23 Aug Boost SEP-1 Compliance: How Clinical Decision Support Tools Improve Sepsis Management
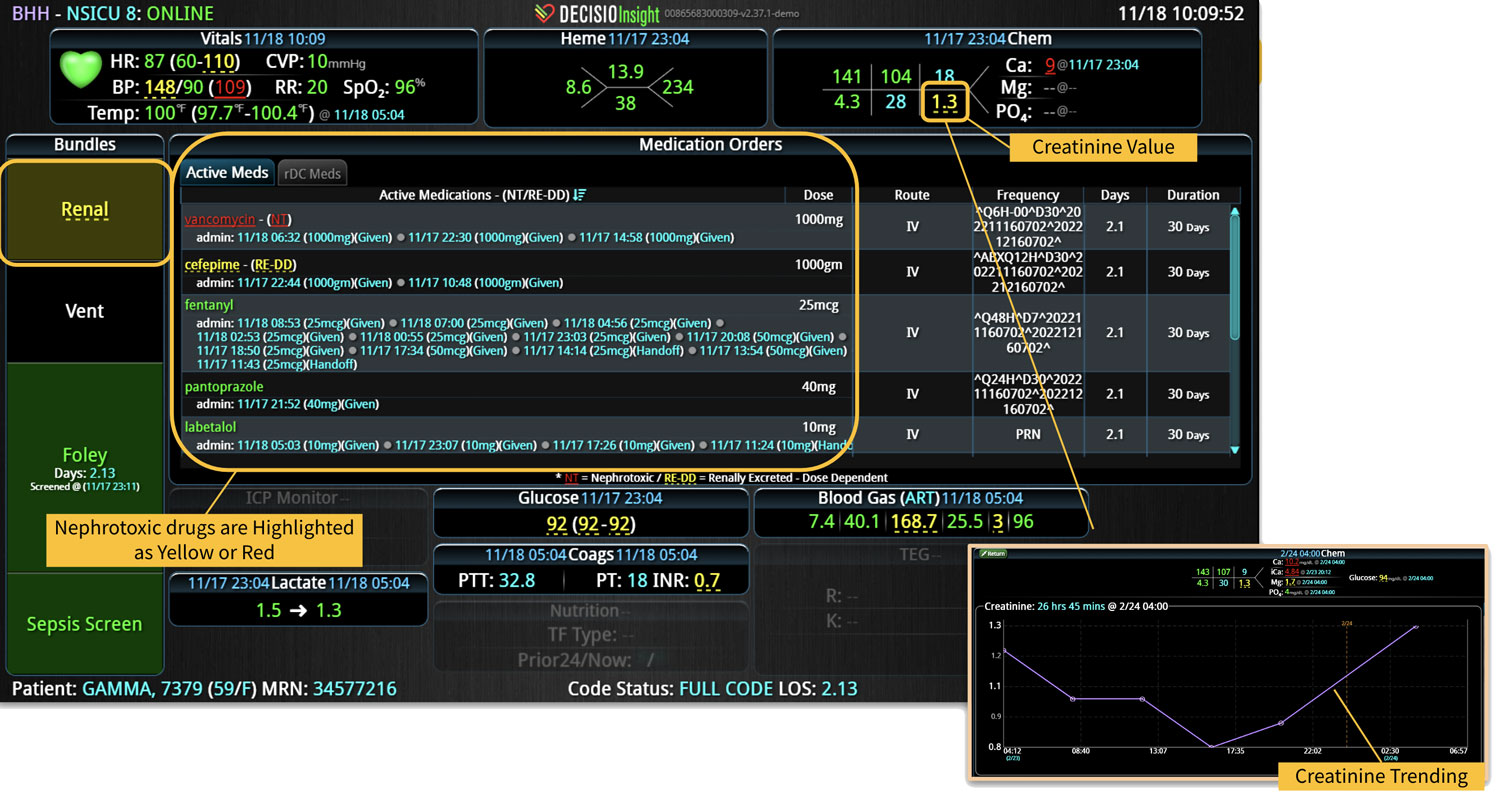
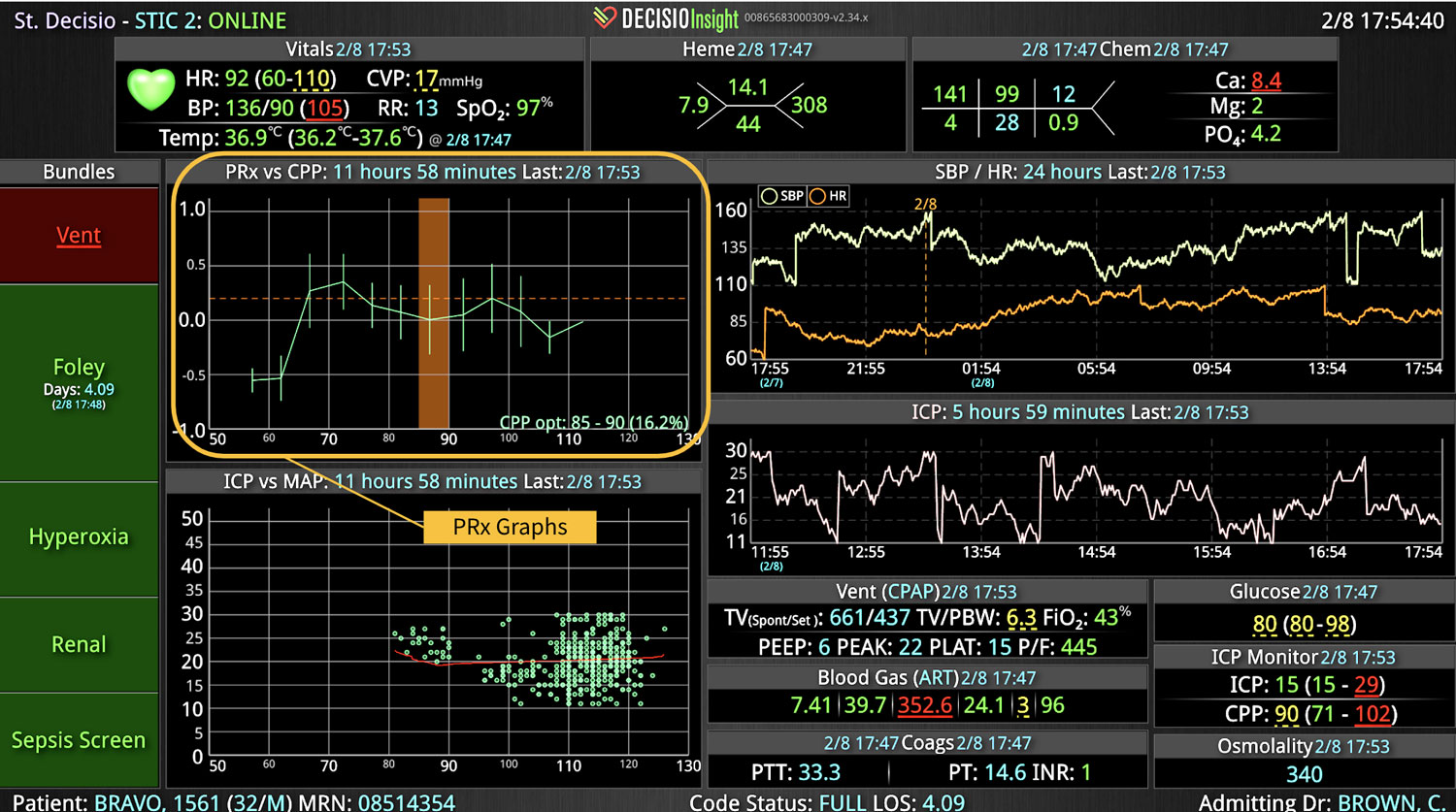
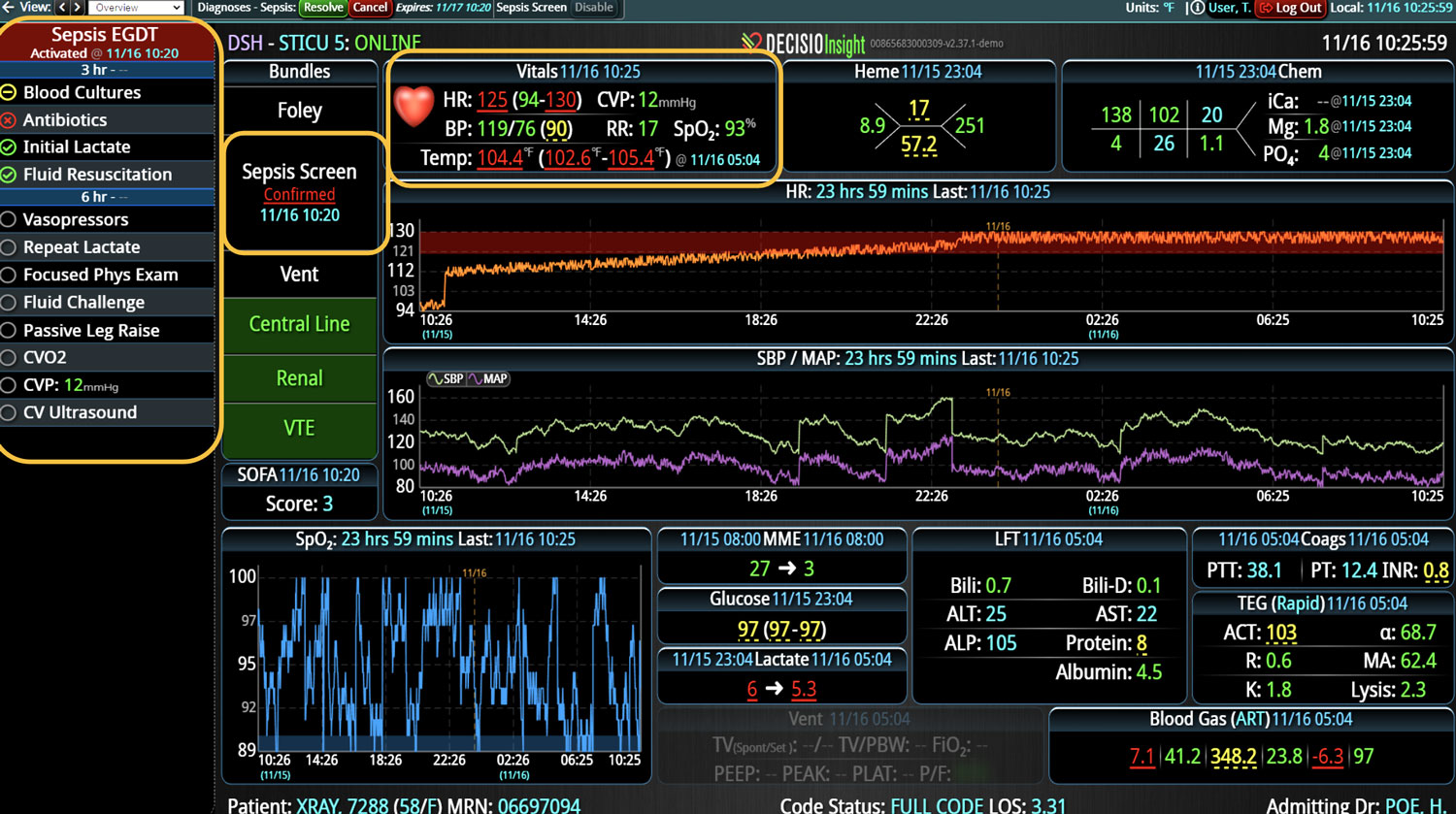
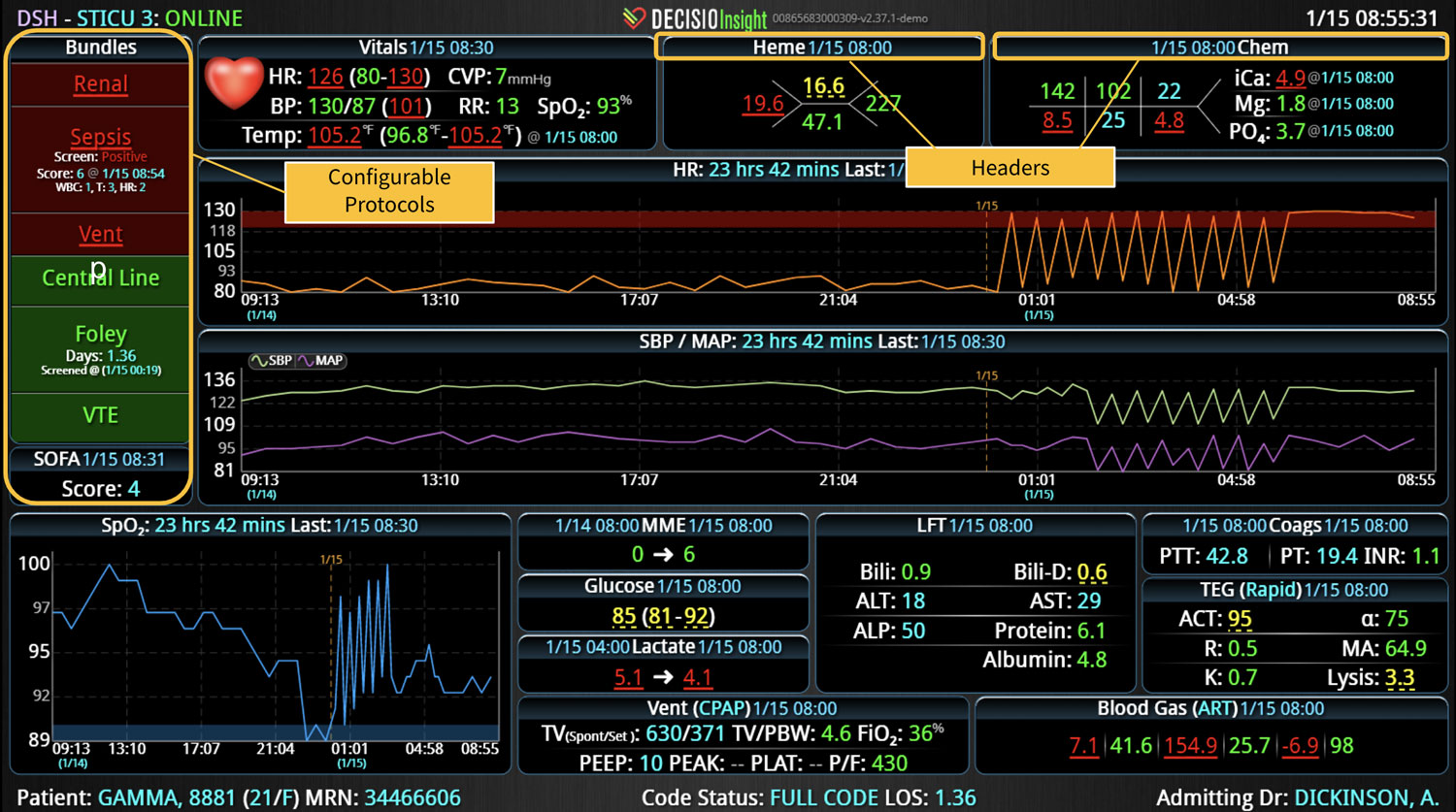
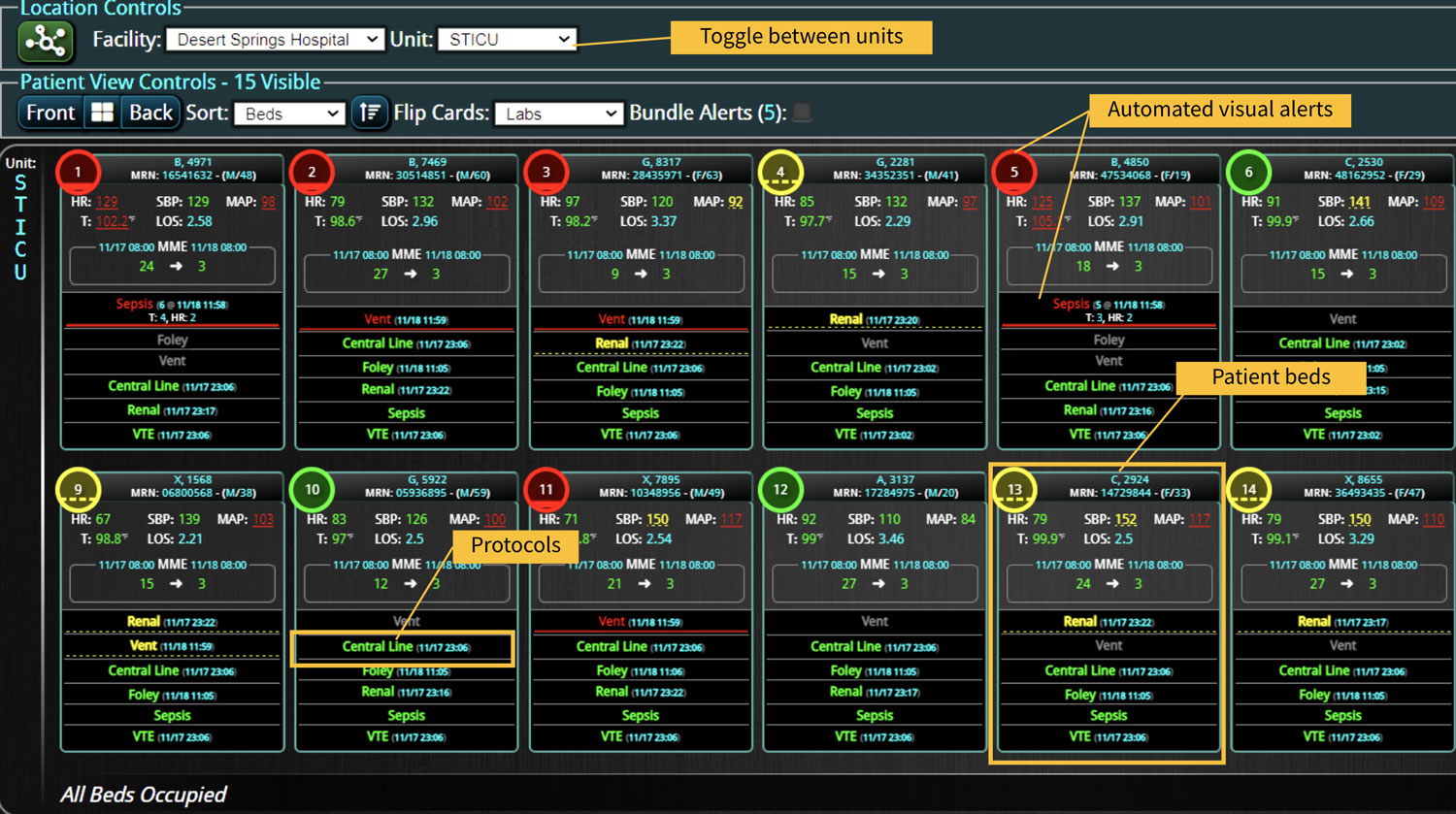
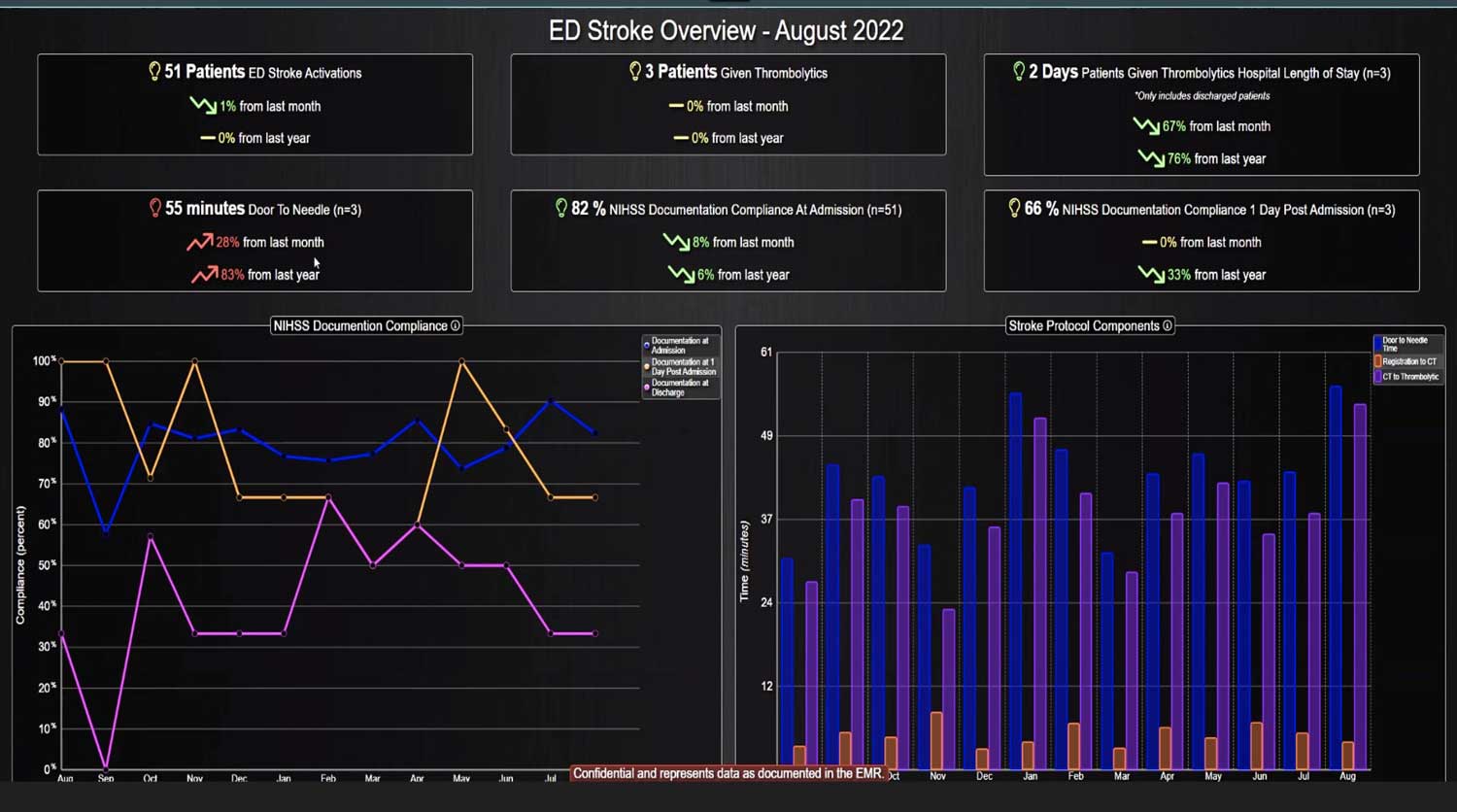
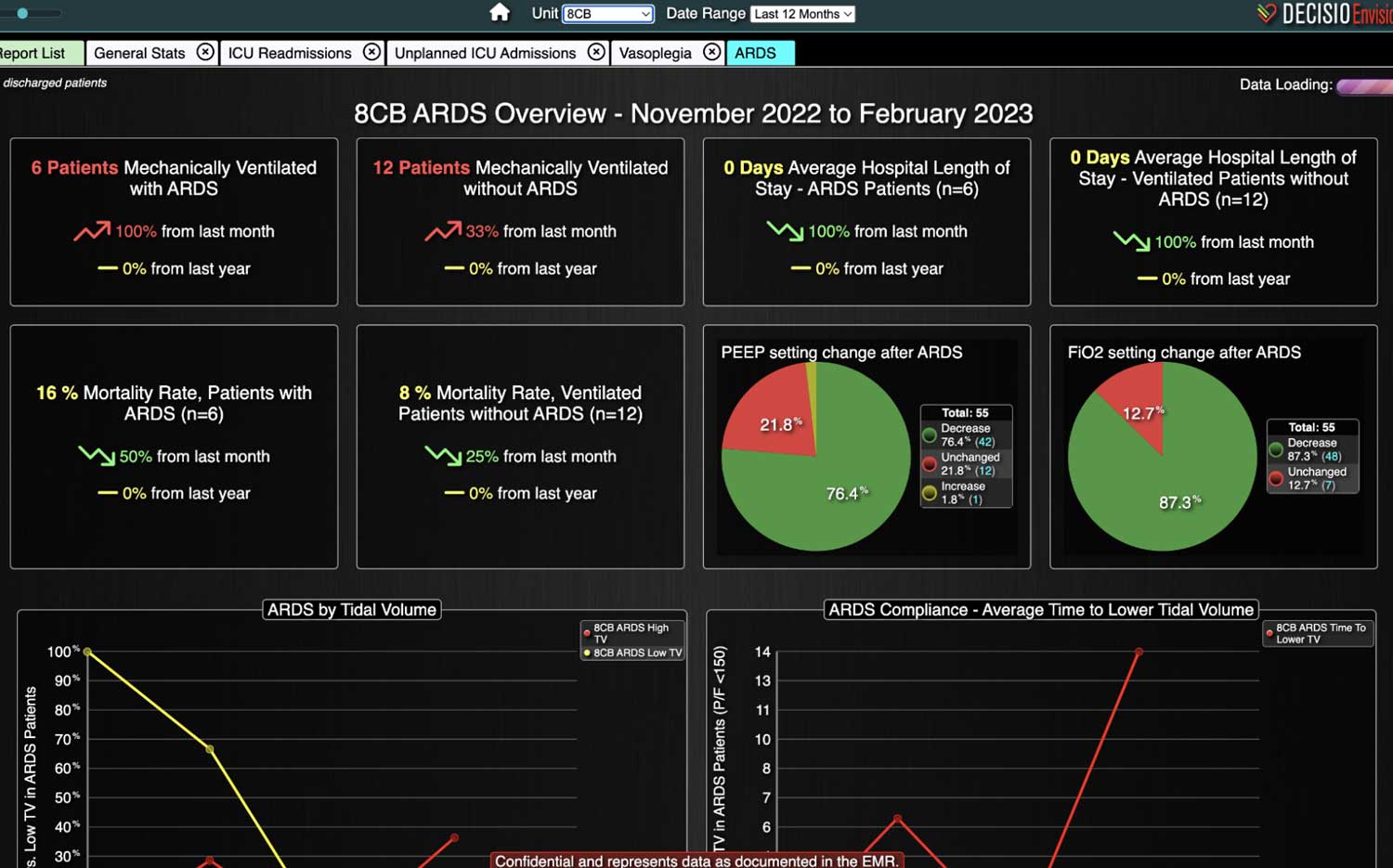
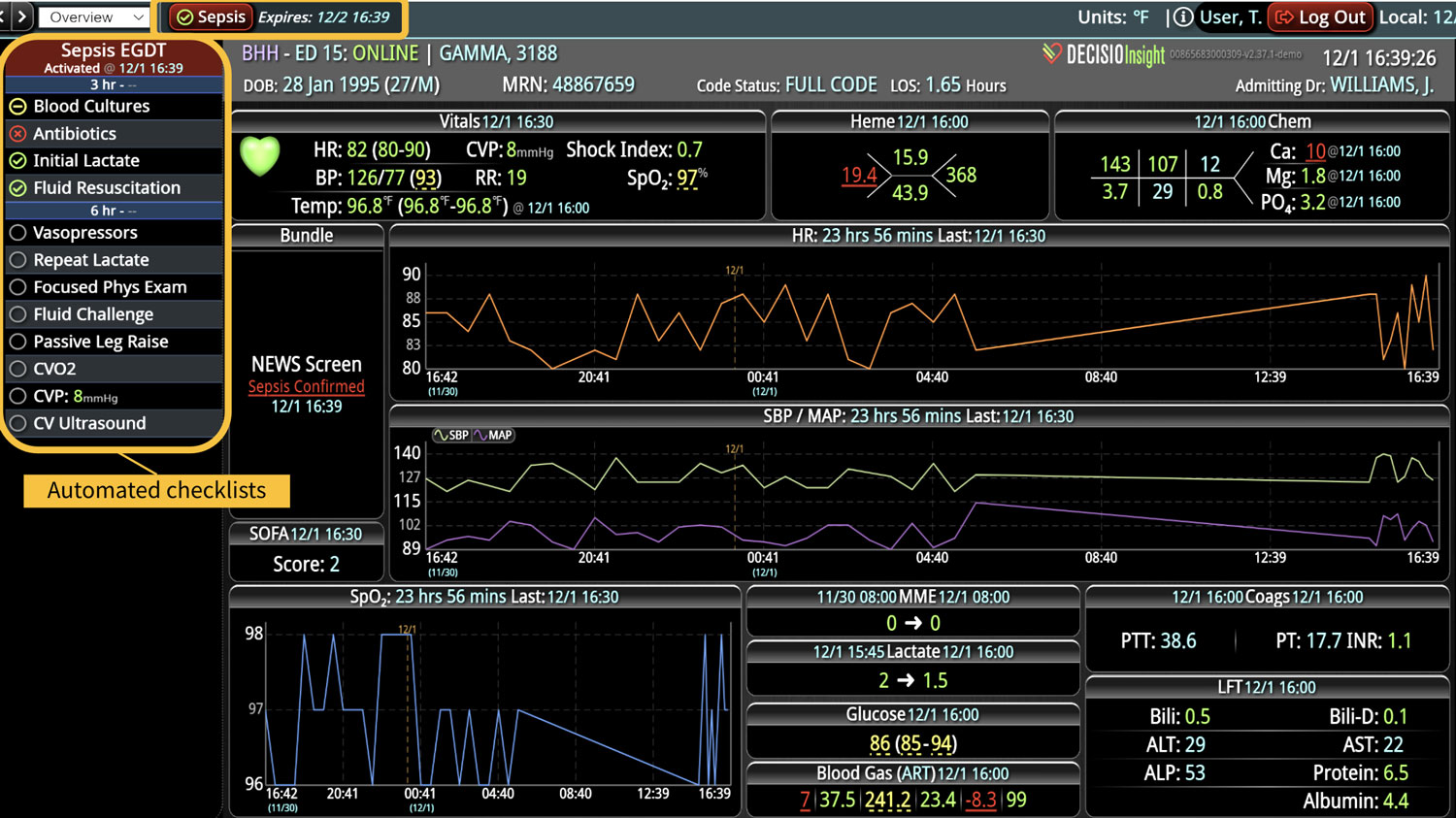
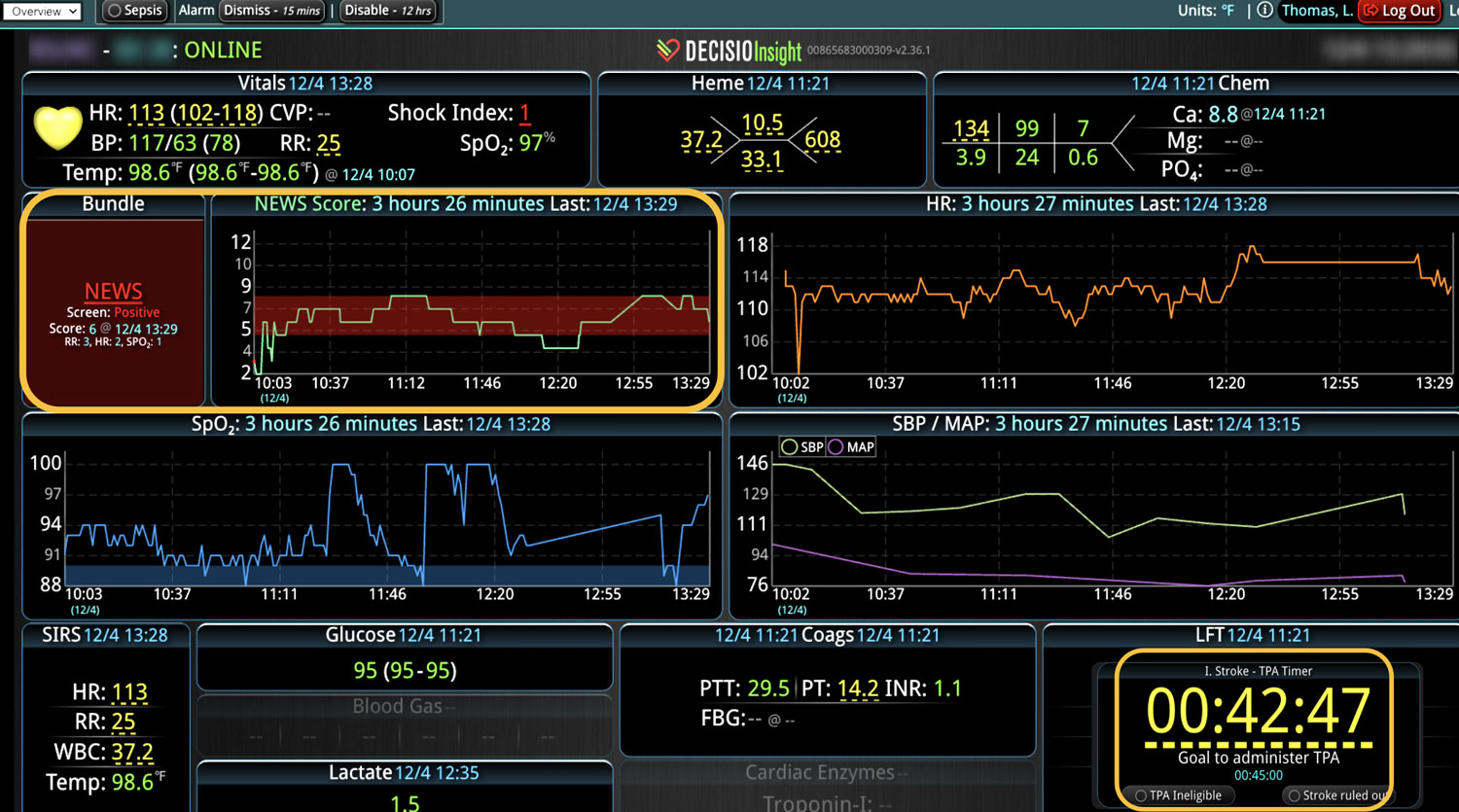
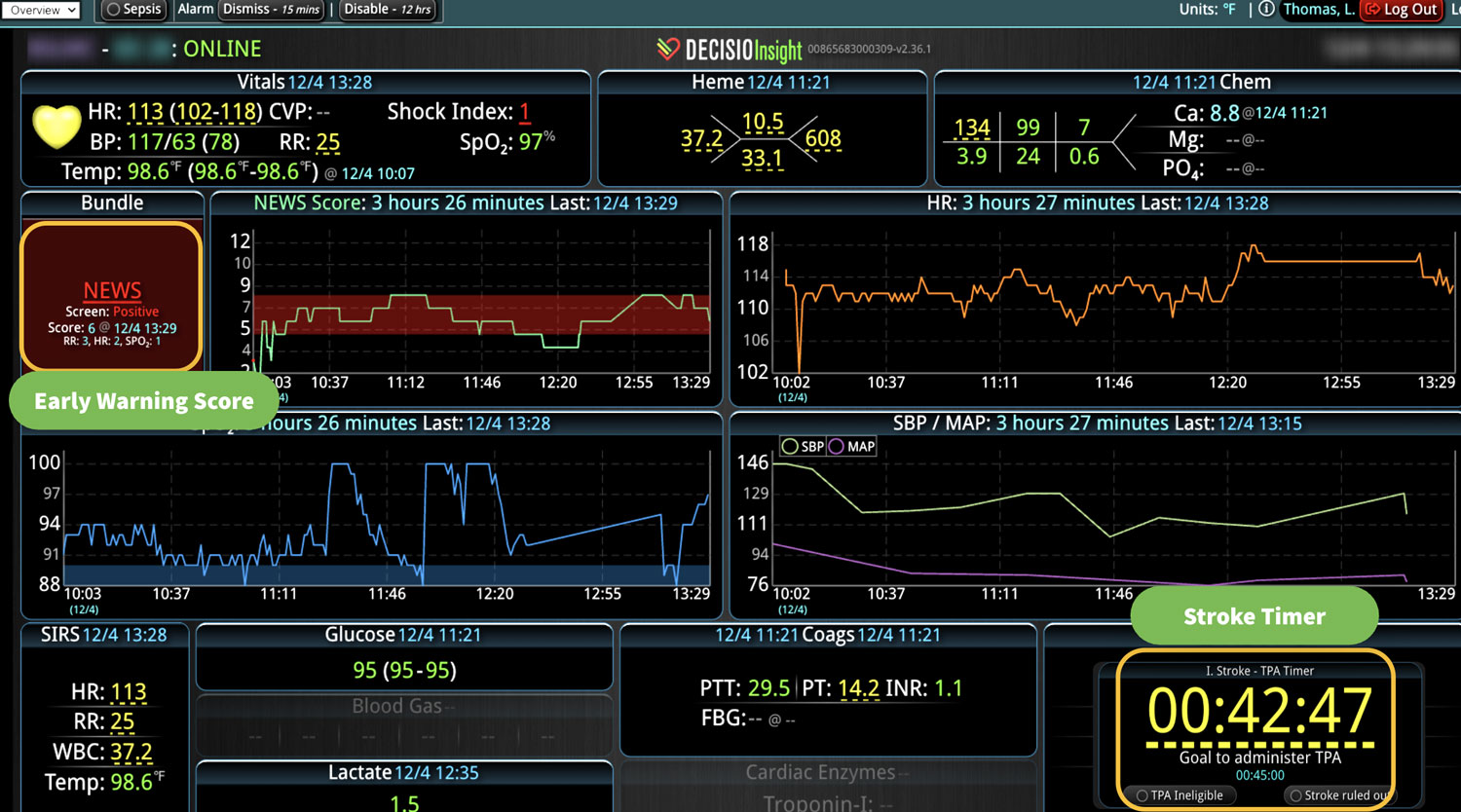
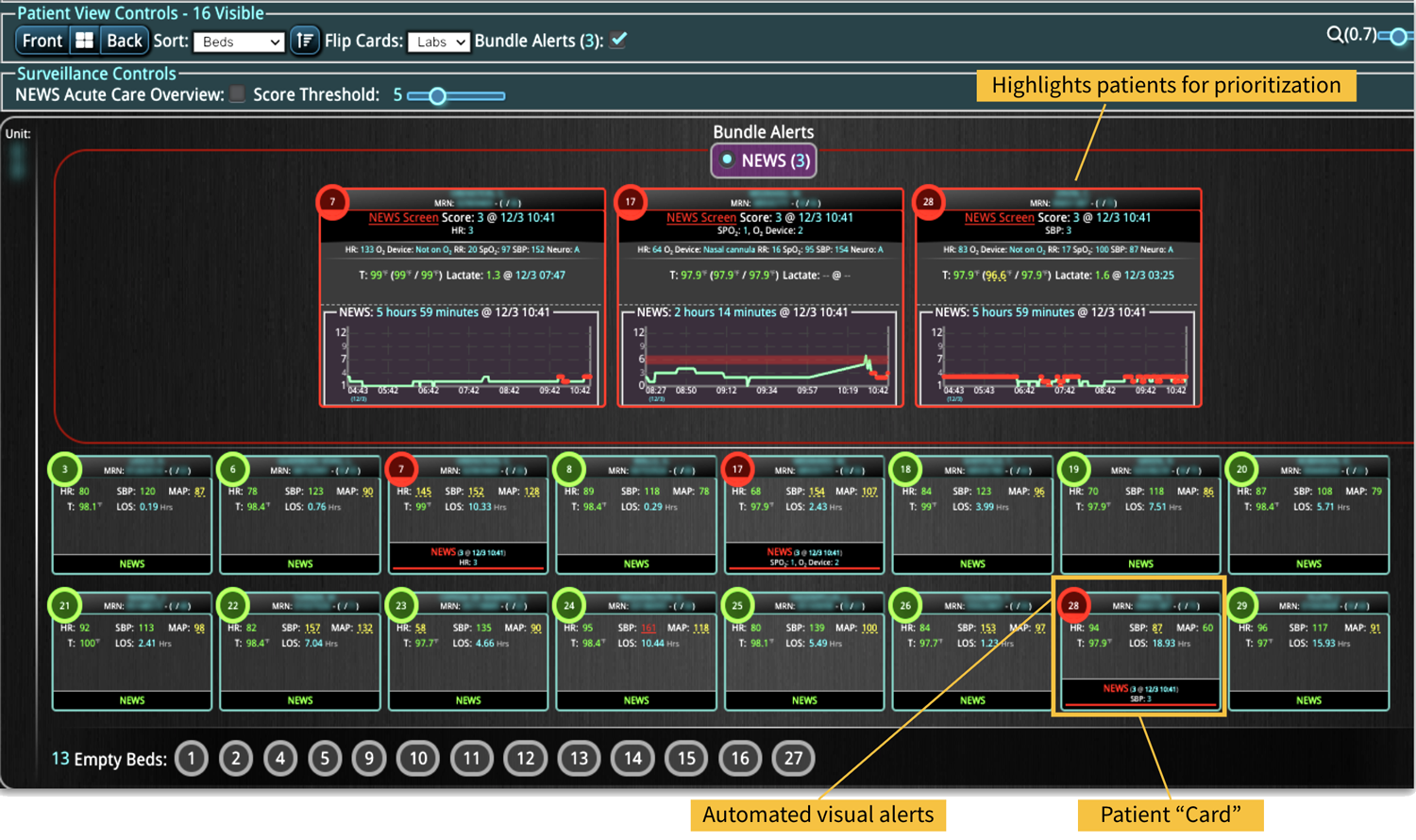
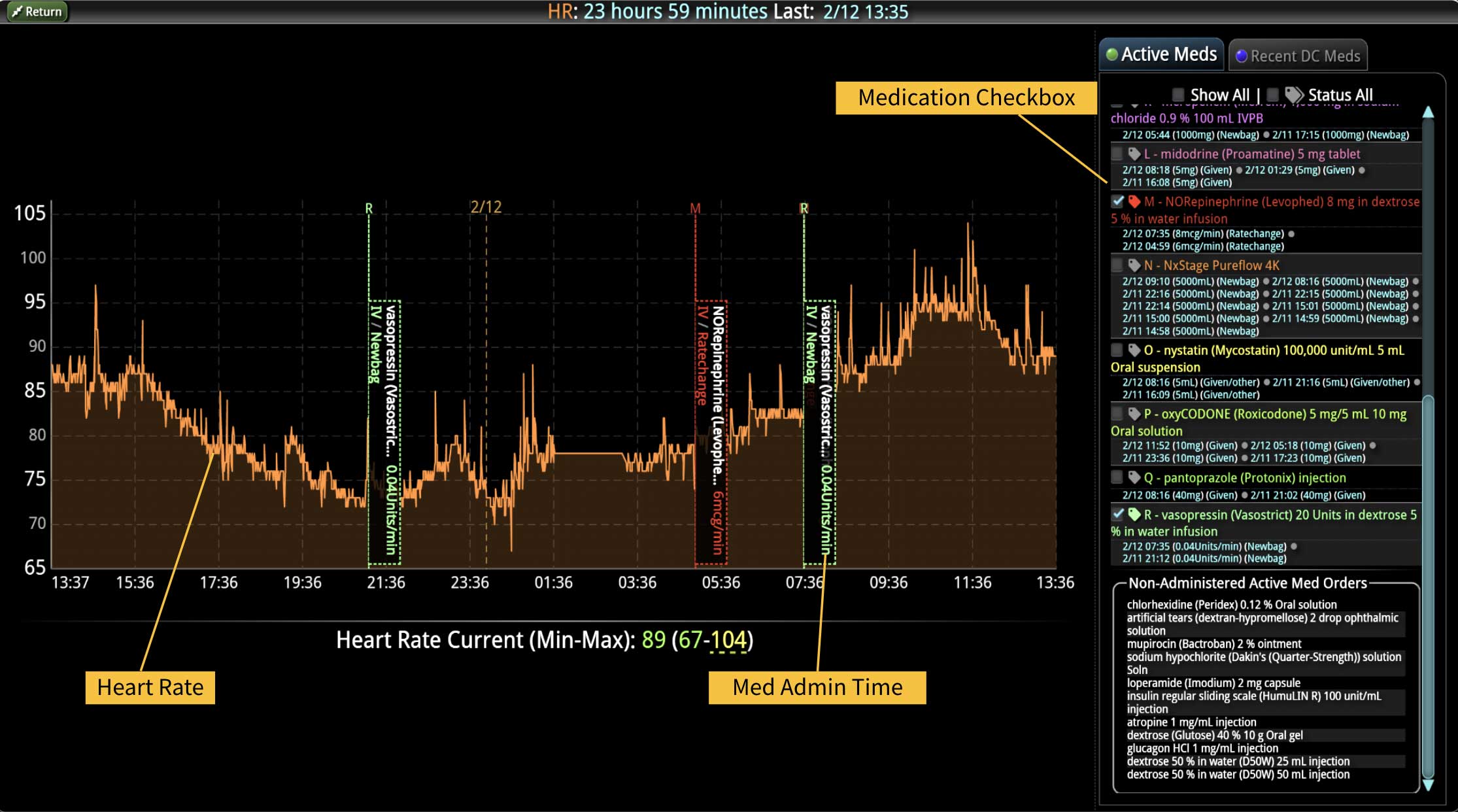
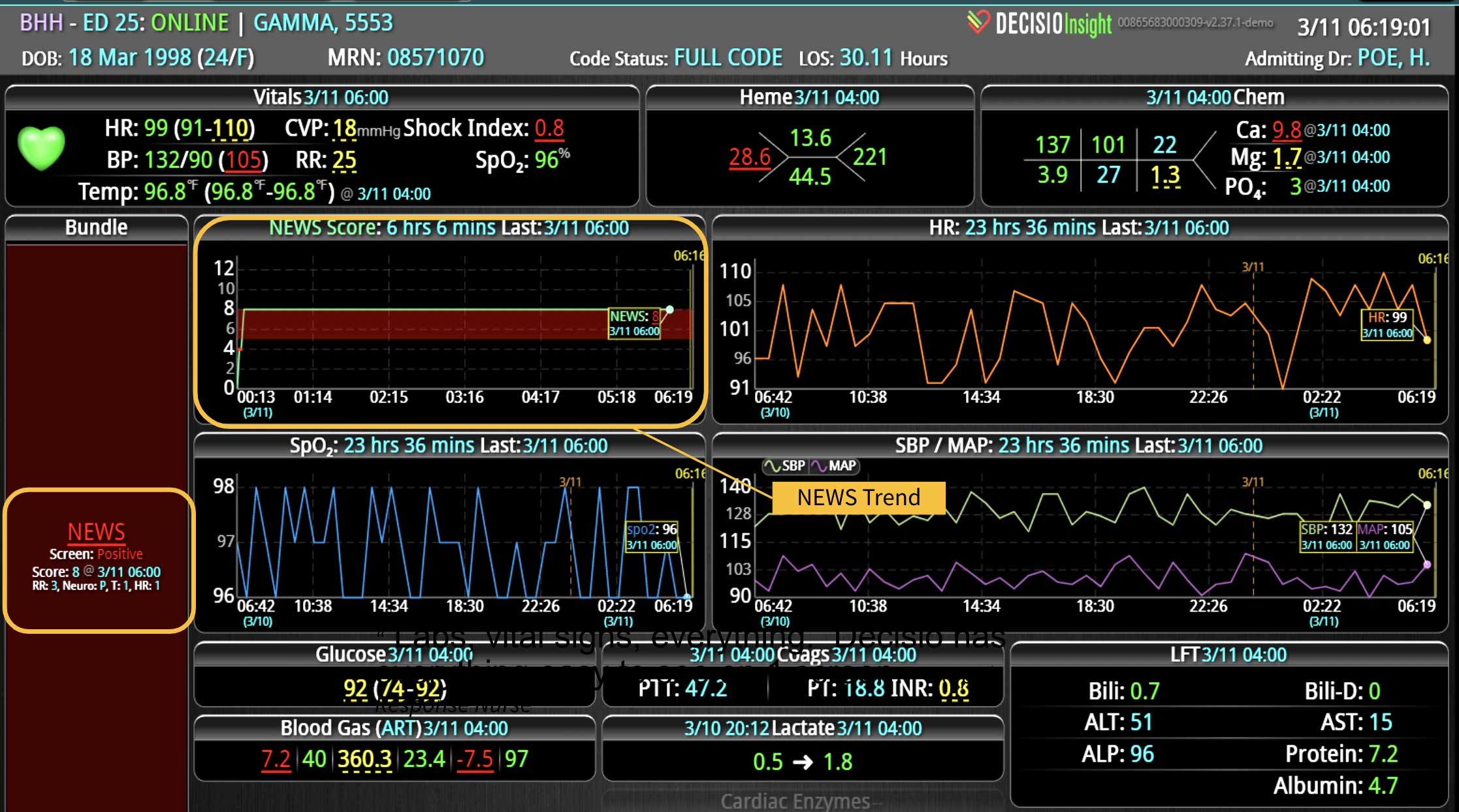
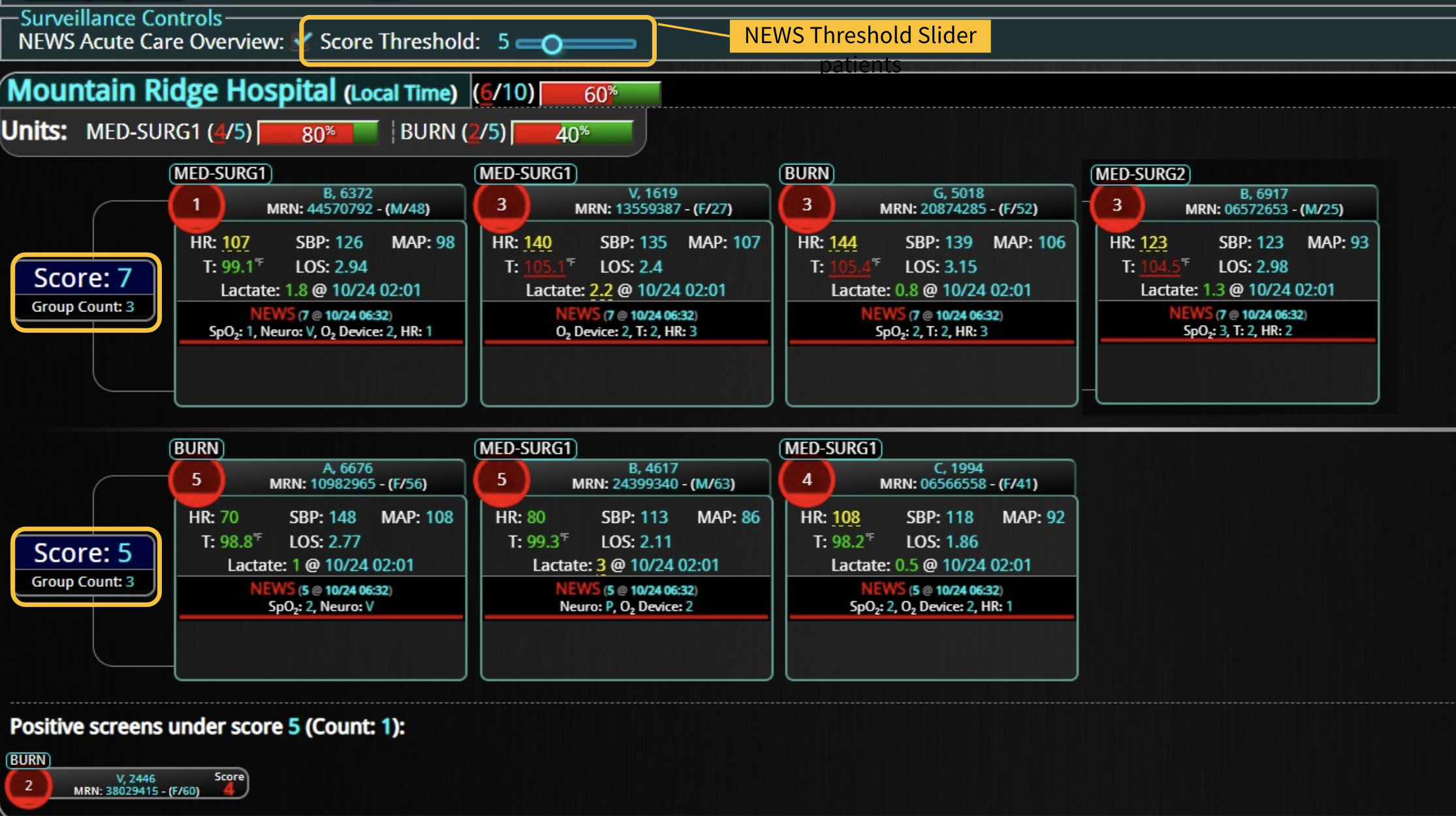
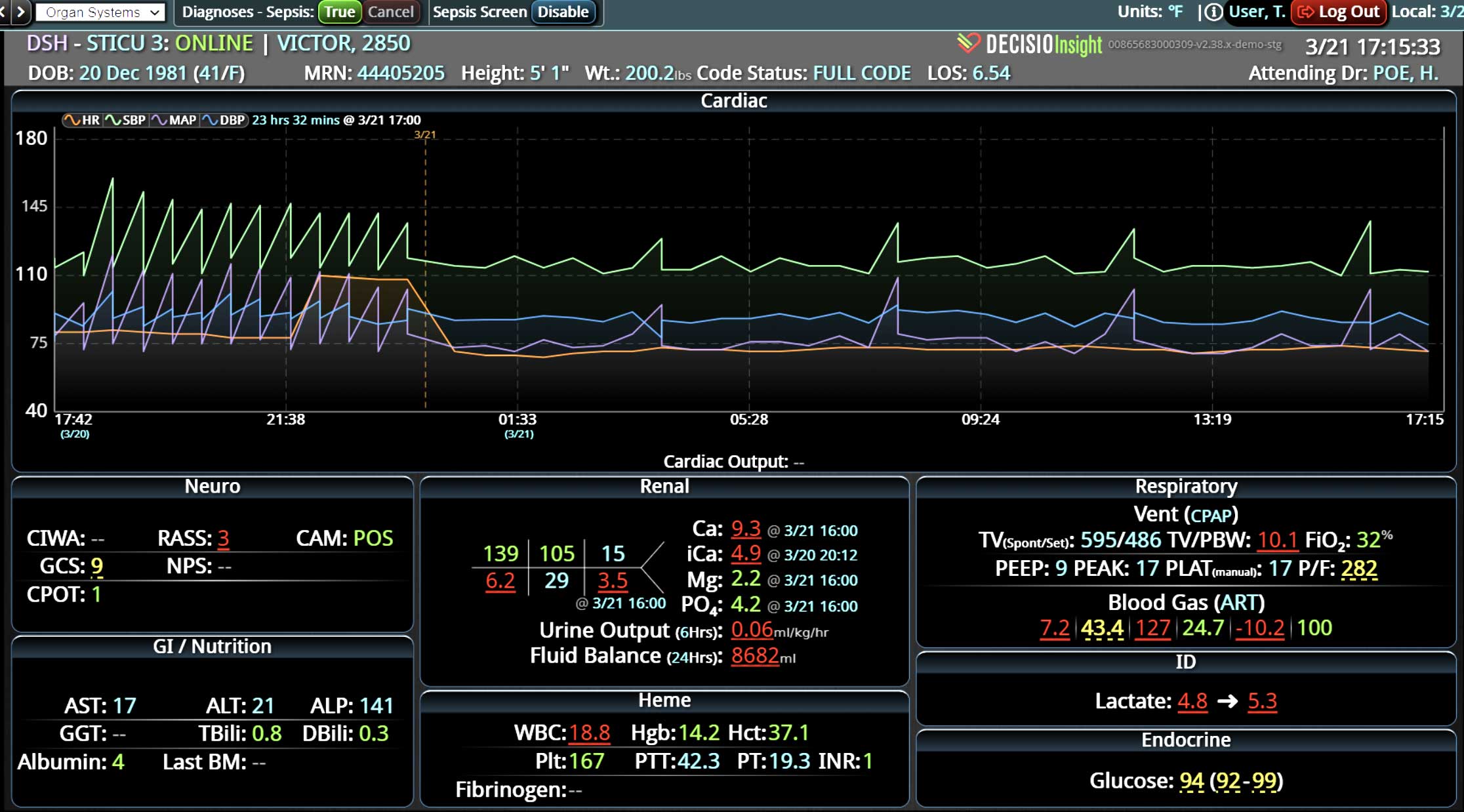
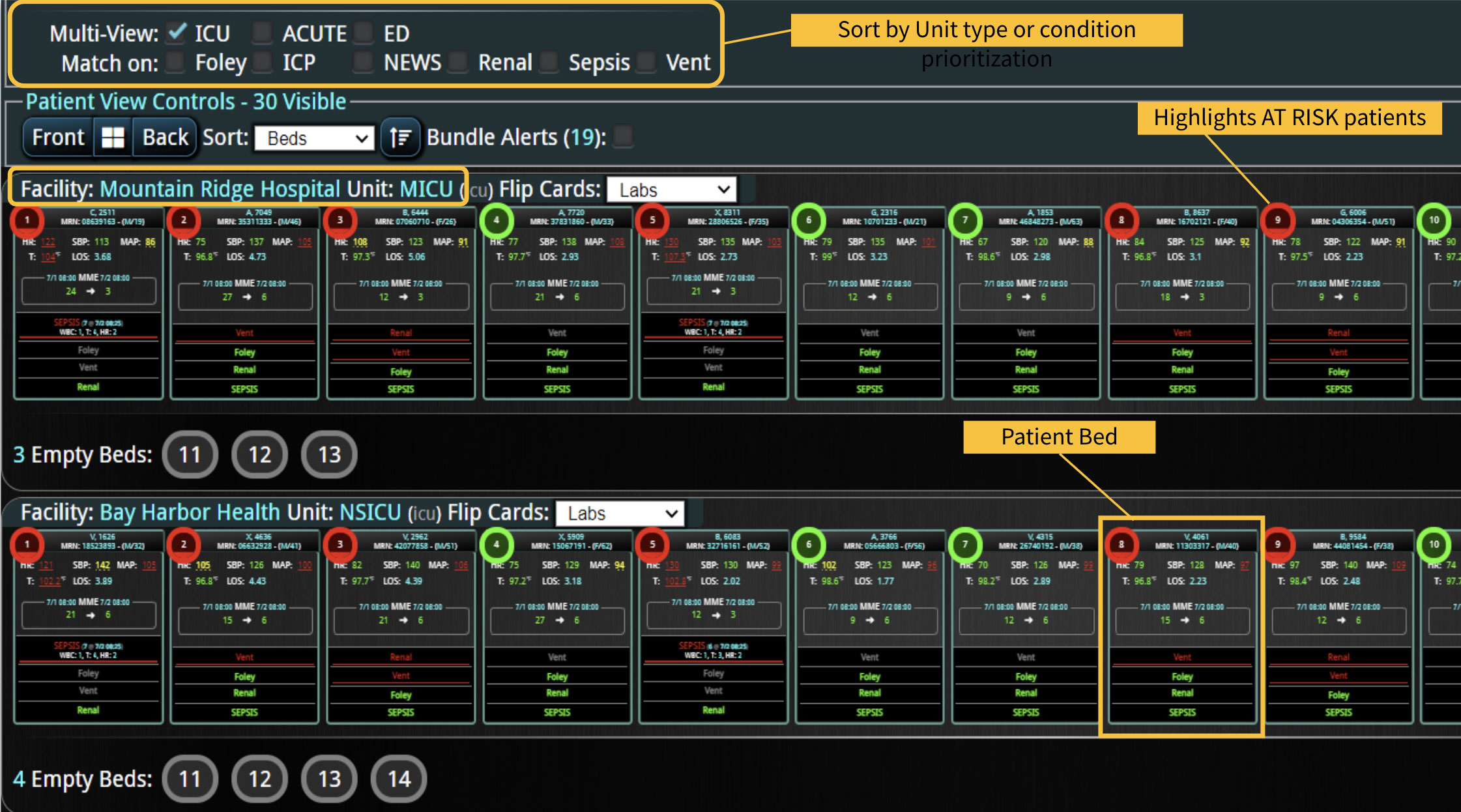
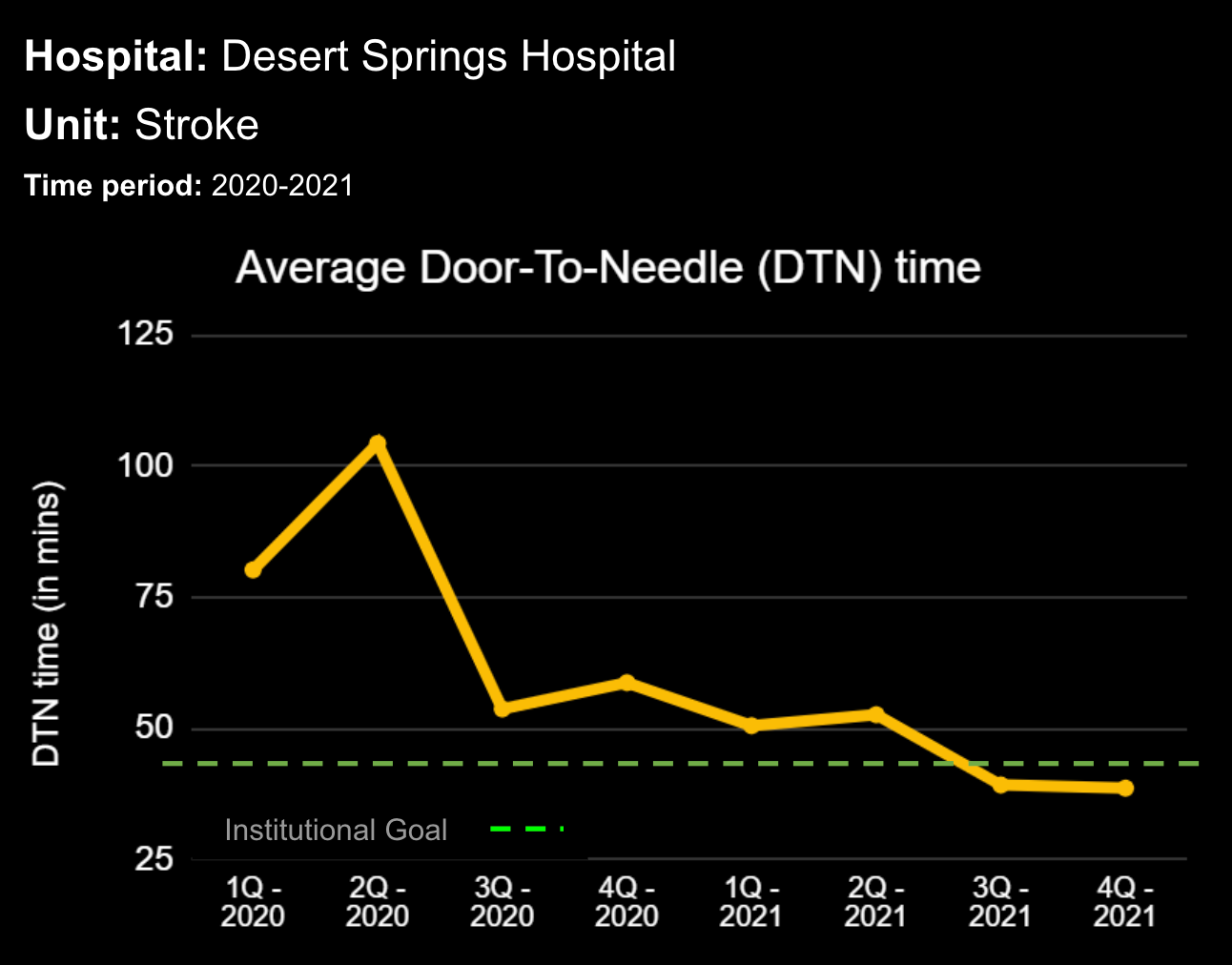
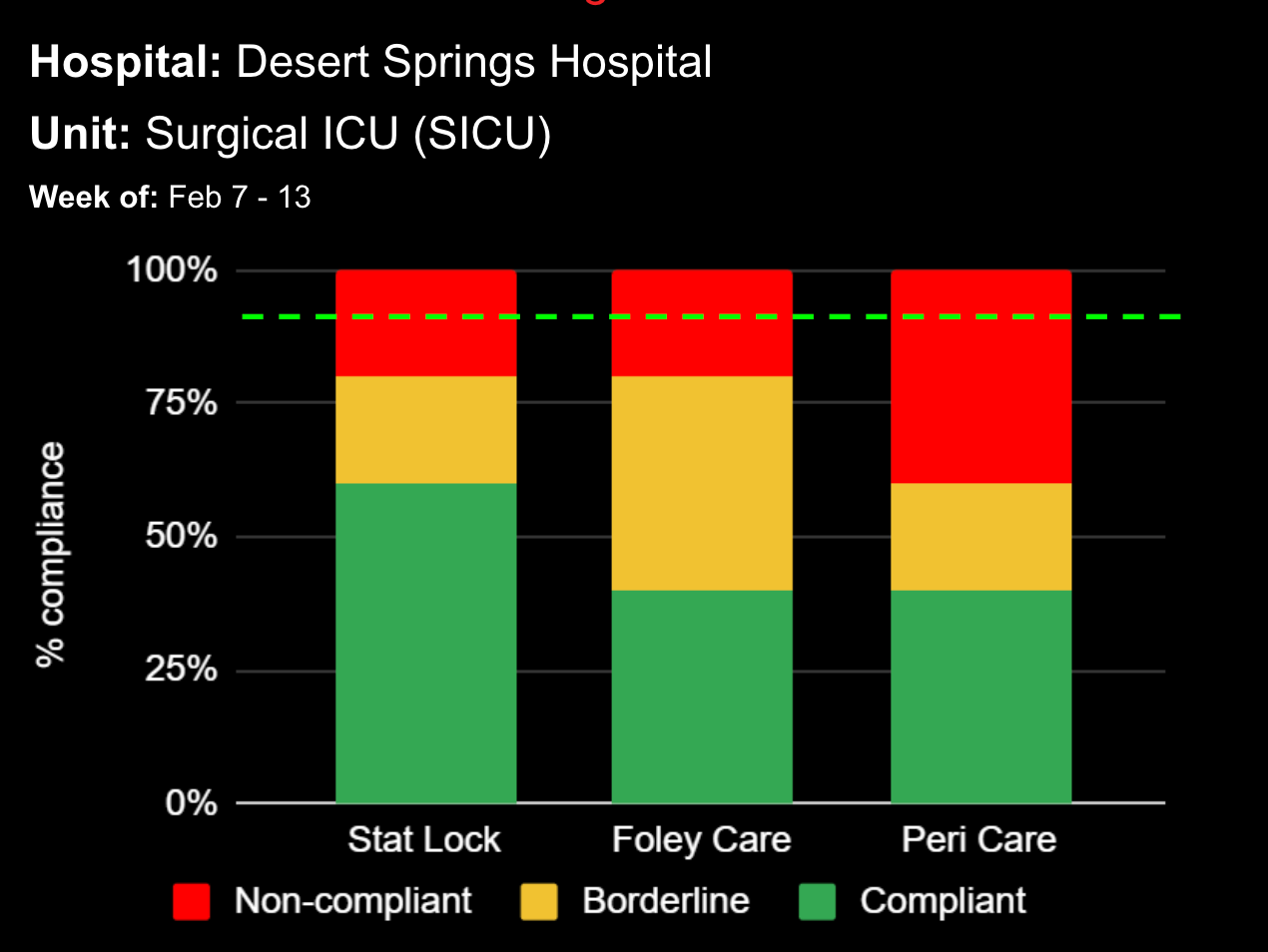
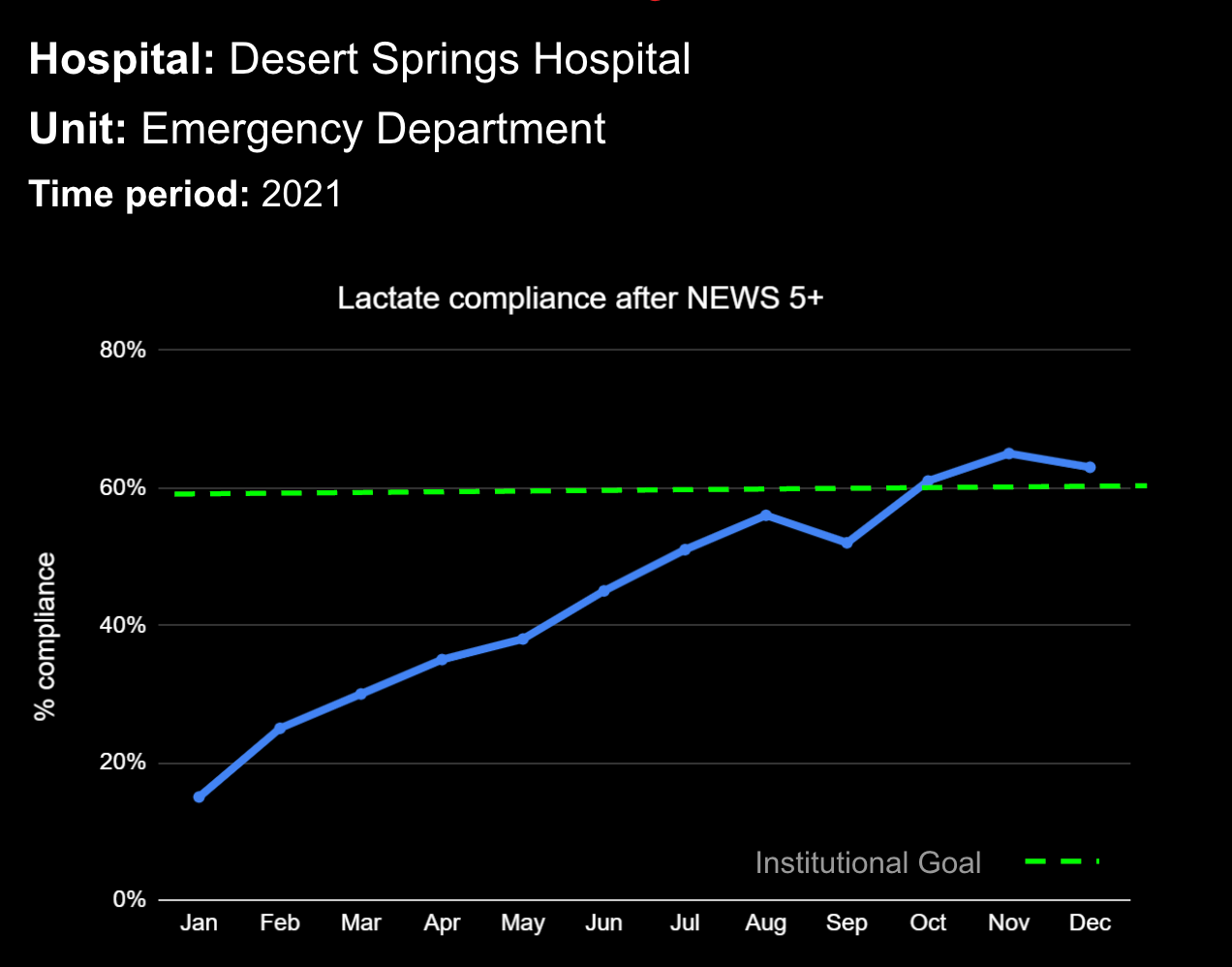
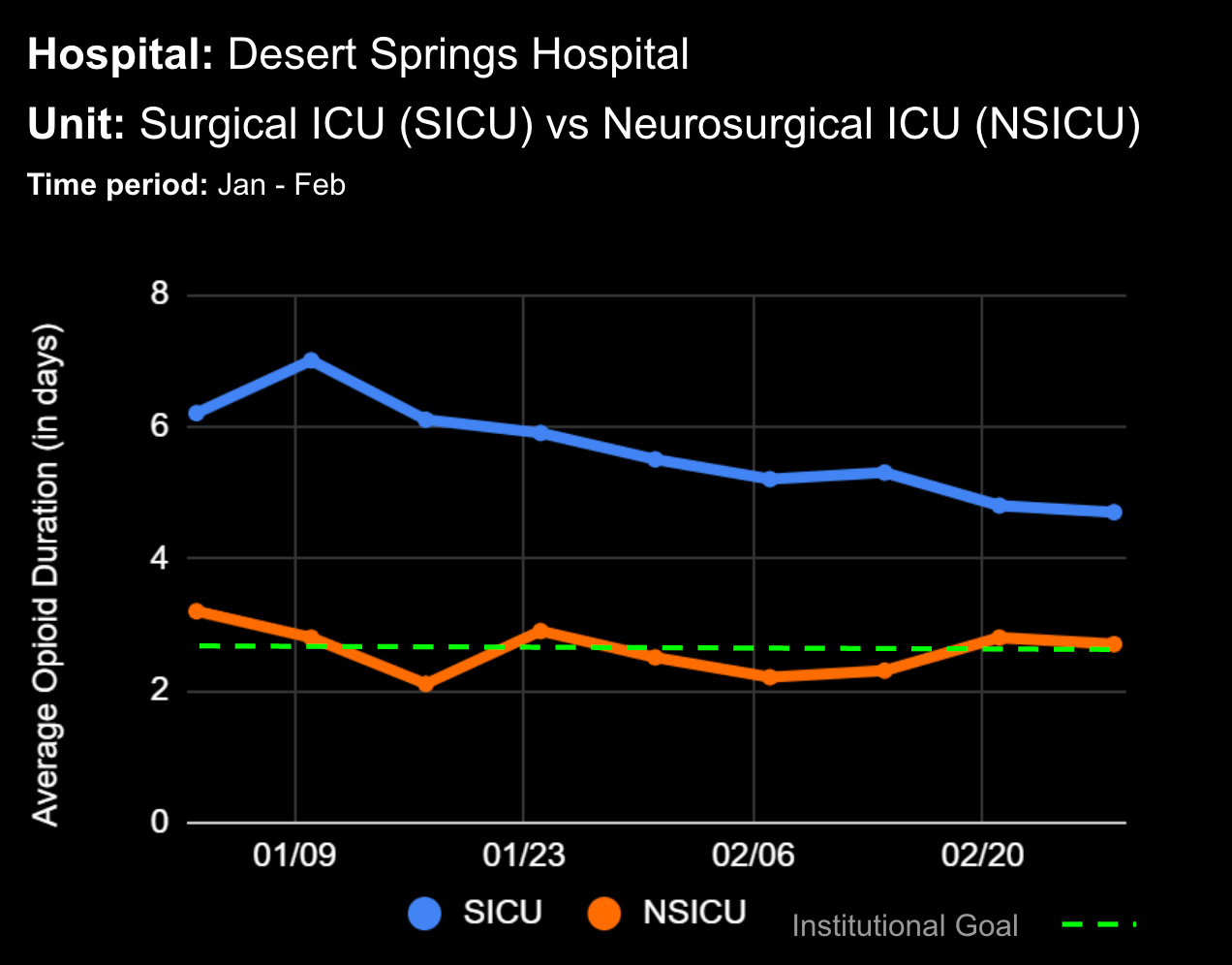
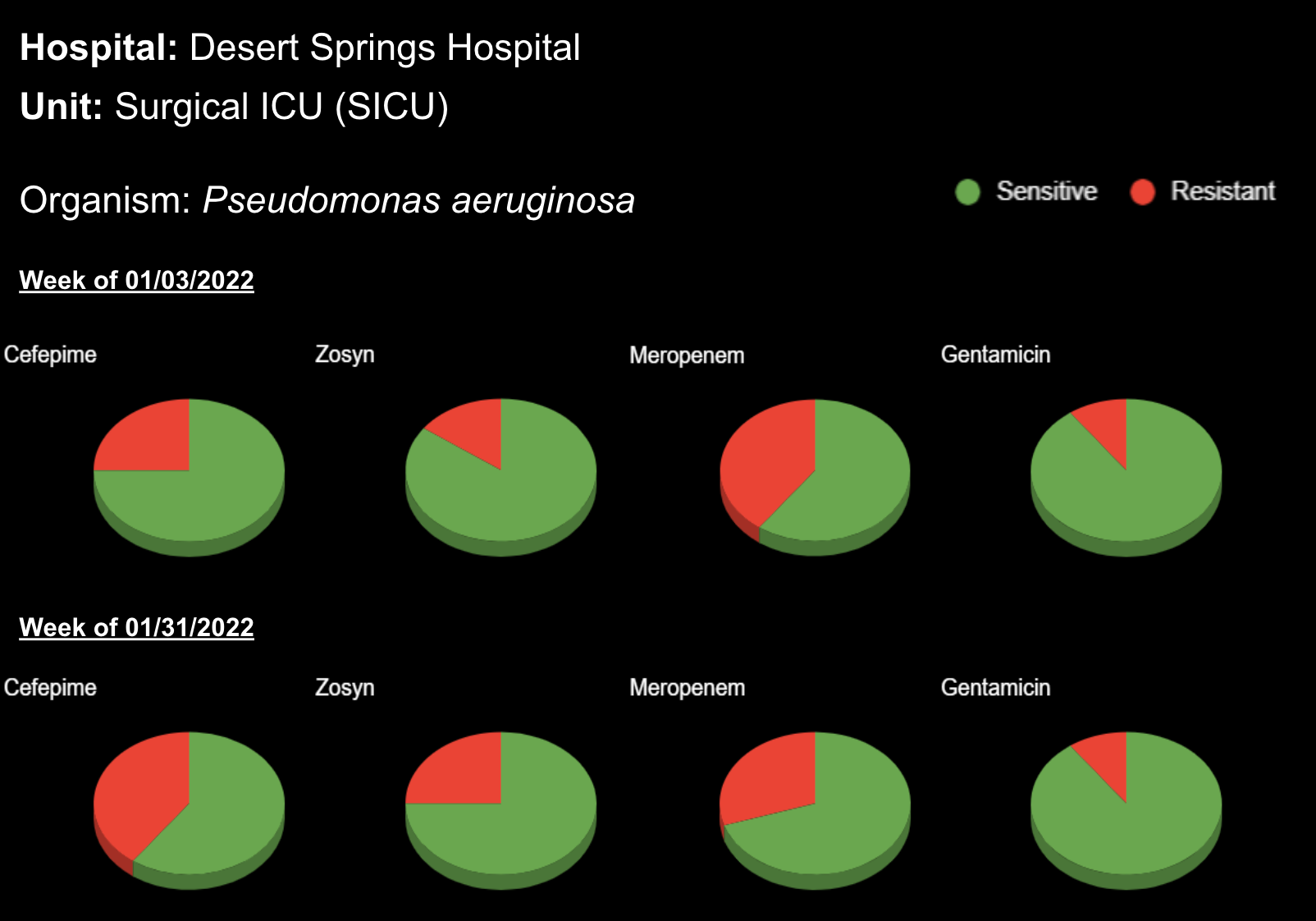
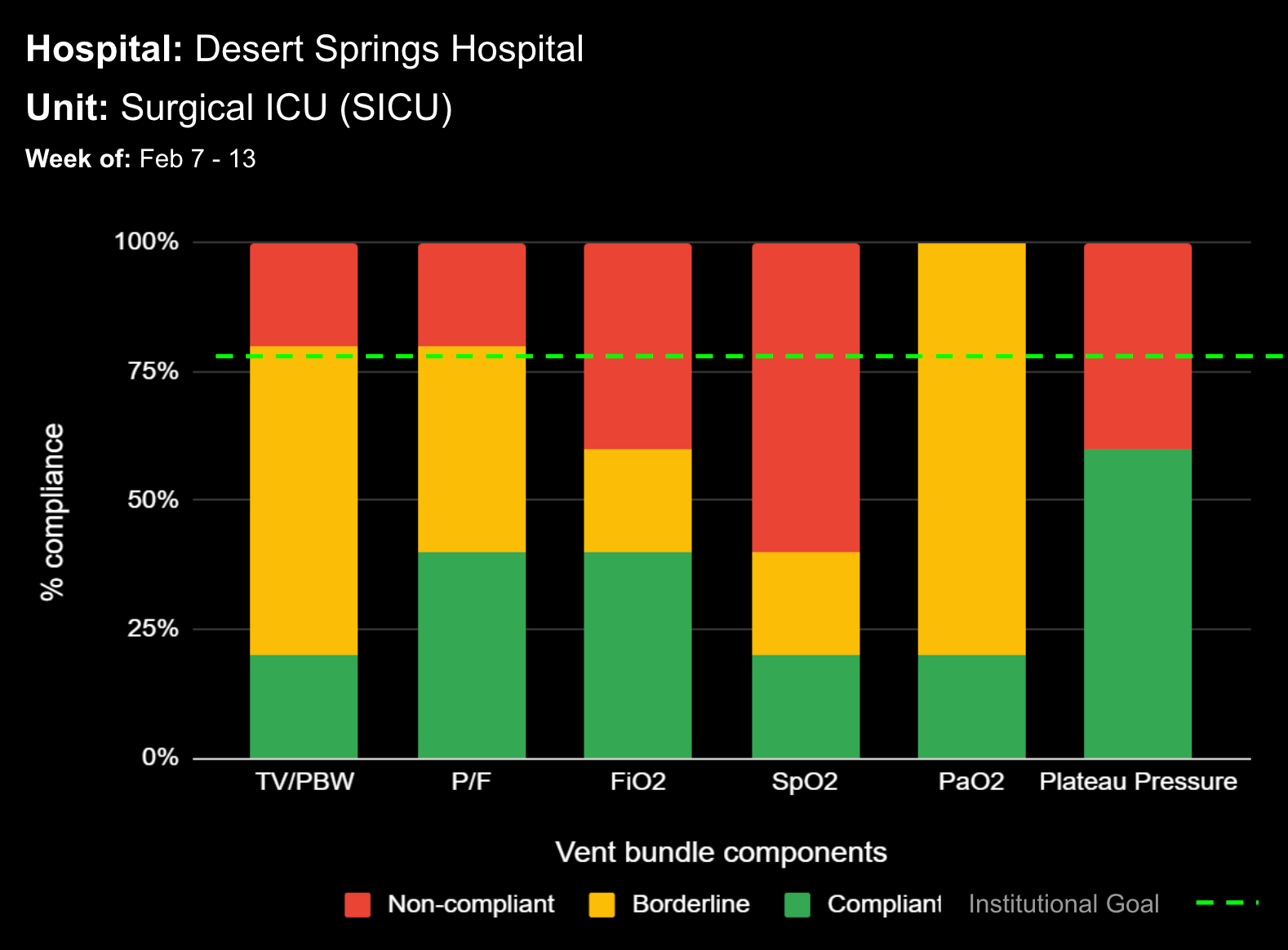
Sepsis is a life-threatening condition that requires rapid identification and treatment. To improve sepsis care and outcomes, the Centers for Medicare & Medicaid Services (CMS) established the SEP-1 quality measure. This article examines how clinical decision support (CDS) tools can enhance compliance with SEP-1 guidelines and improve sepsis management, with a focus on Decisio Health's InsightIQ solution. Understanding SEP-1 and Sepsis Management Guidelines The SEP-1 measure requires hospitals to report on the management of patients with severe sepsis or septic shock. Key components include a 3-hour bundle (obtaining blood cultures, administering antibiotics, measuring serum lactate, and administering fluids) and a 6-hour bundle (re-measuring serum lactate if initially elevated)[1]. Compliance with the SEP-1 bundle has been associated with reduced in-hospital mortality from 27% to 22%[2]. Challenges in Achieving SEP-1 Compliance Healthcare organizations face several barriers to implementing sepsis protocols effectively. These include nursing staff shortages, challenges in identifying sepsis, and institutional resource constraints[3][4][5]. These obstacles can significantly hinder the timely and accurate implementation of sepsis management protocols. Clinical Decision Support Tools for Sepsis Management Clinical decision support tools are designed to assist healthcare providers in making informed decisions about patient care. In the context of sepsis management, CDS tools can provide real-time alerts for potential sepsis cases,...