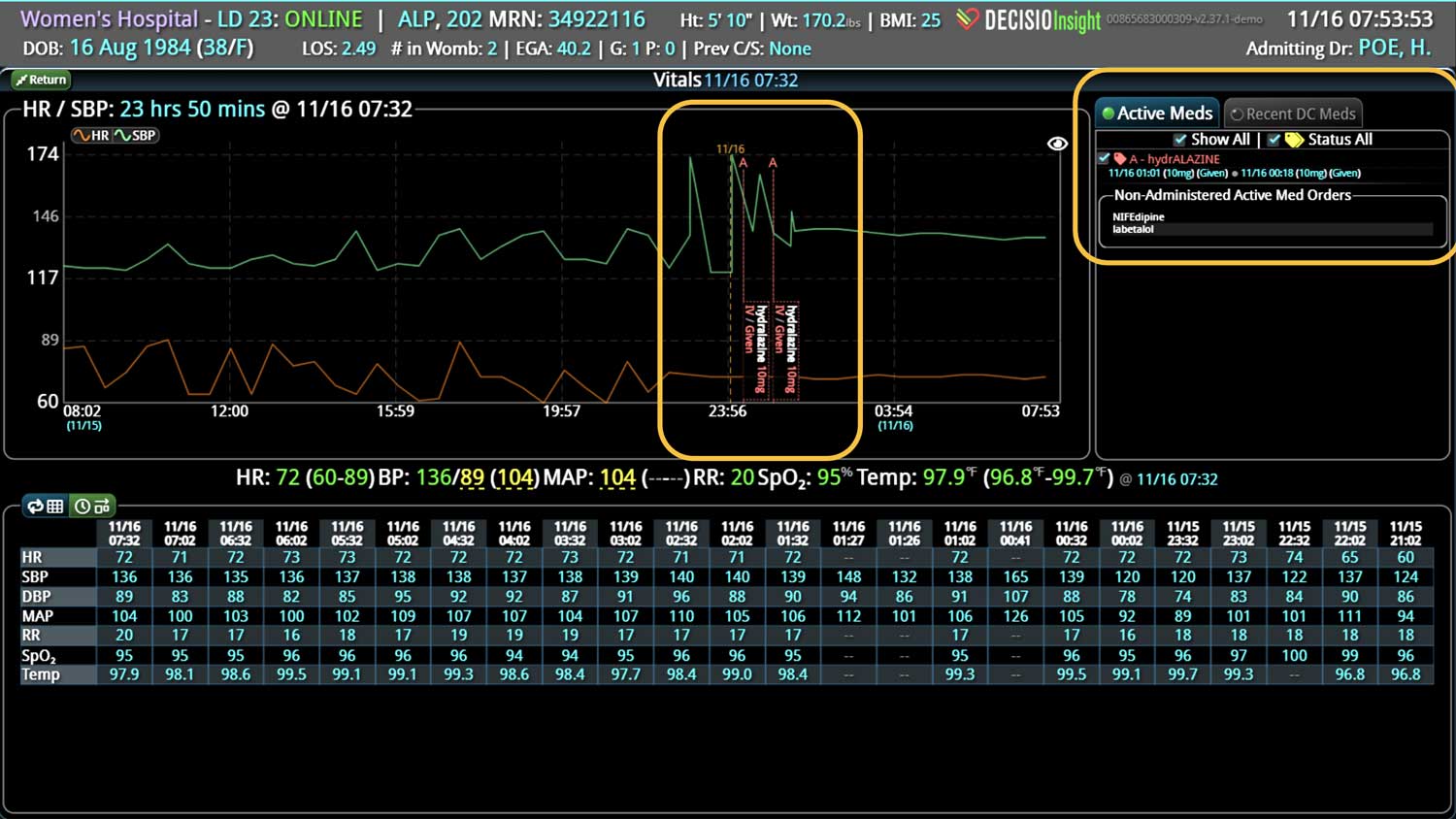
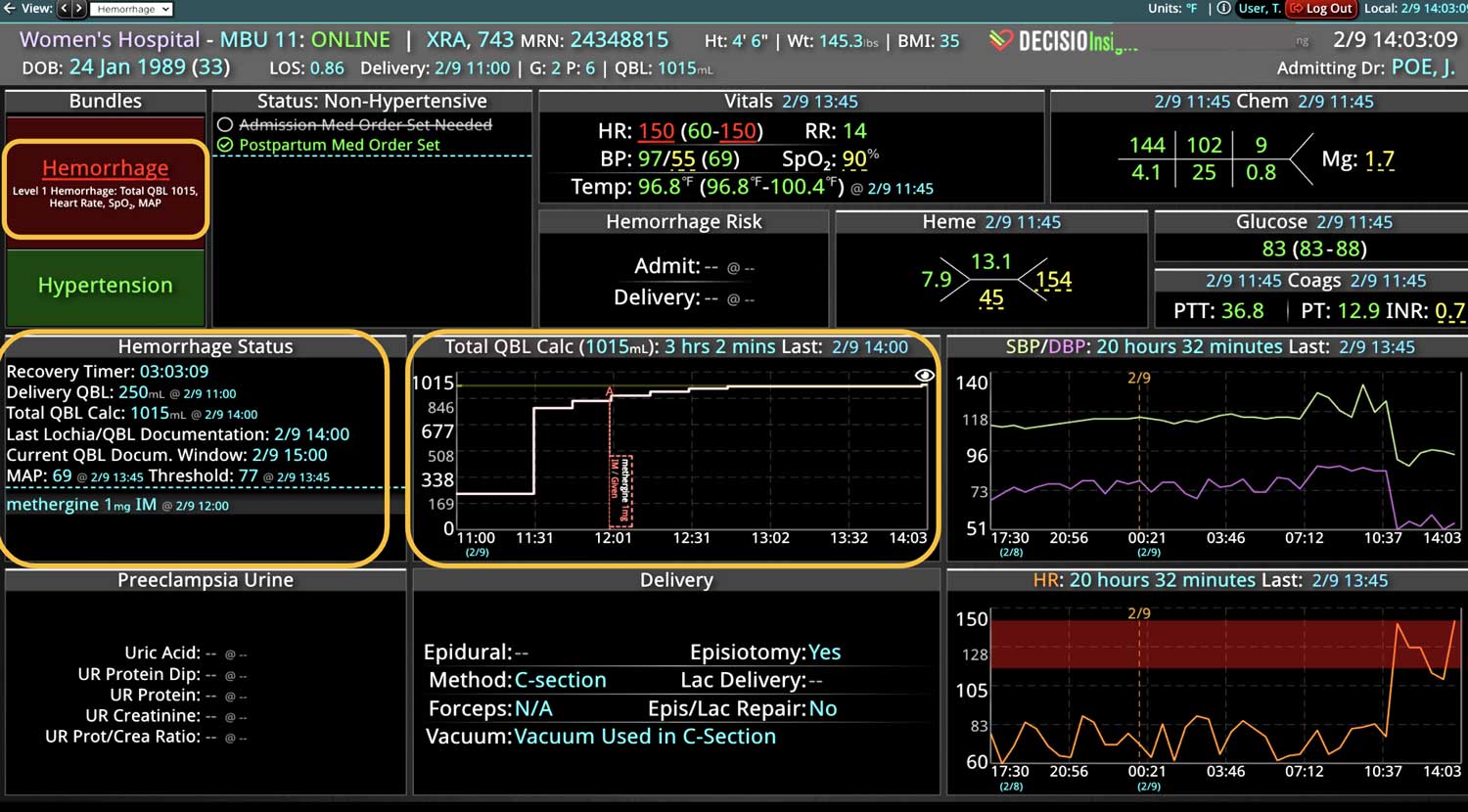
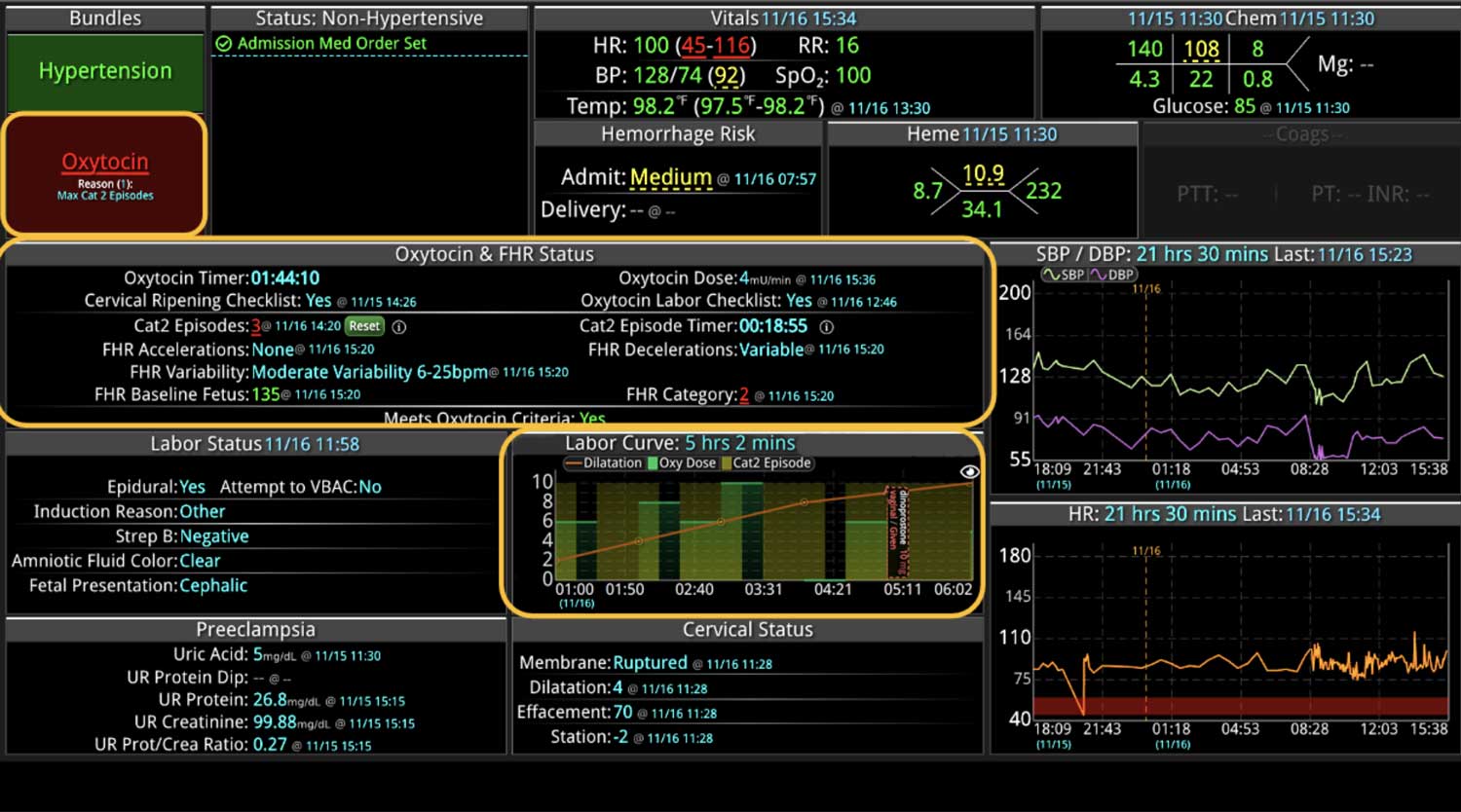
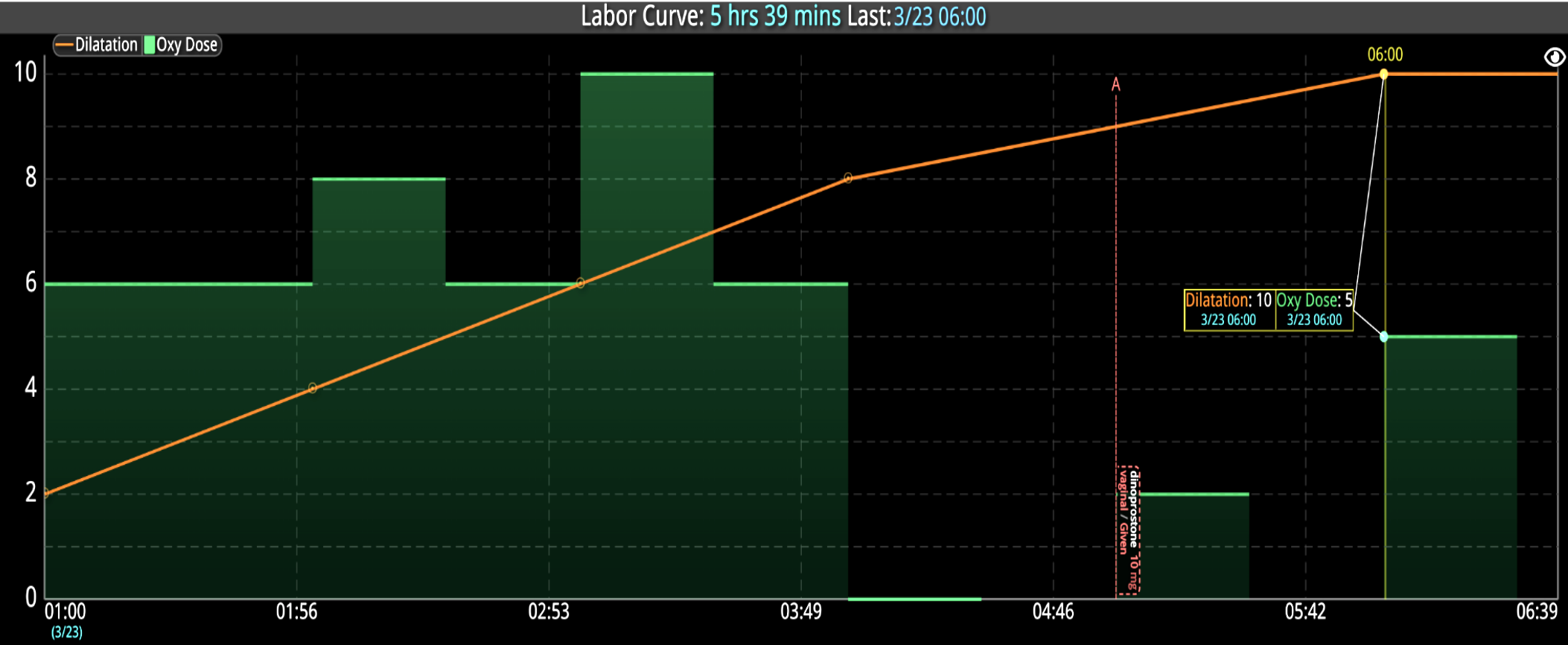
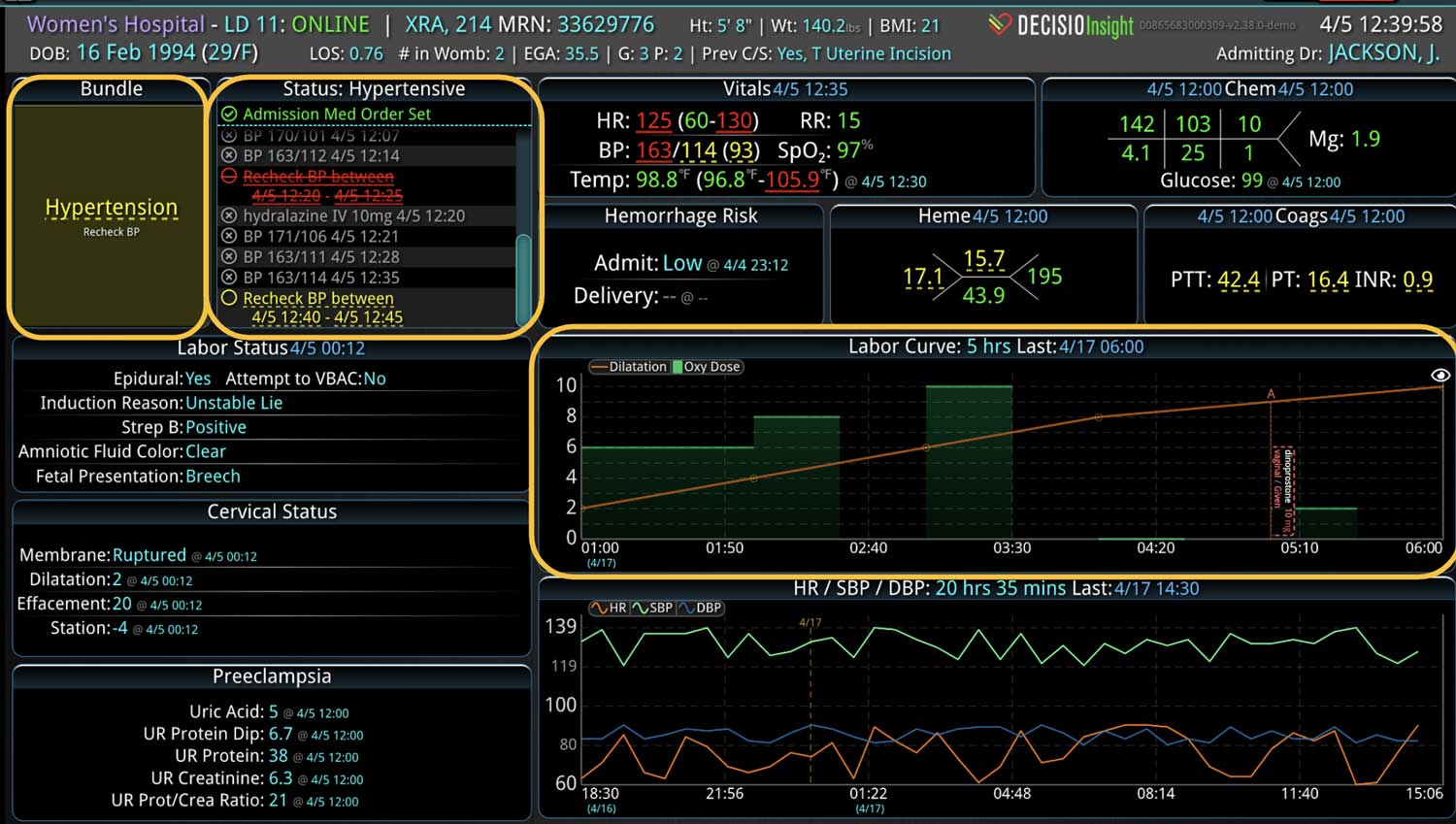
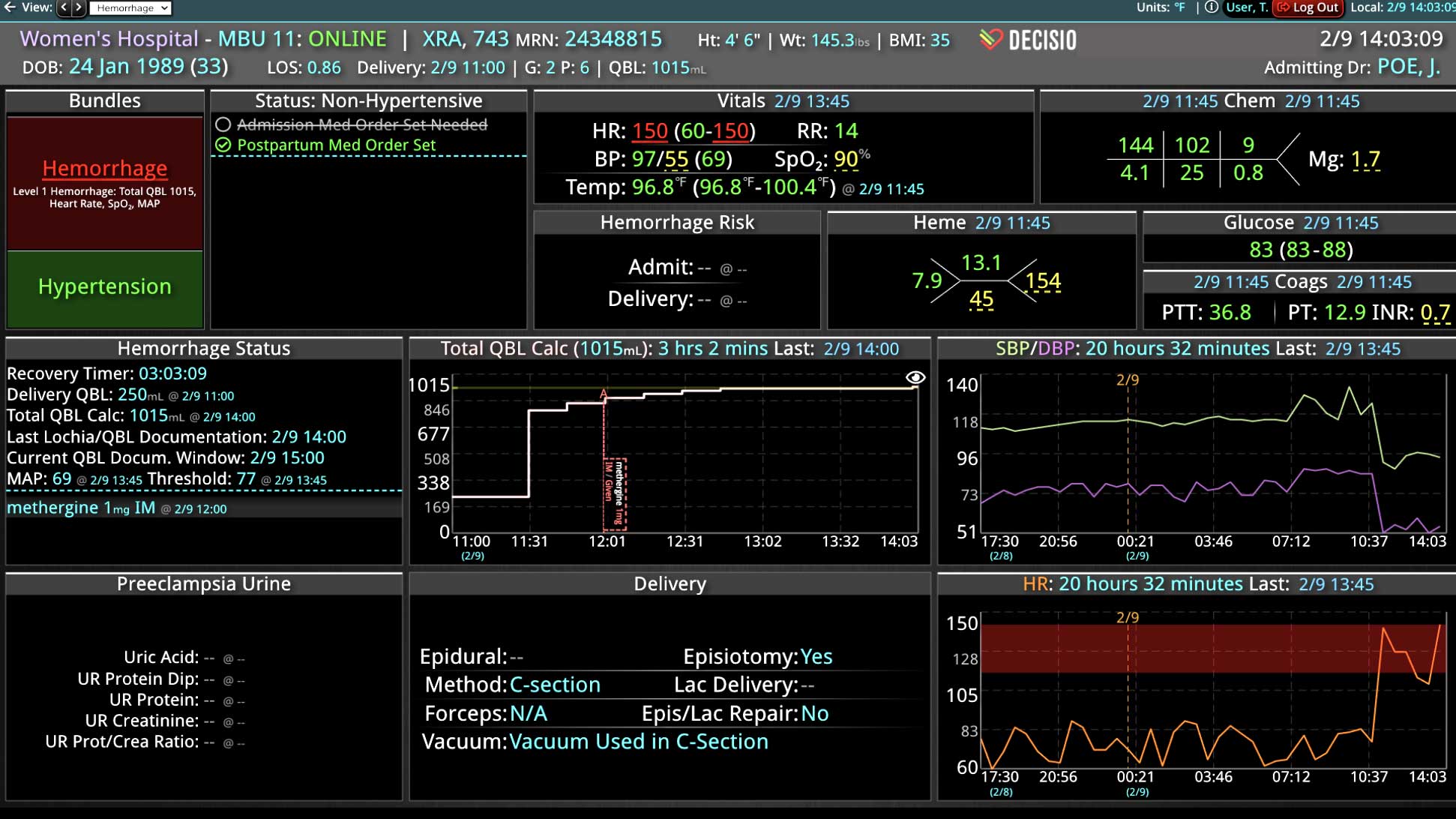
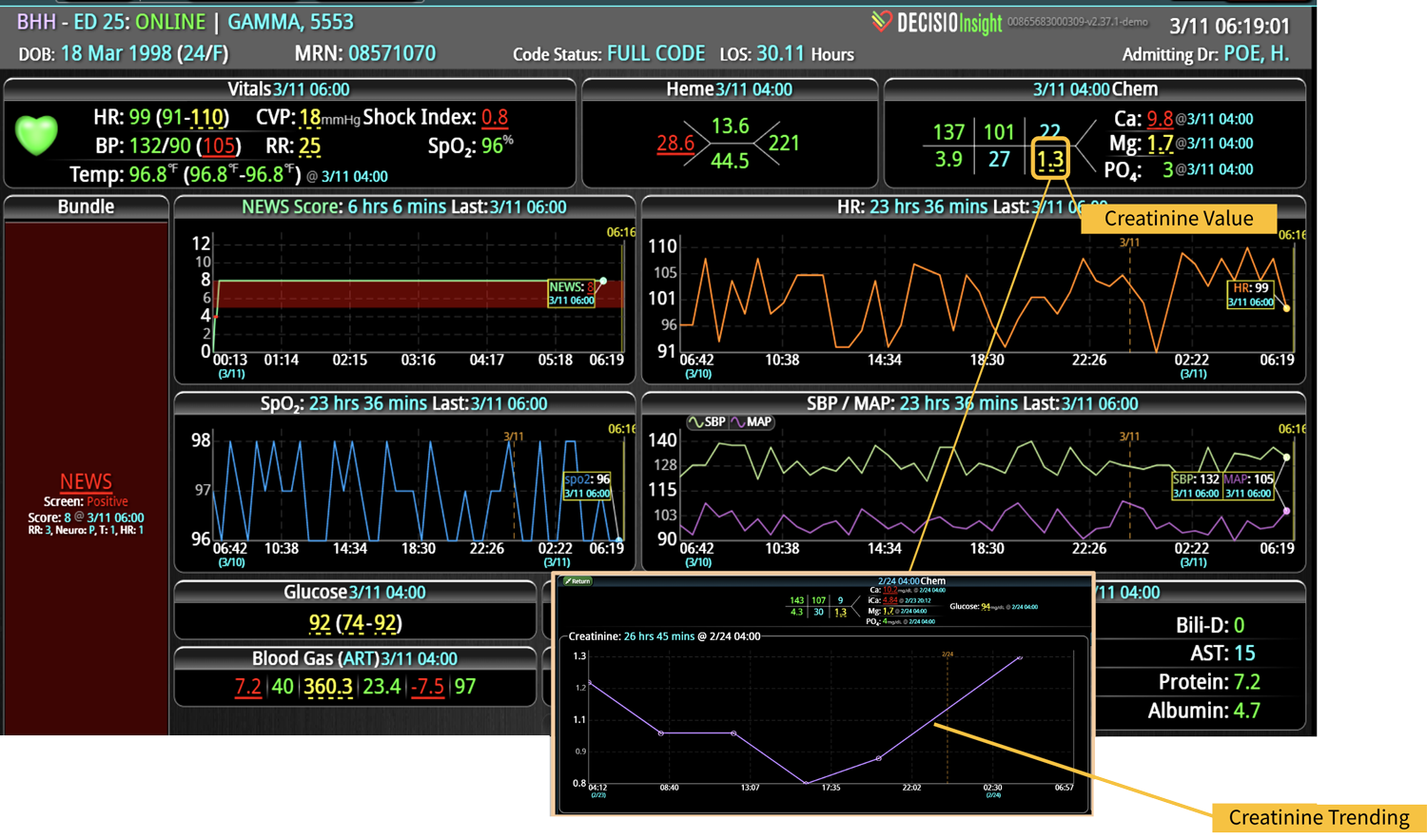
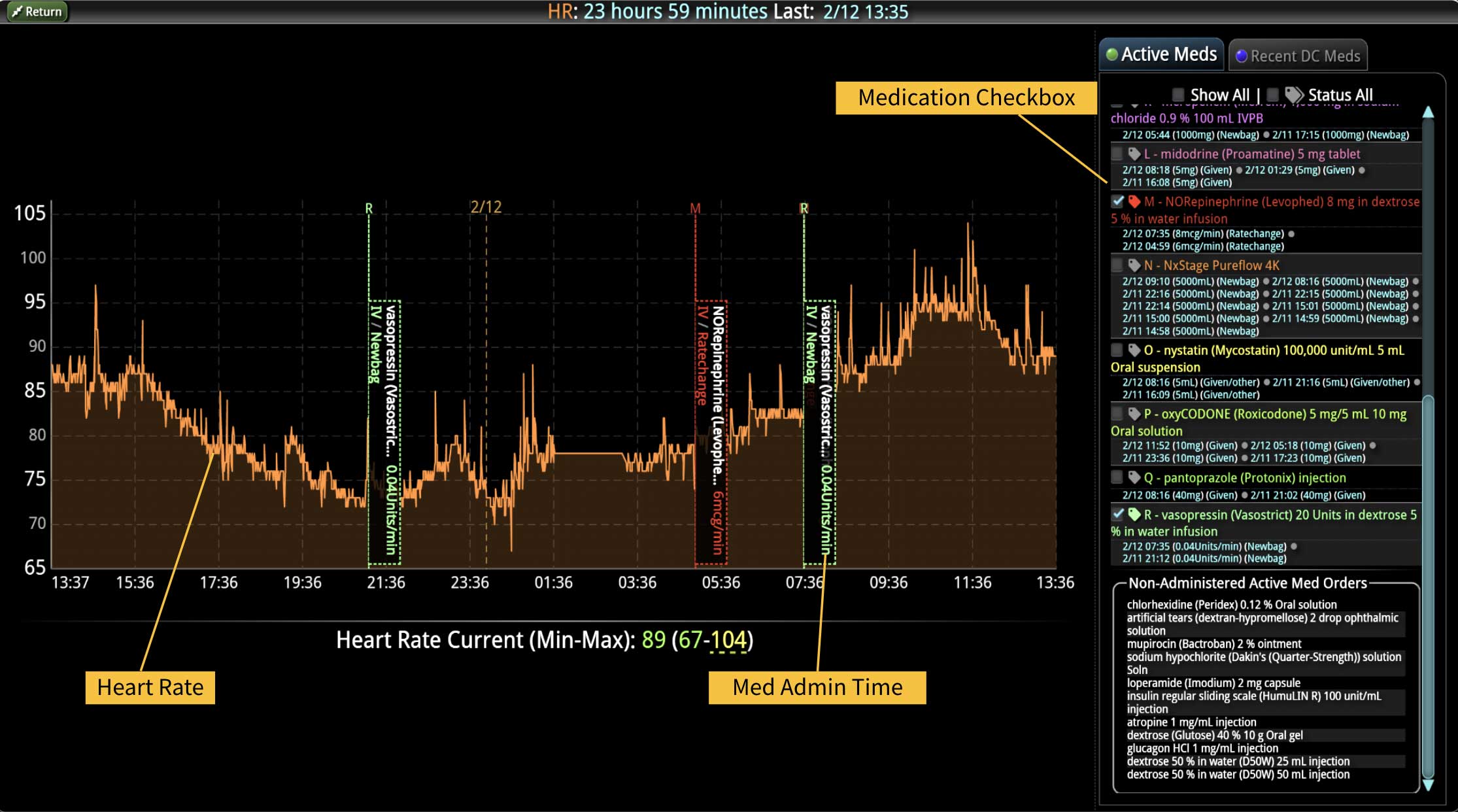
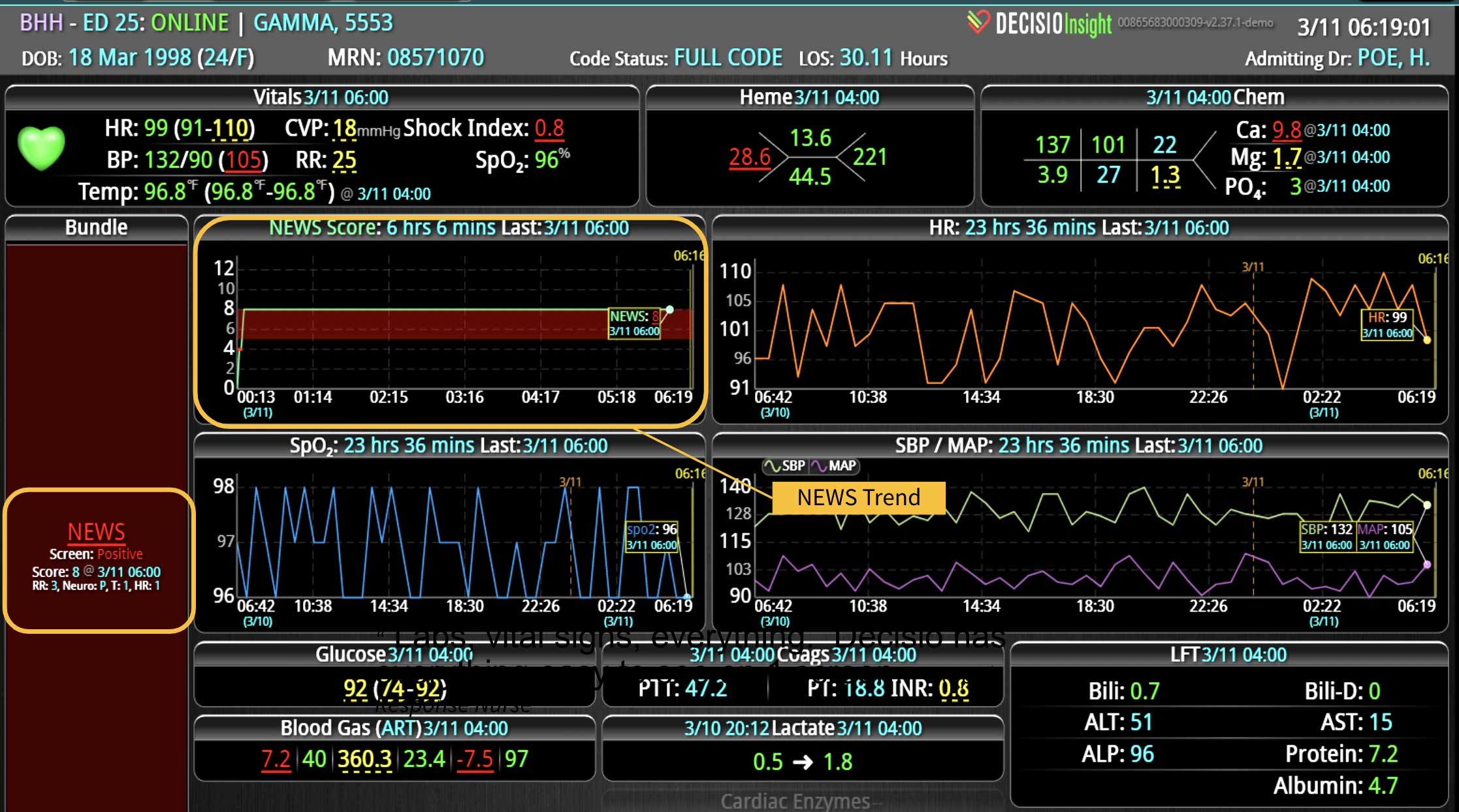
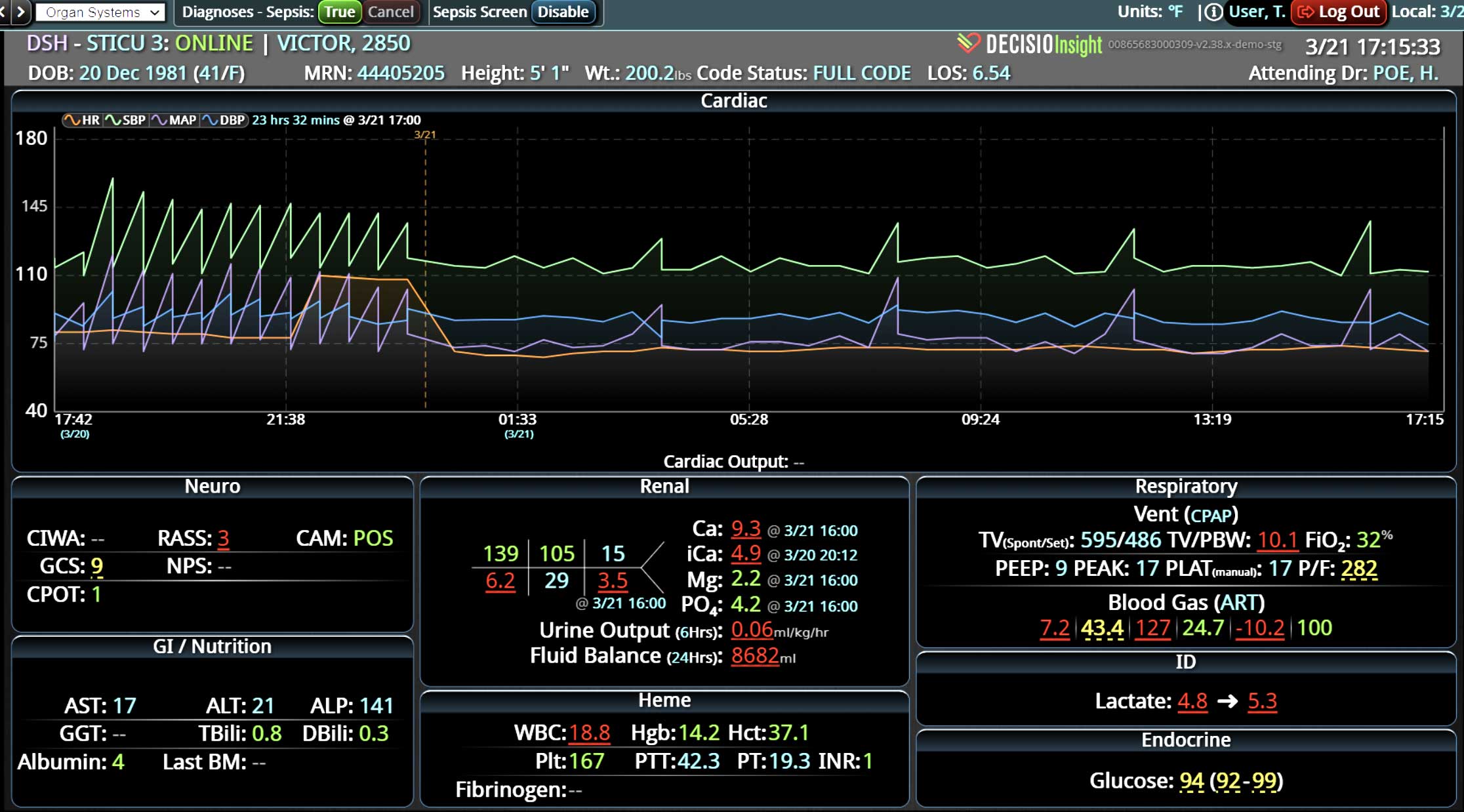
Analyzing and determining the extent of AKI is challenging. Using a visual clinical decision support tool with validated staging and recognition for AKI can help identify patients transitioning into different stages of injury severity.
Methods
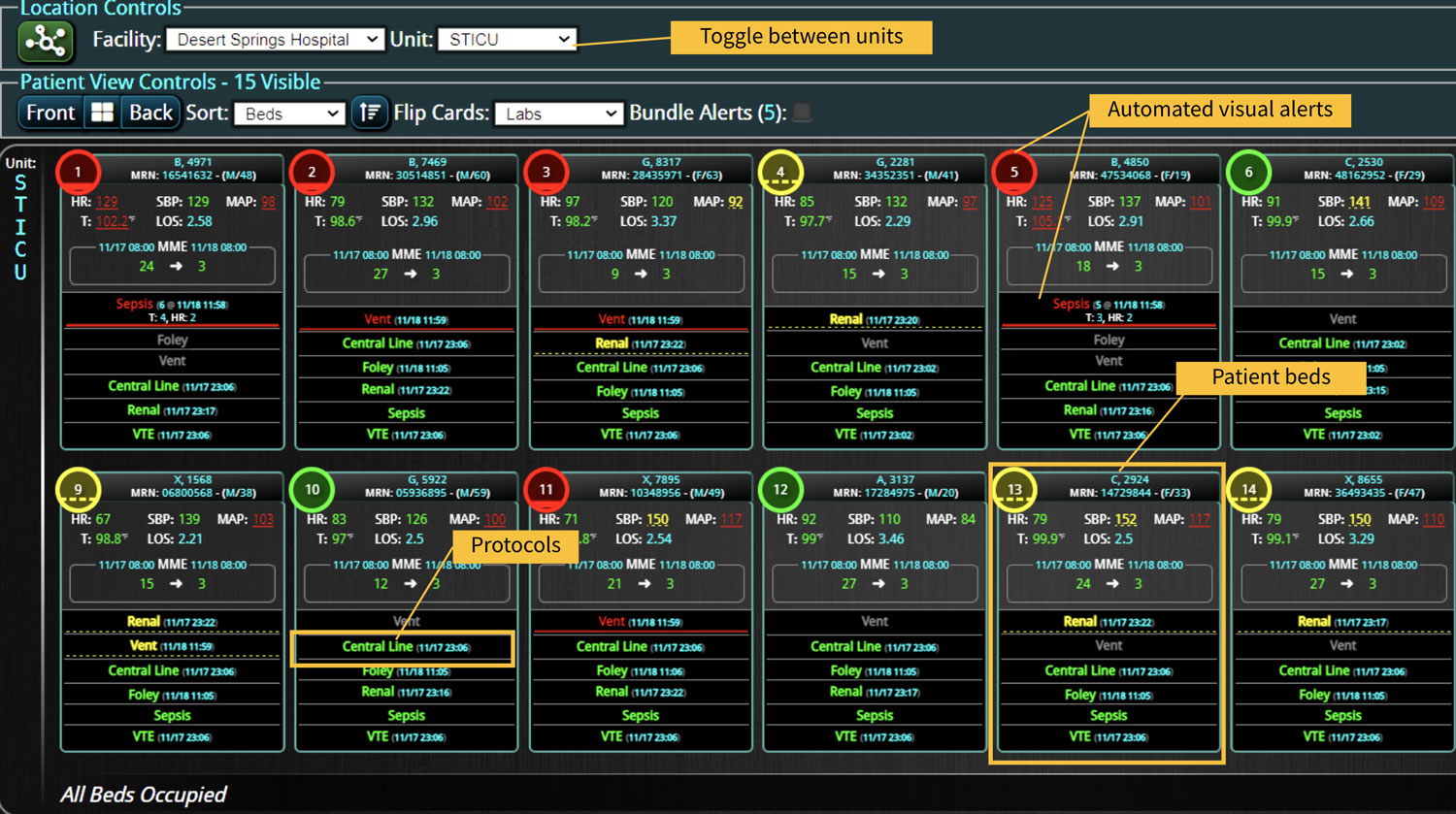
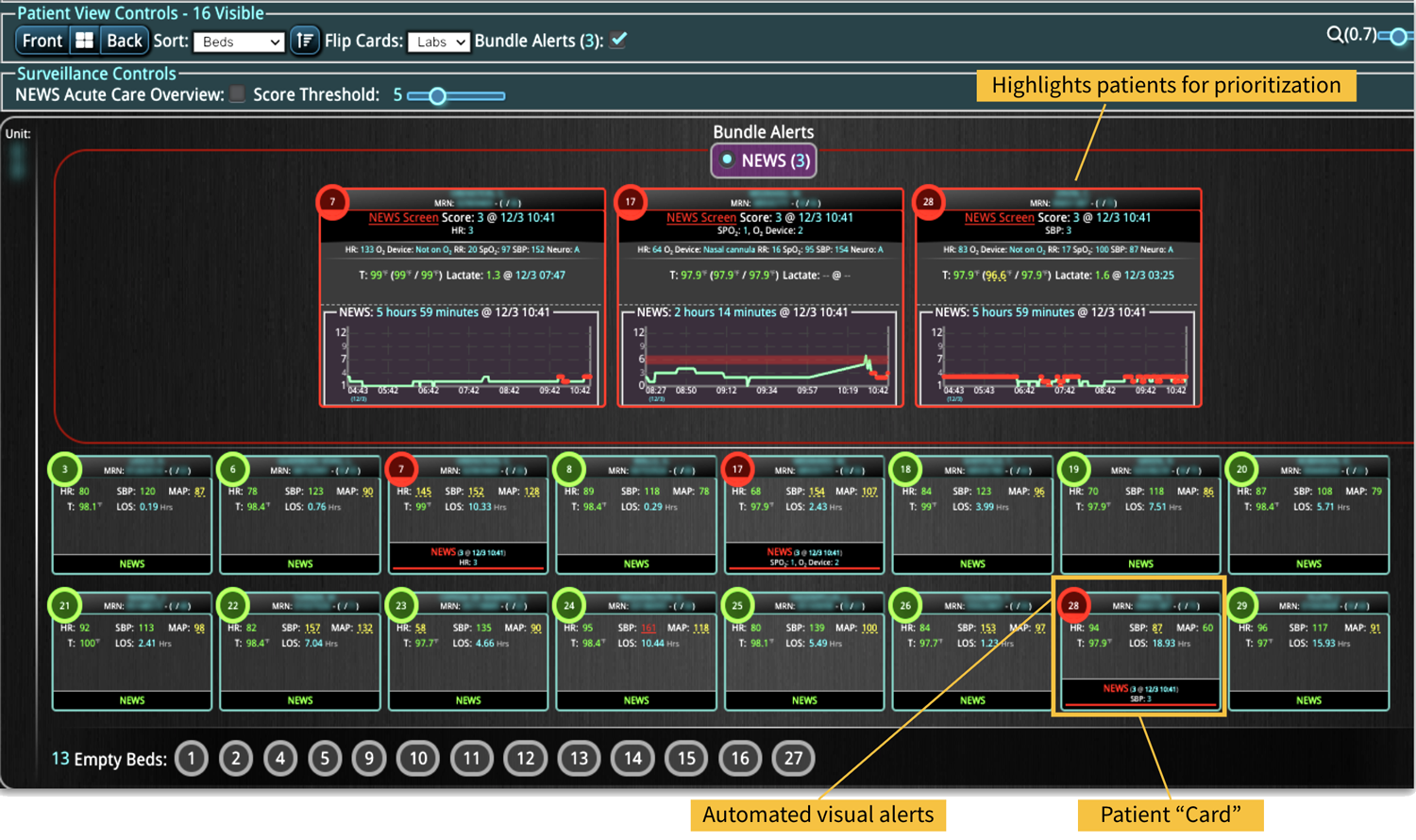
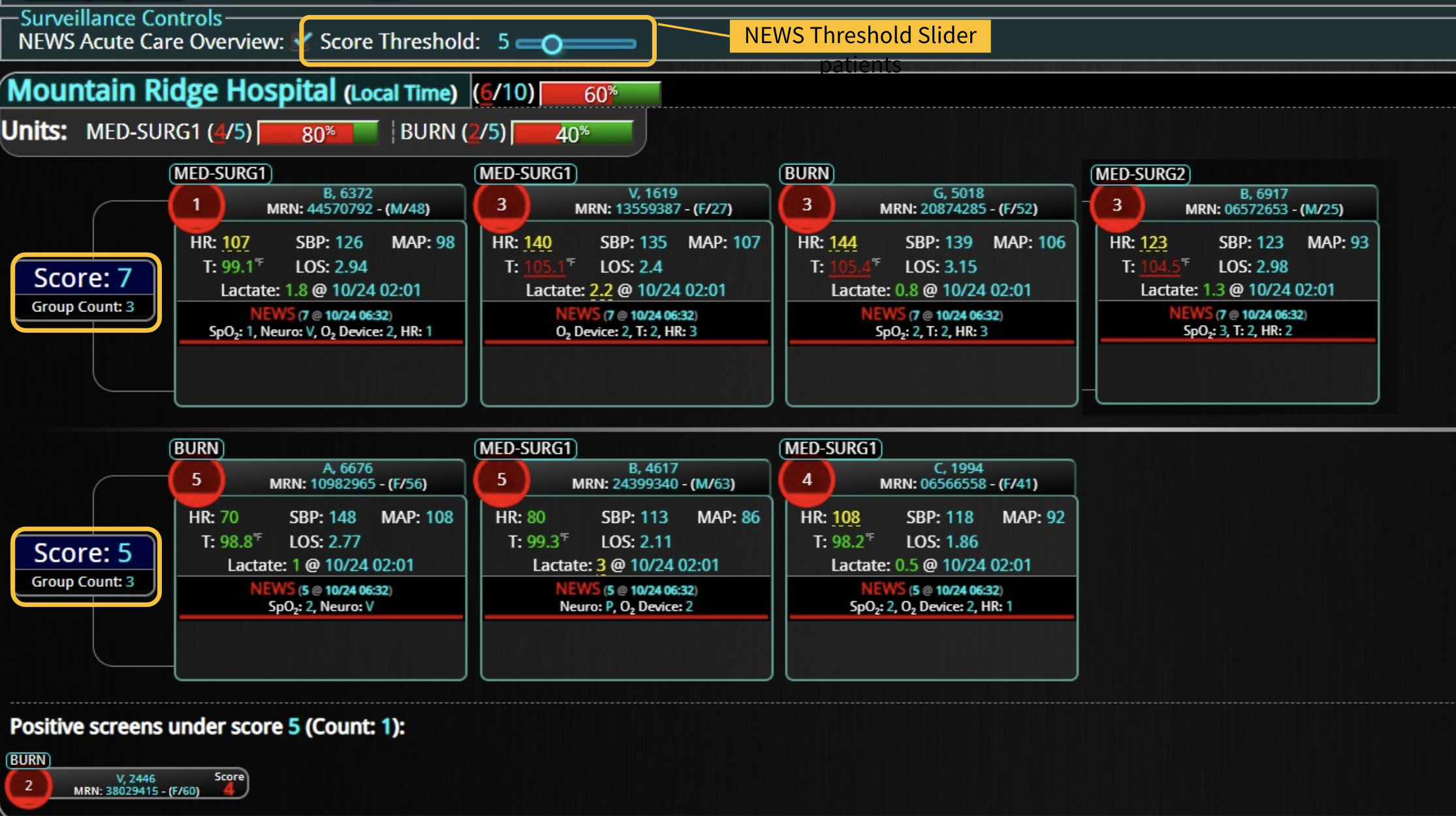
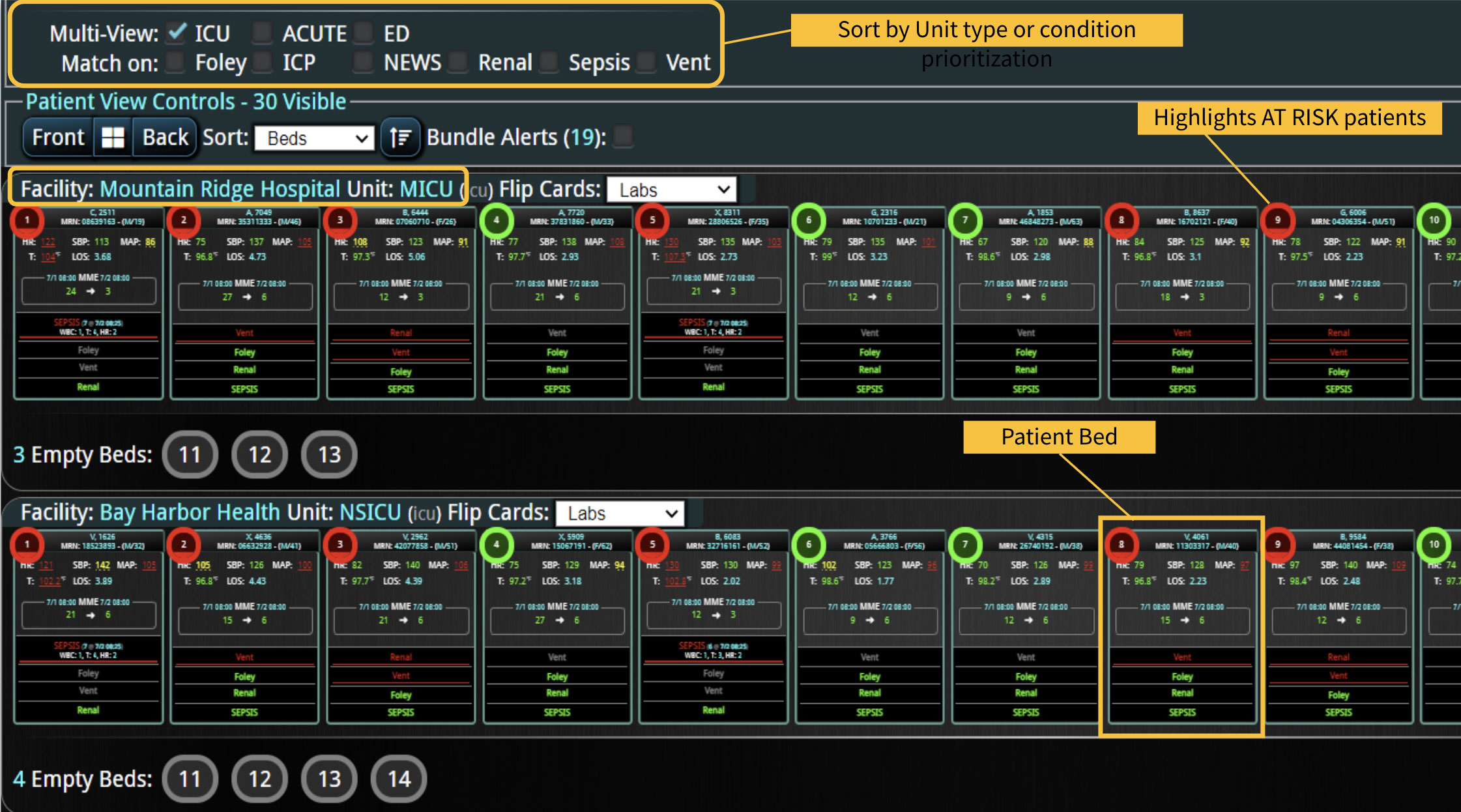
A commercially available clinical surveillance and decision support dashboard system was implemented in 12 of the 34 beds in a surgical intensive care unit (SICU) at an academic medical and regional level I trauma center. An automated AKI bundle based on the Kidney Disease: Improve Global Outcomes (KDIGO) criteria stages was implemented to aid in identification of patients in various stages. A pre-post analysis was performed on SICU beds with (WDB) and without the dashboard (WODB) to assess the impact of the bundle to identify patients with AKI and minimize ongoing renal dysfunction. Data five months prior to and 14 months after implementation were compared. Patients with known chronic or end-stage renal disease were excluded.
Results
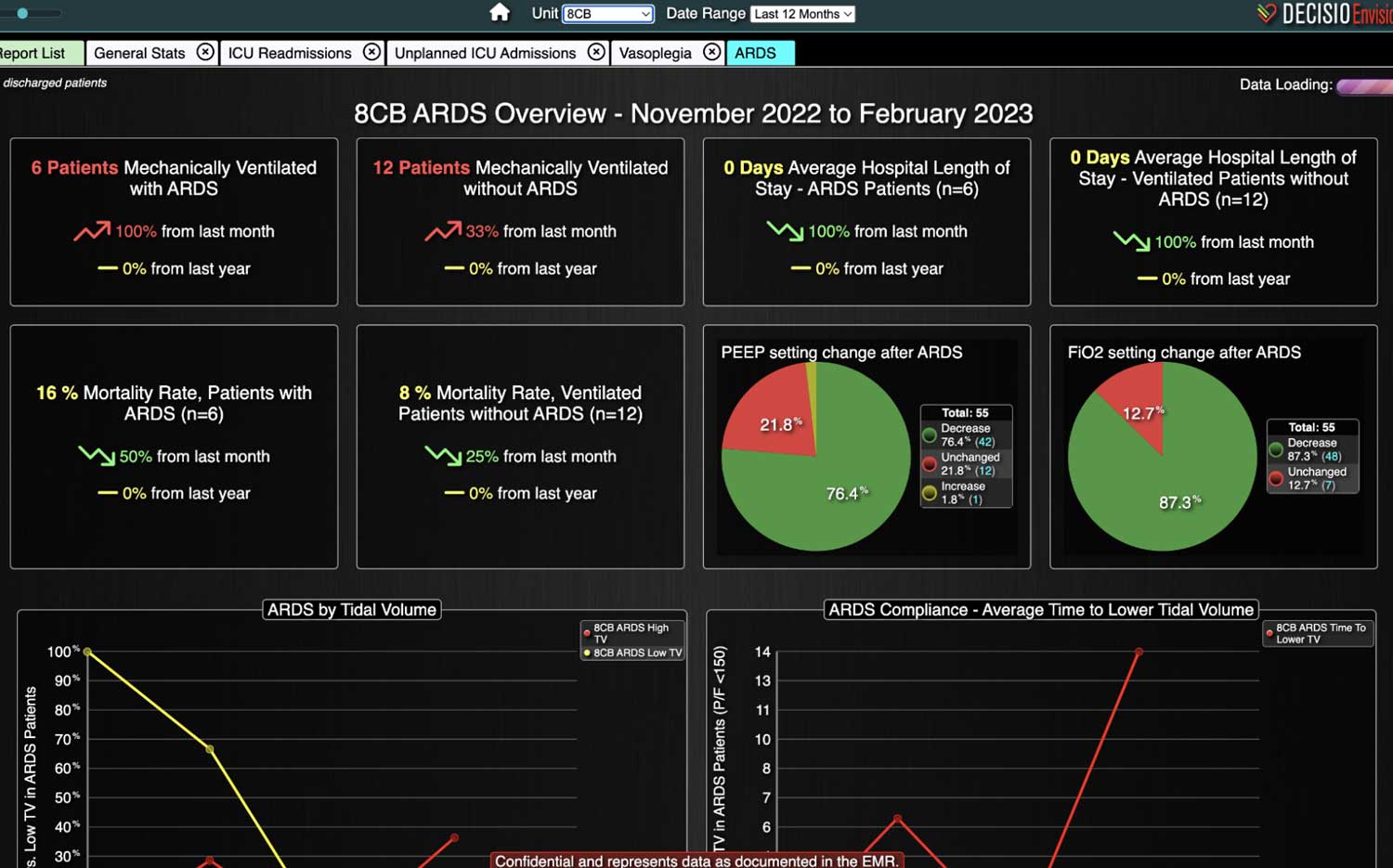
A total of 2,813 patients were included (988 patients in WDB and 1,825 patients in WODB). Age and gender were similar in patients among groups and over time. Overall, AKI incidence was reduced in WDB after implementation (pre, 28.8% v post, 22.4%; P=0.04). Individual KDIGO stages of AKI were reduced in WDB post-implementation, but none were statistically significant. There were no differences in overall AKI incidence (pre-26.6% v post-25.7%; P=0.682) or individual KDIGO stages in WODB. The length of stay in the SICU or hospital was similar in all patients and on subgroup analysis between individual KDIGO stages. No difference in mortality was demonstrated between WDB and WODB cohorts.
Conclusions
Implementing a visual clinical decision support tool was associated with a statistically significant decrease in overall AKI incidence in patients with a dashboard. Integration of an AKI bundle in the SICU patients may aid clinicians to identify AKI in real time and rapidly adjust medications or implement therapies to improve quality of care and outcomes.