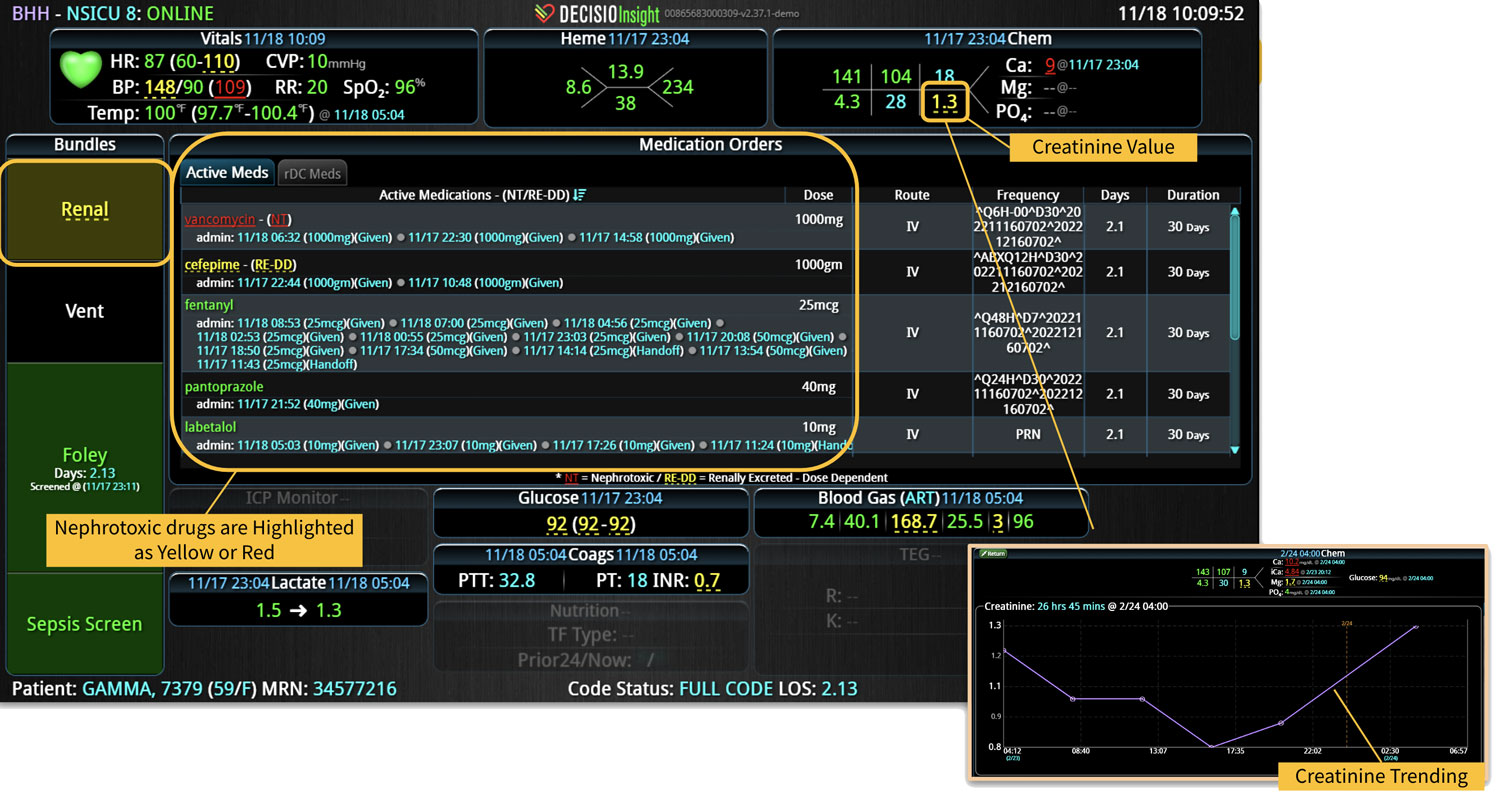
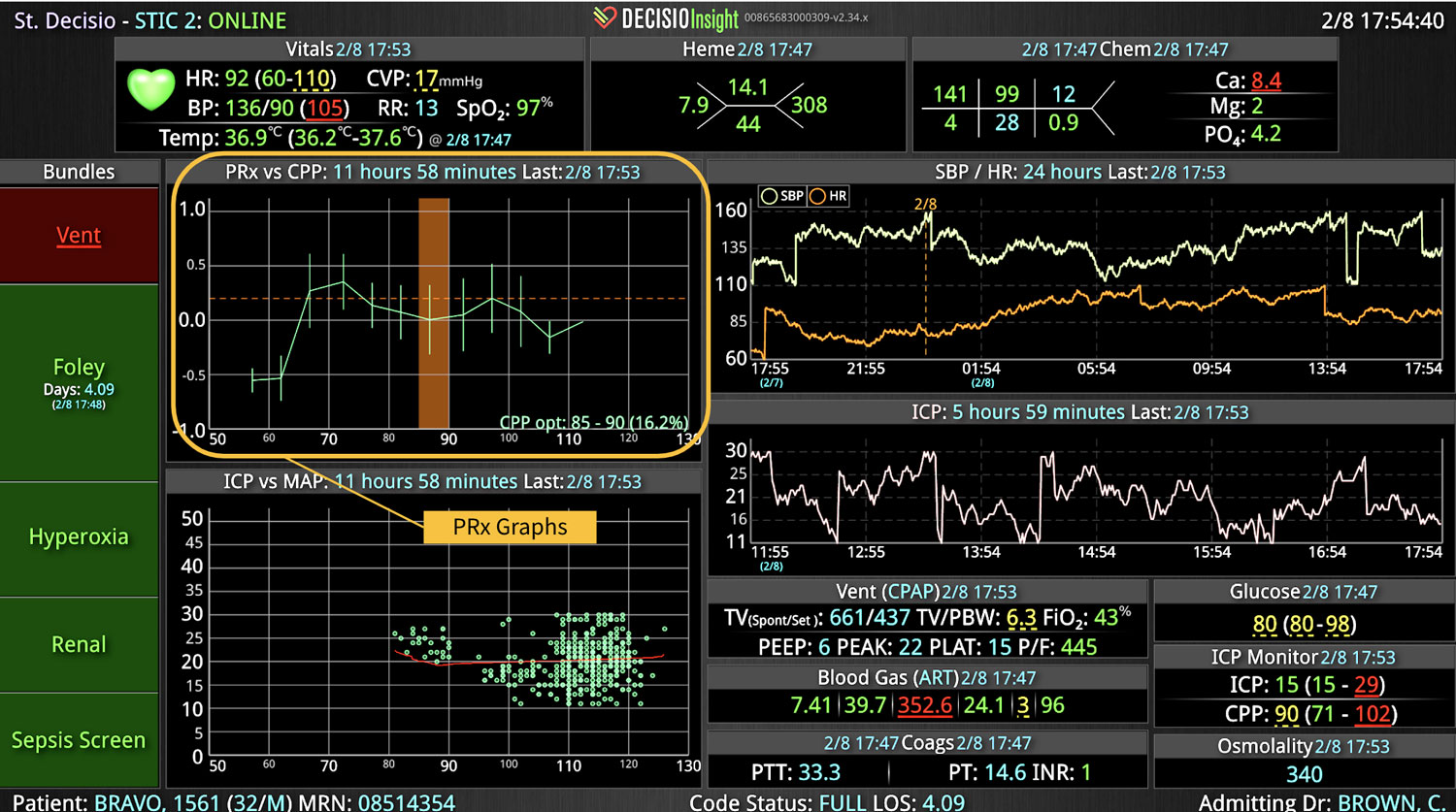
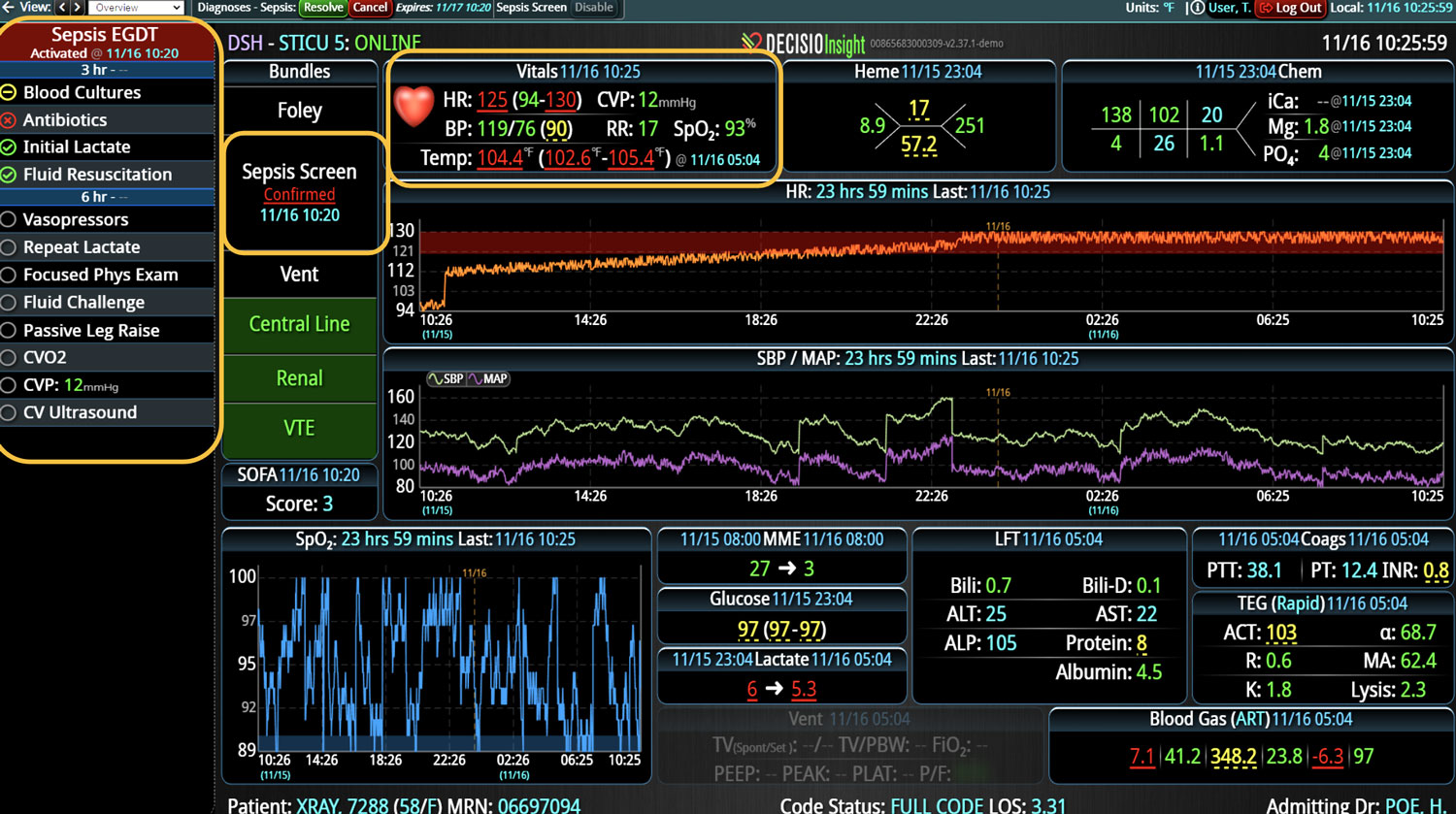
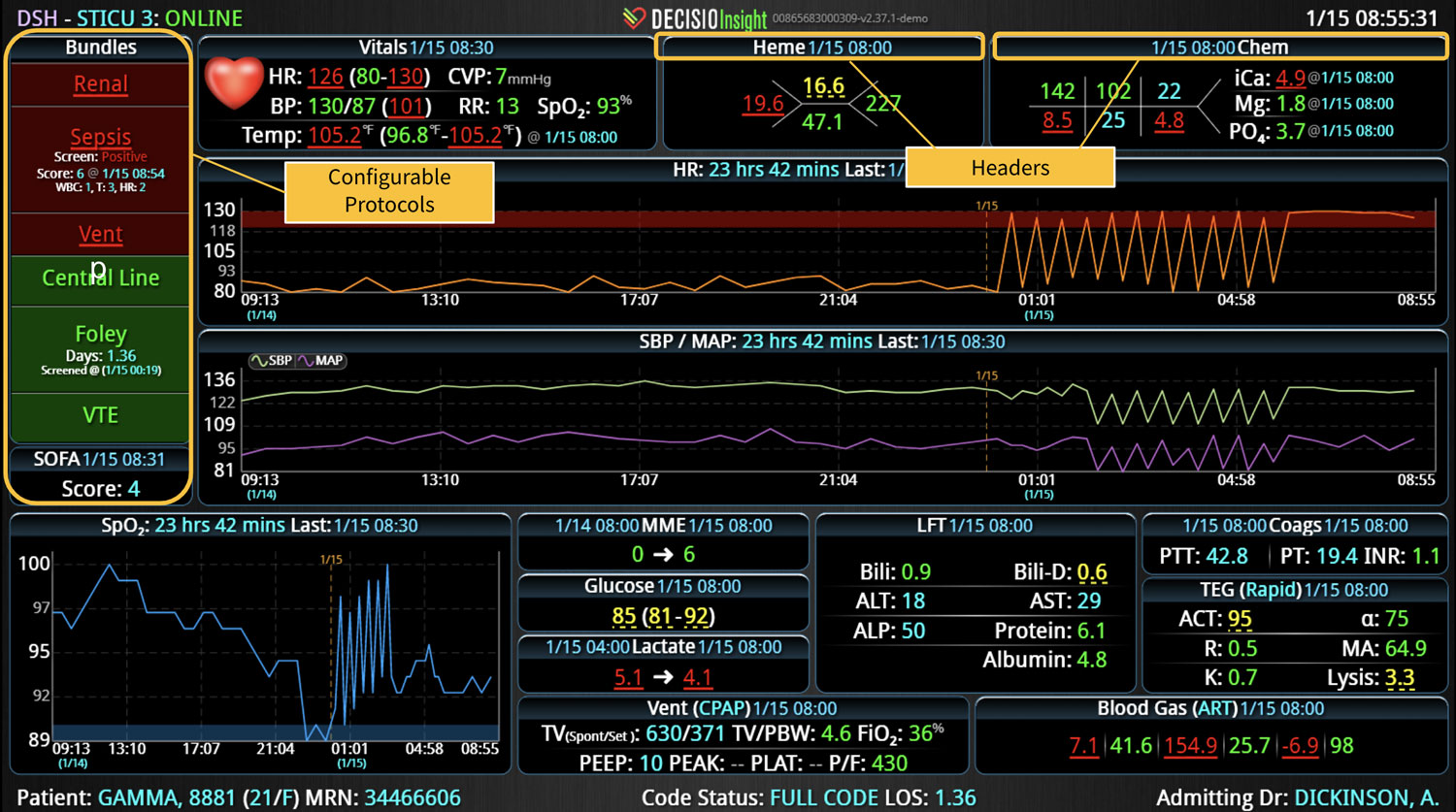
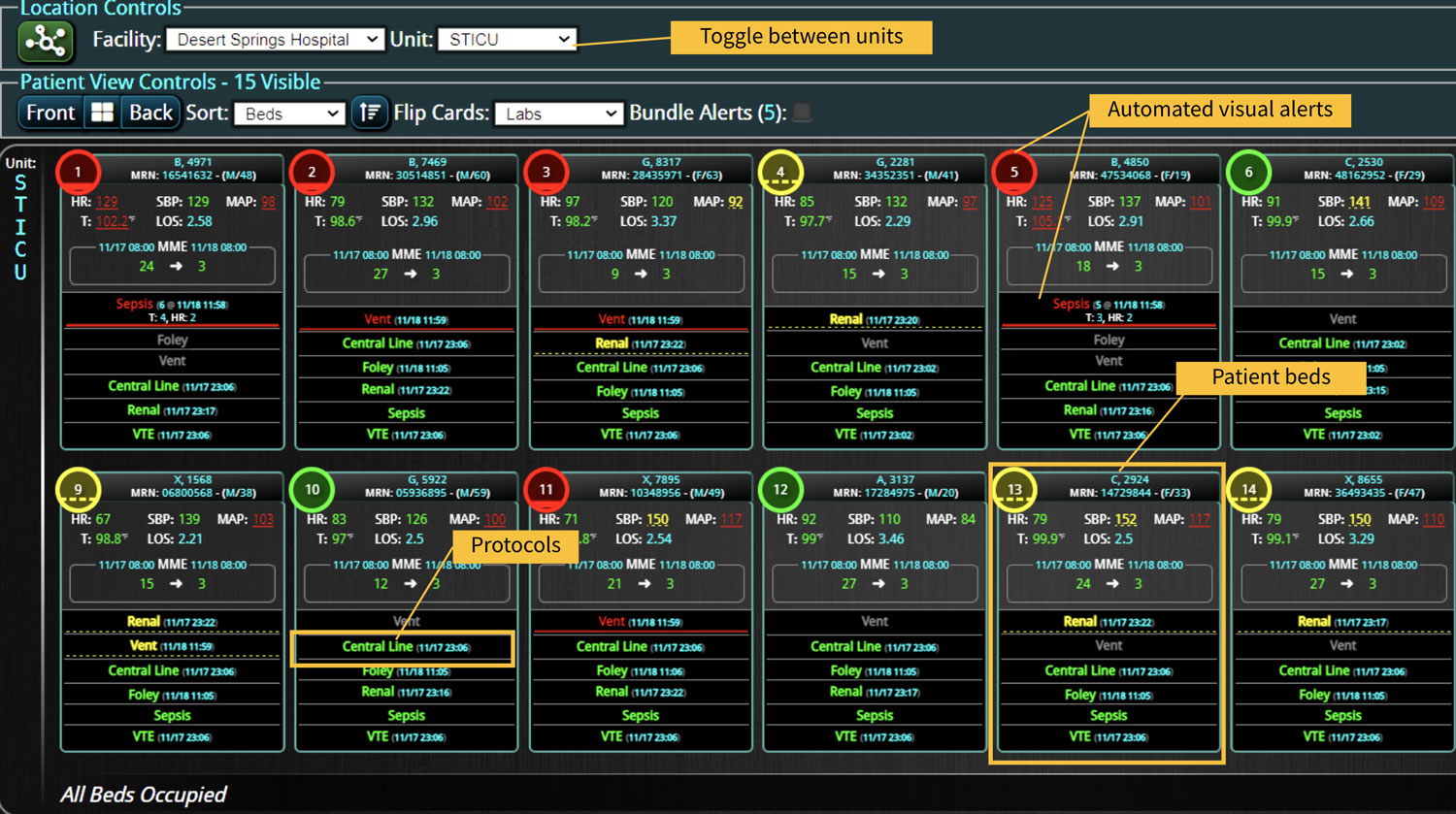
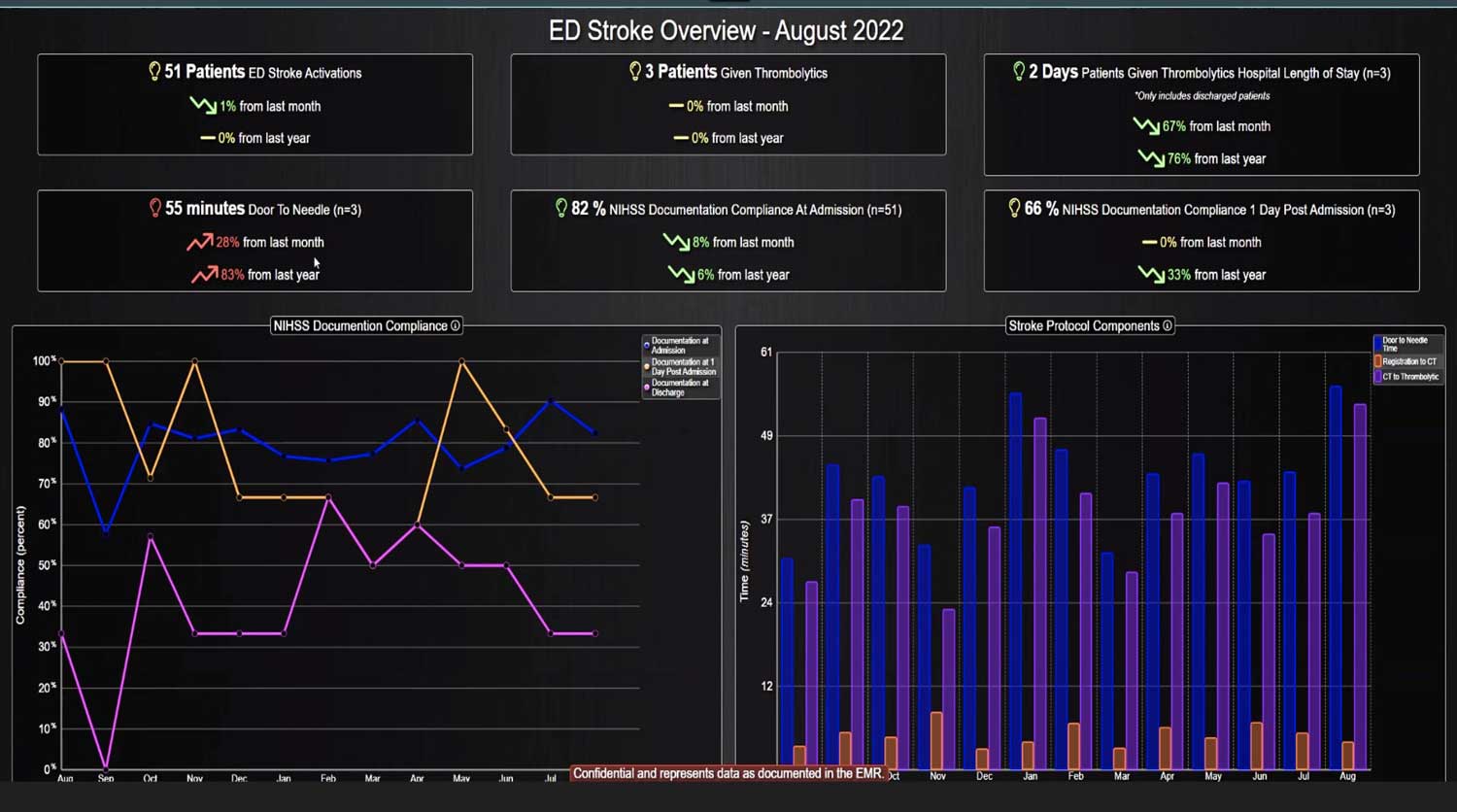
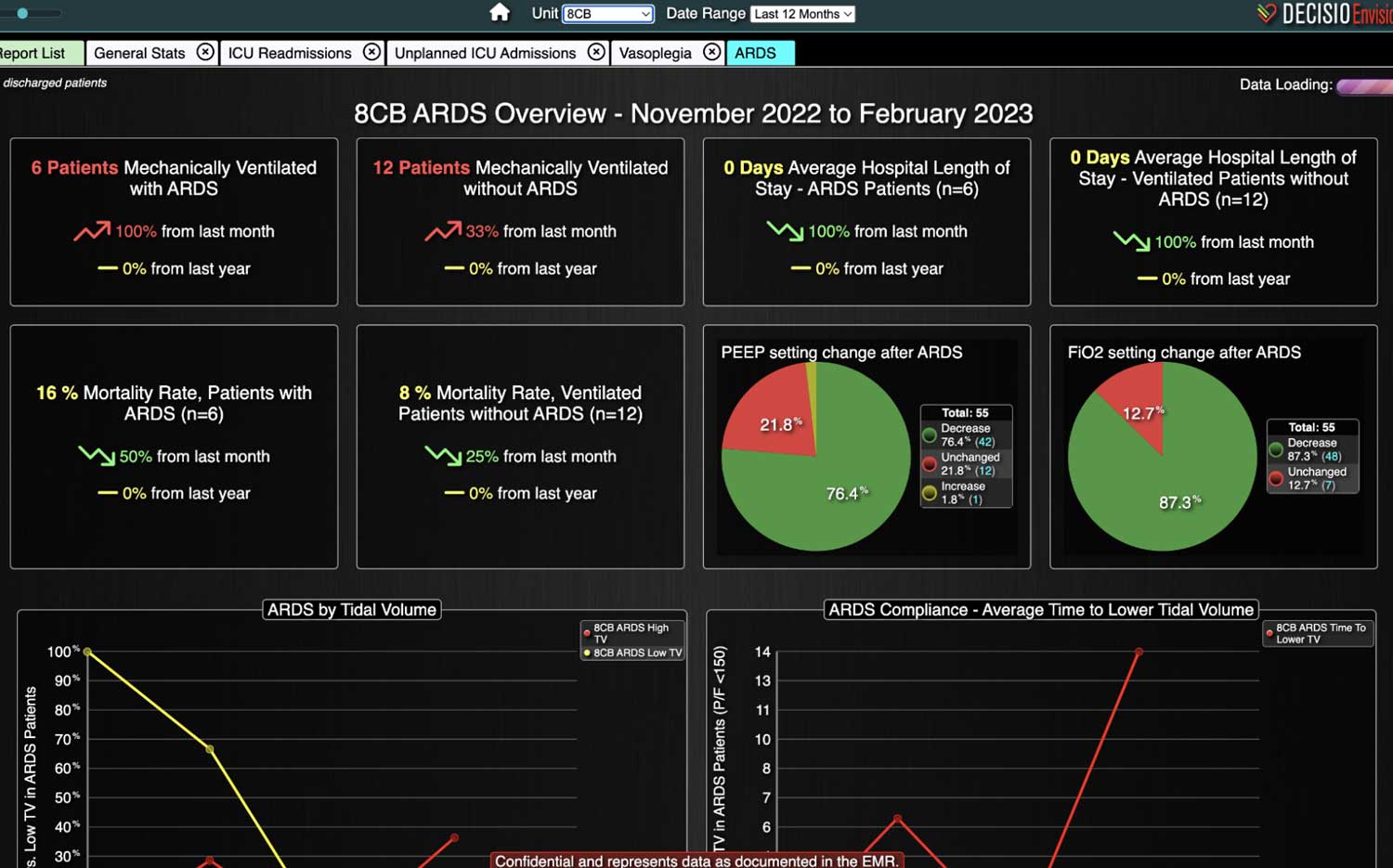
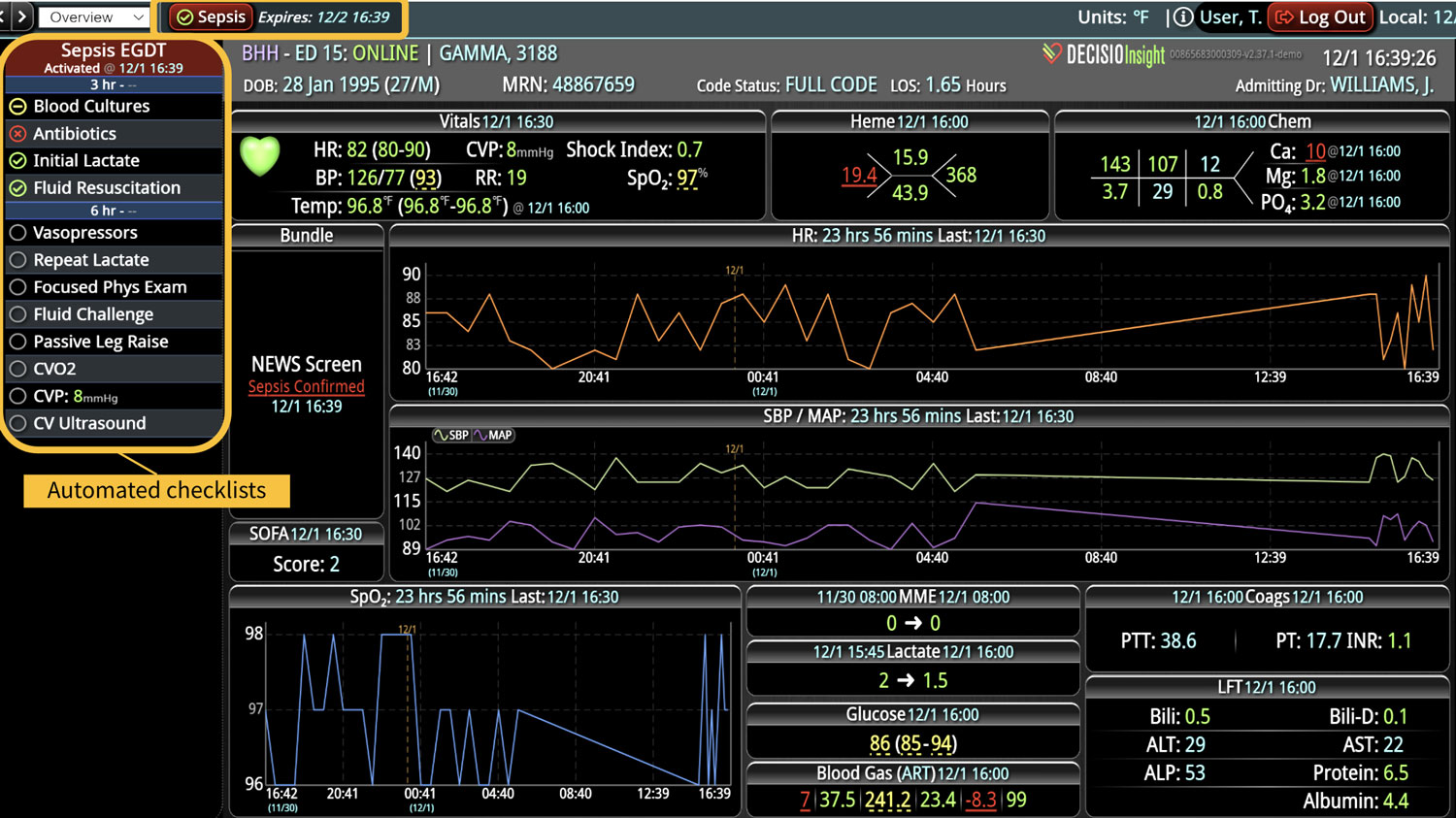
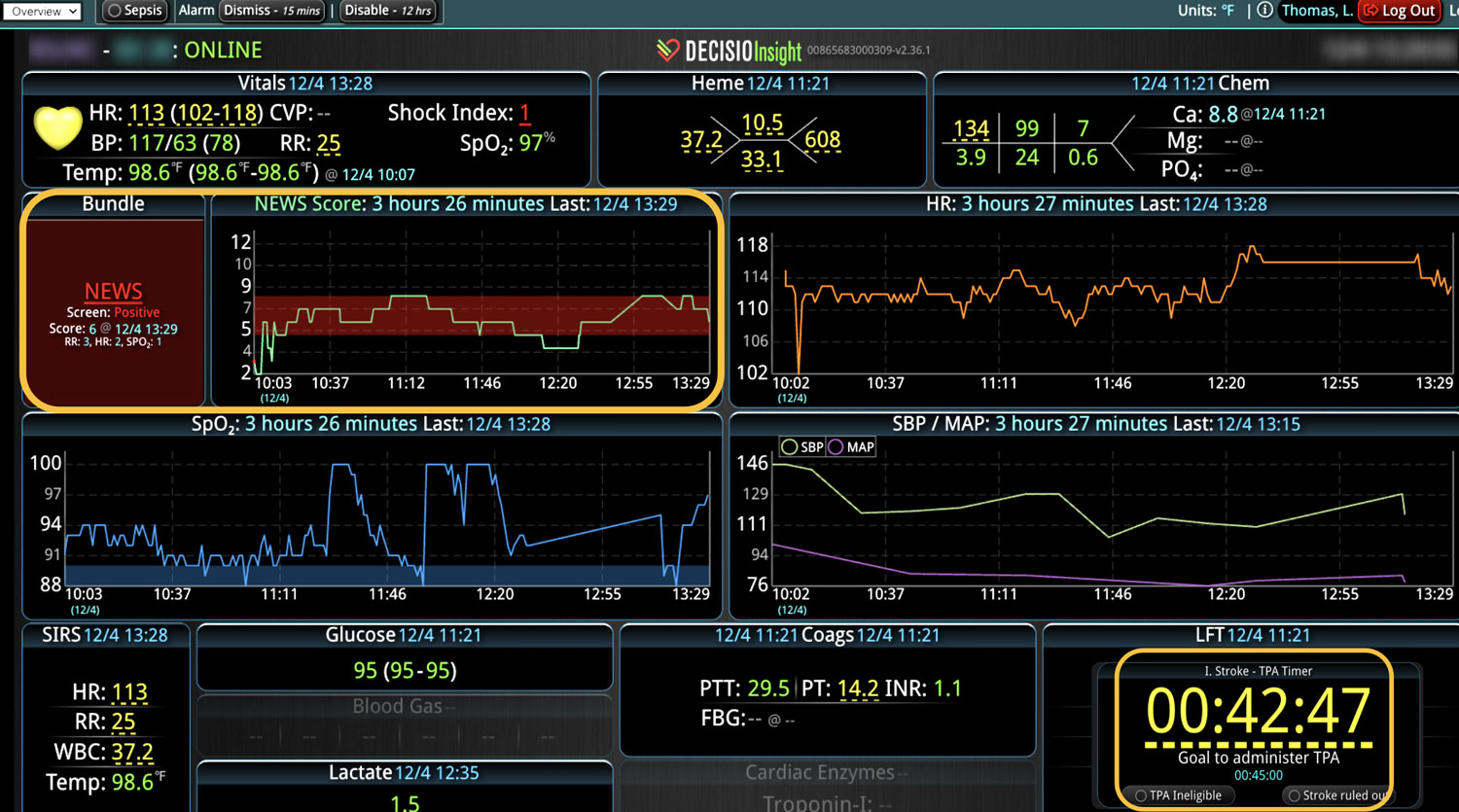
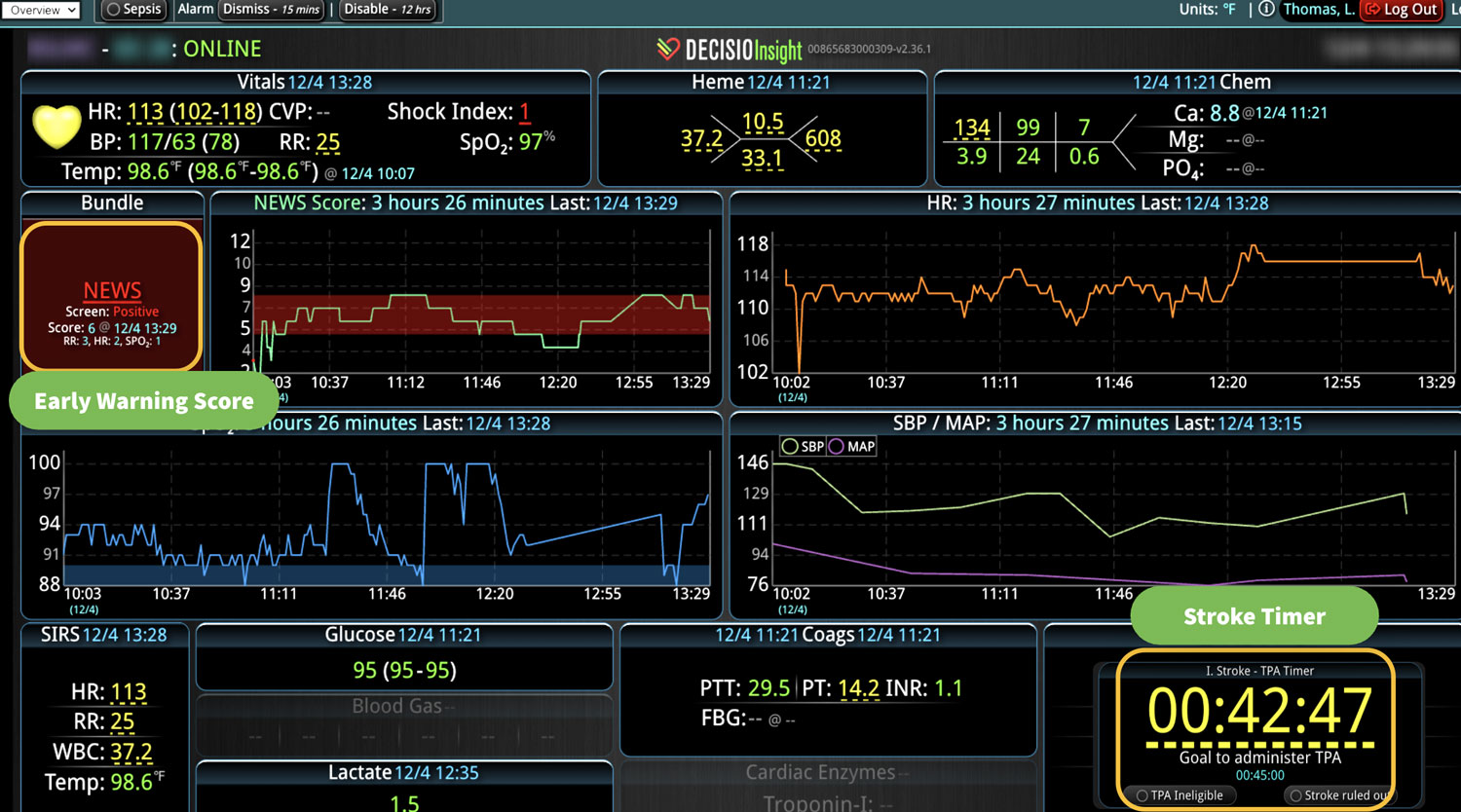
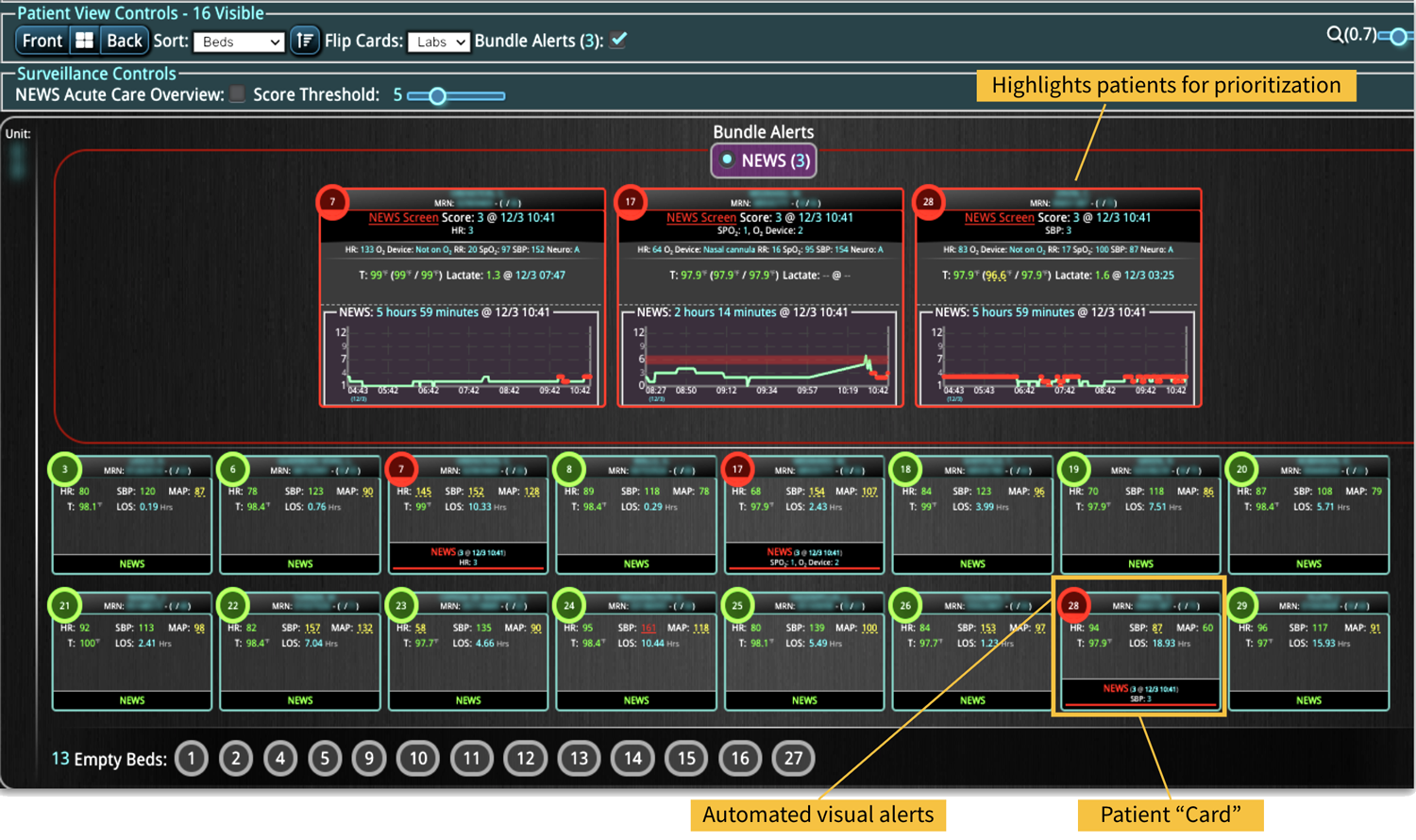
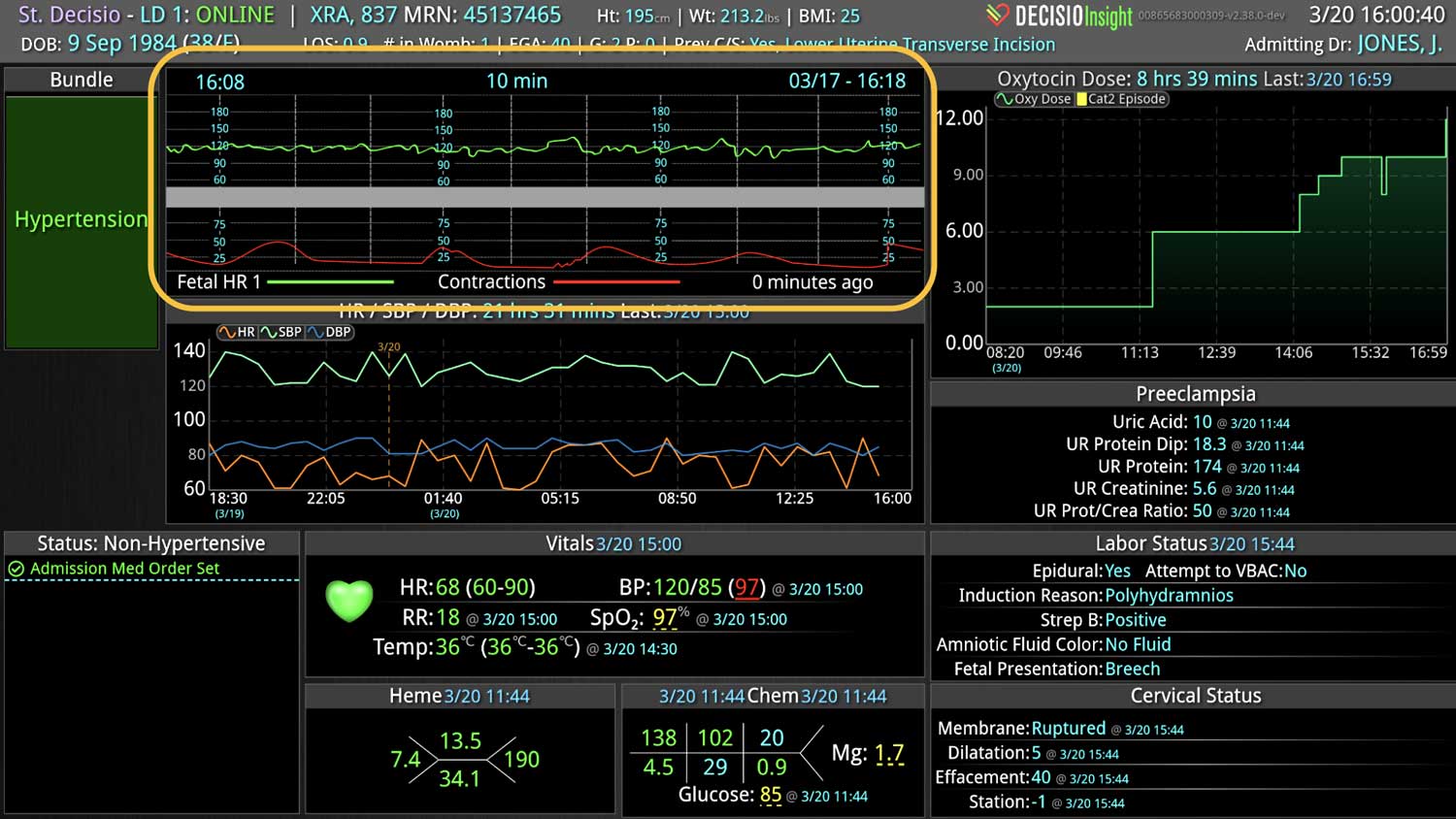
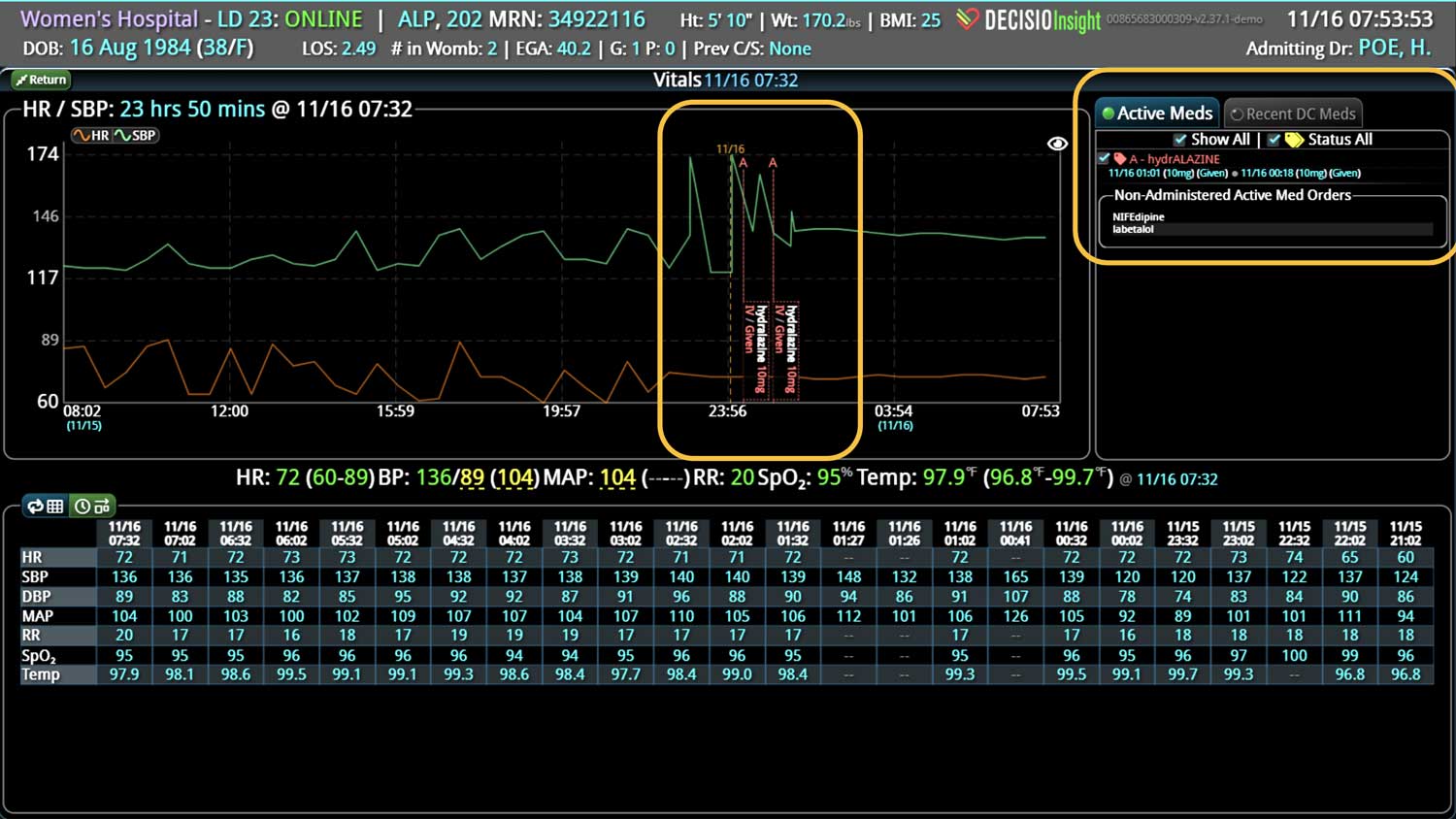
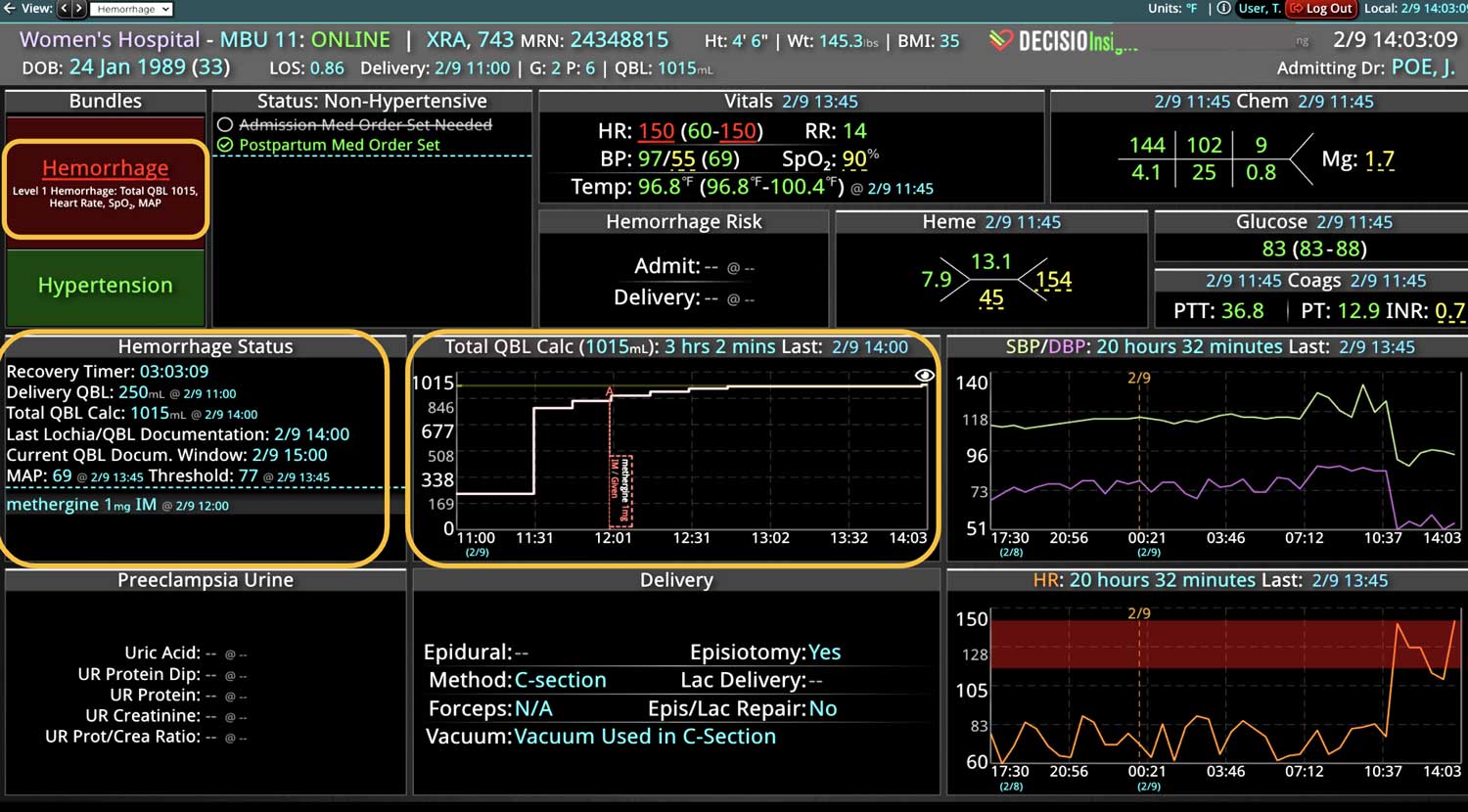
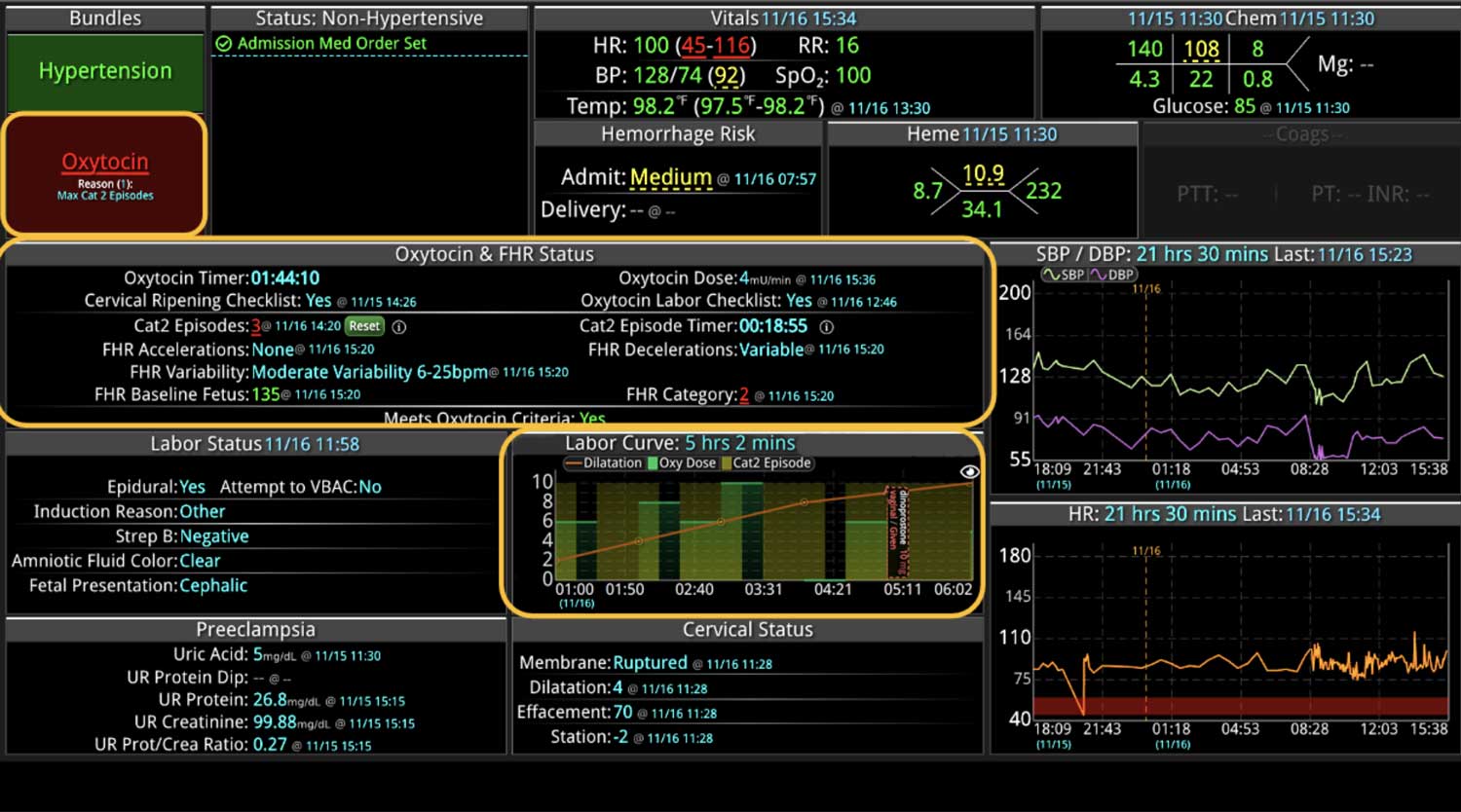
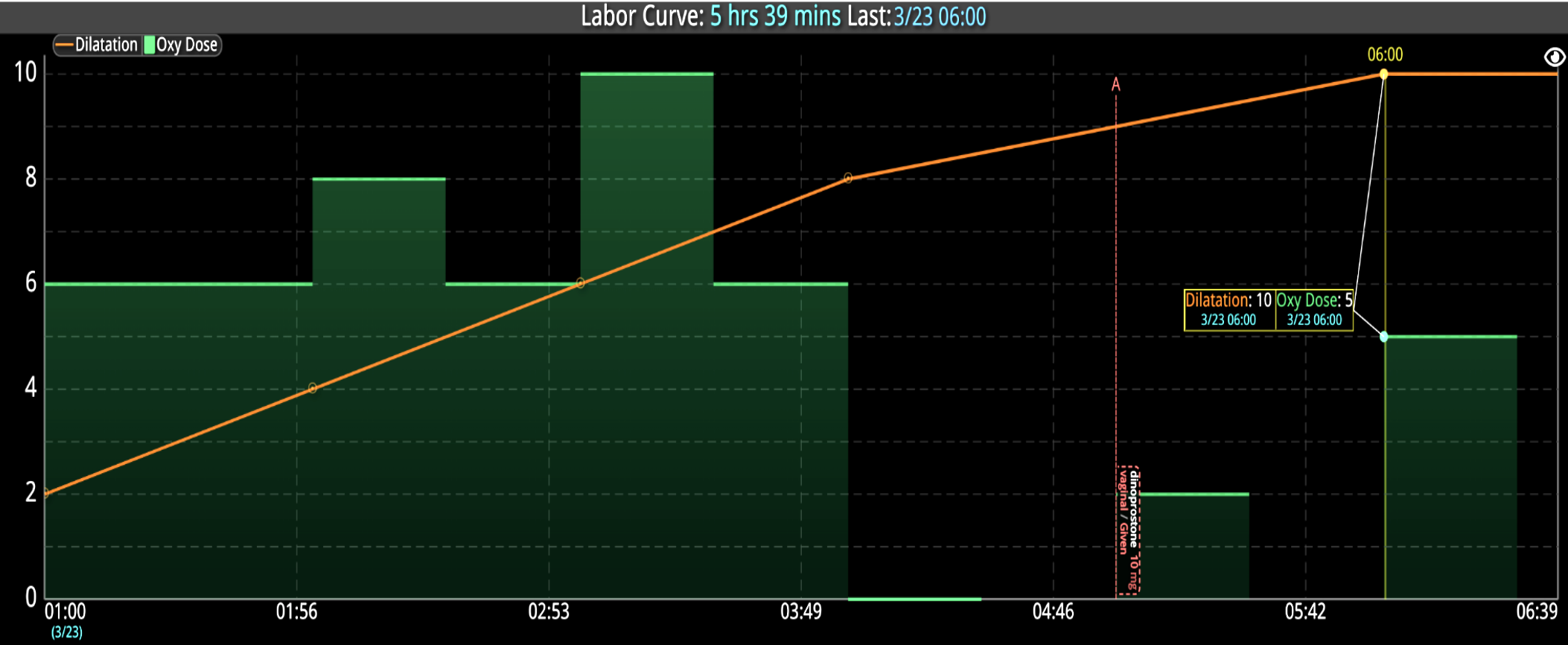
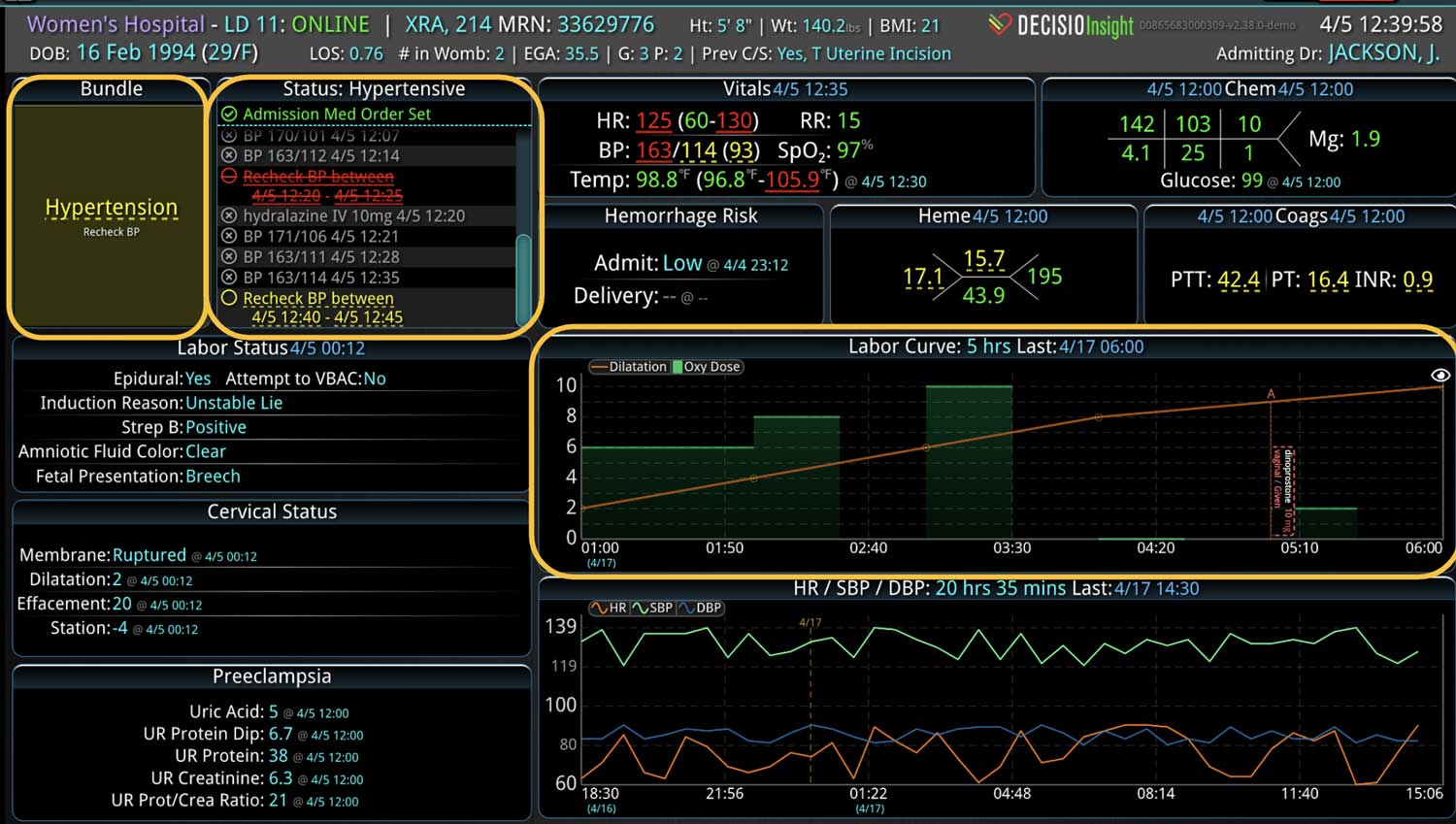
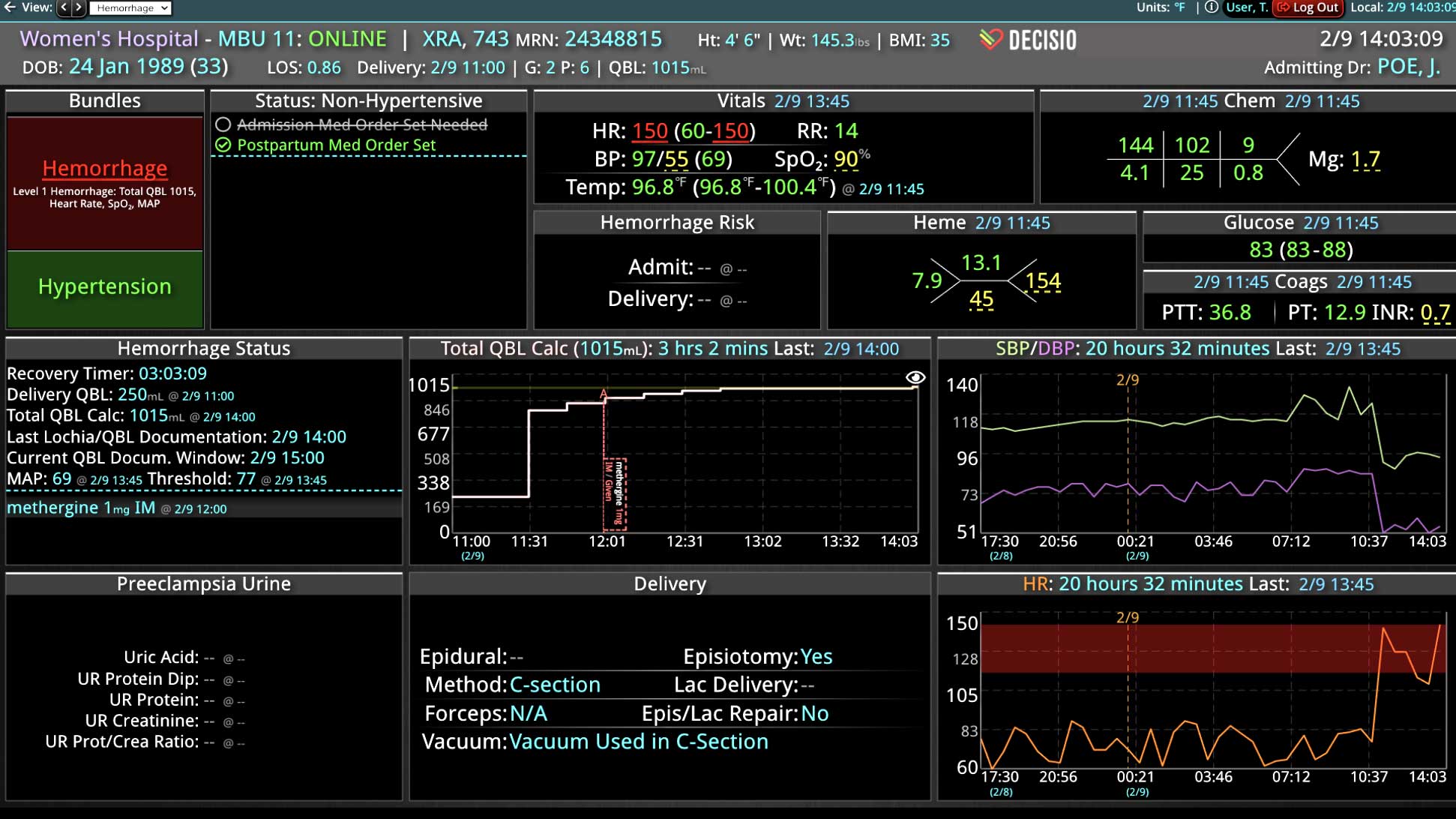
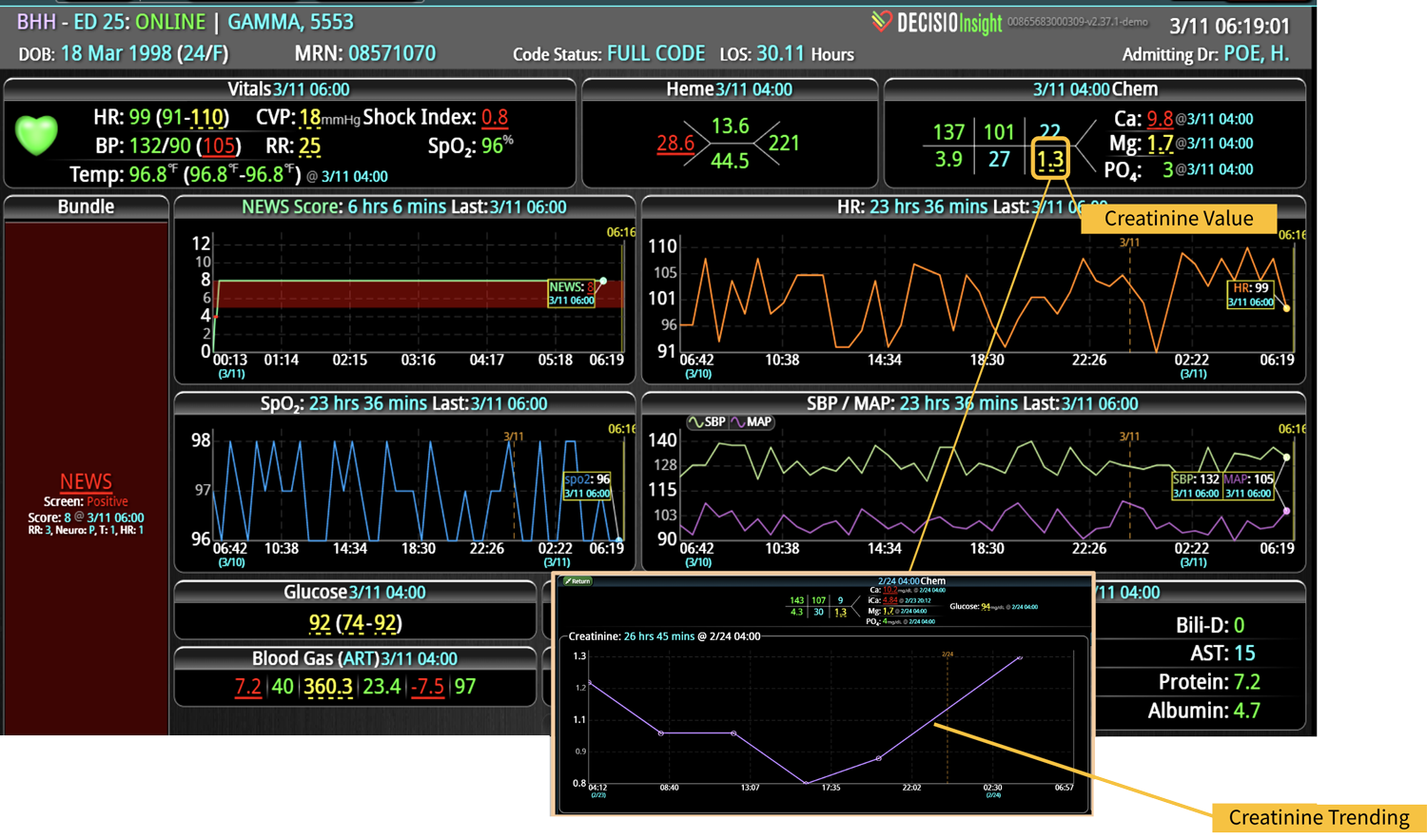
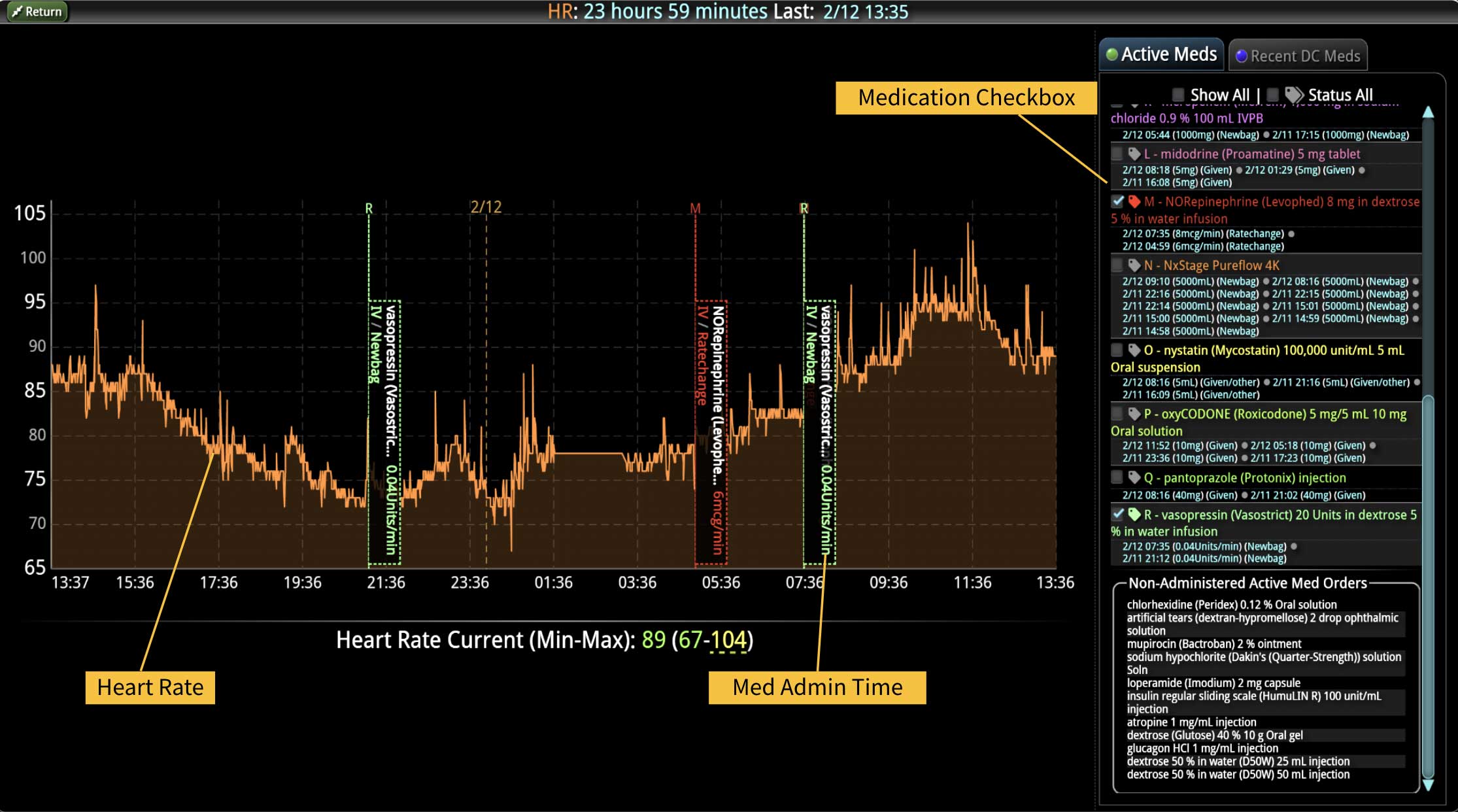
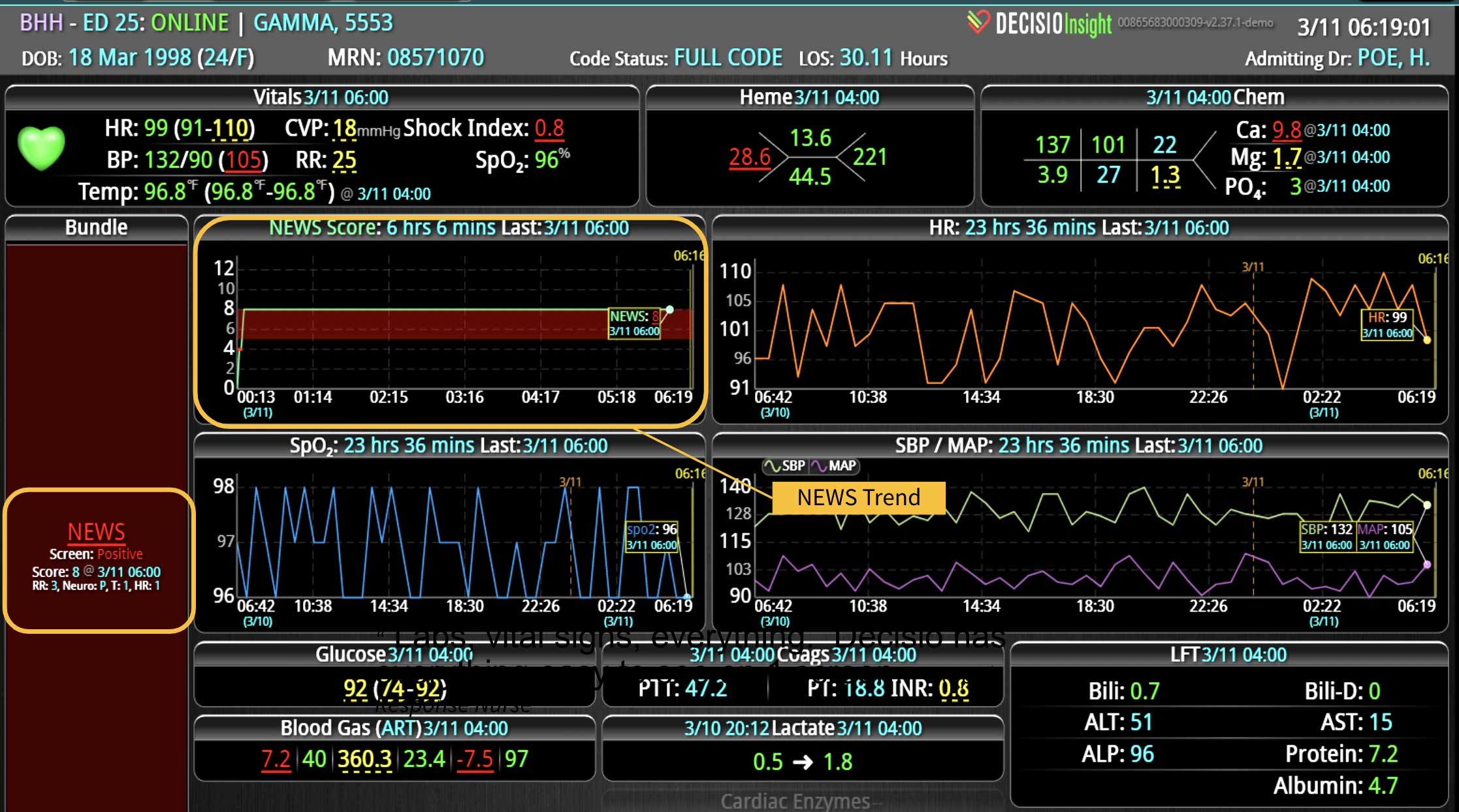
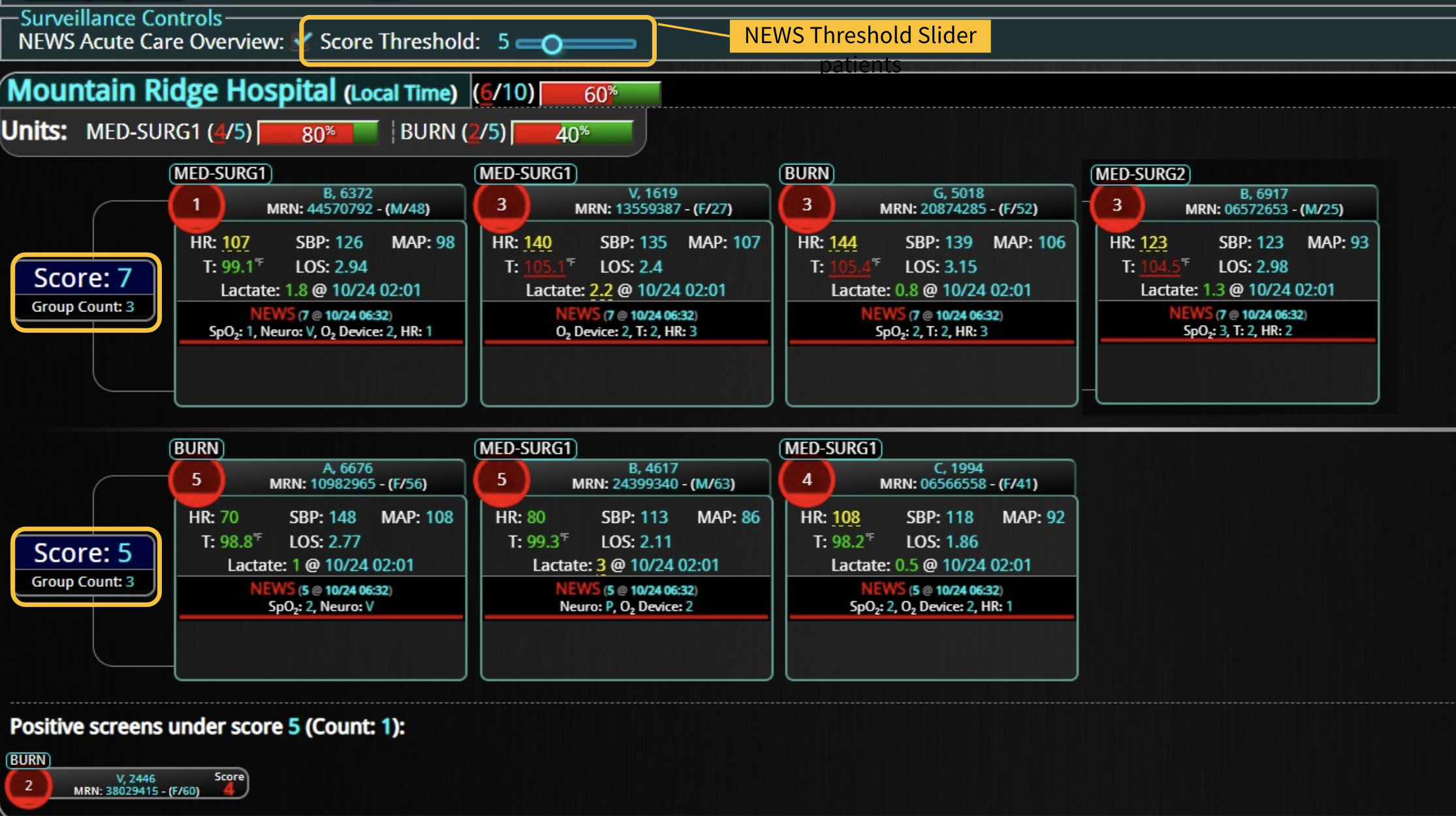
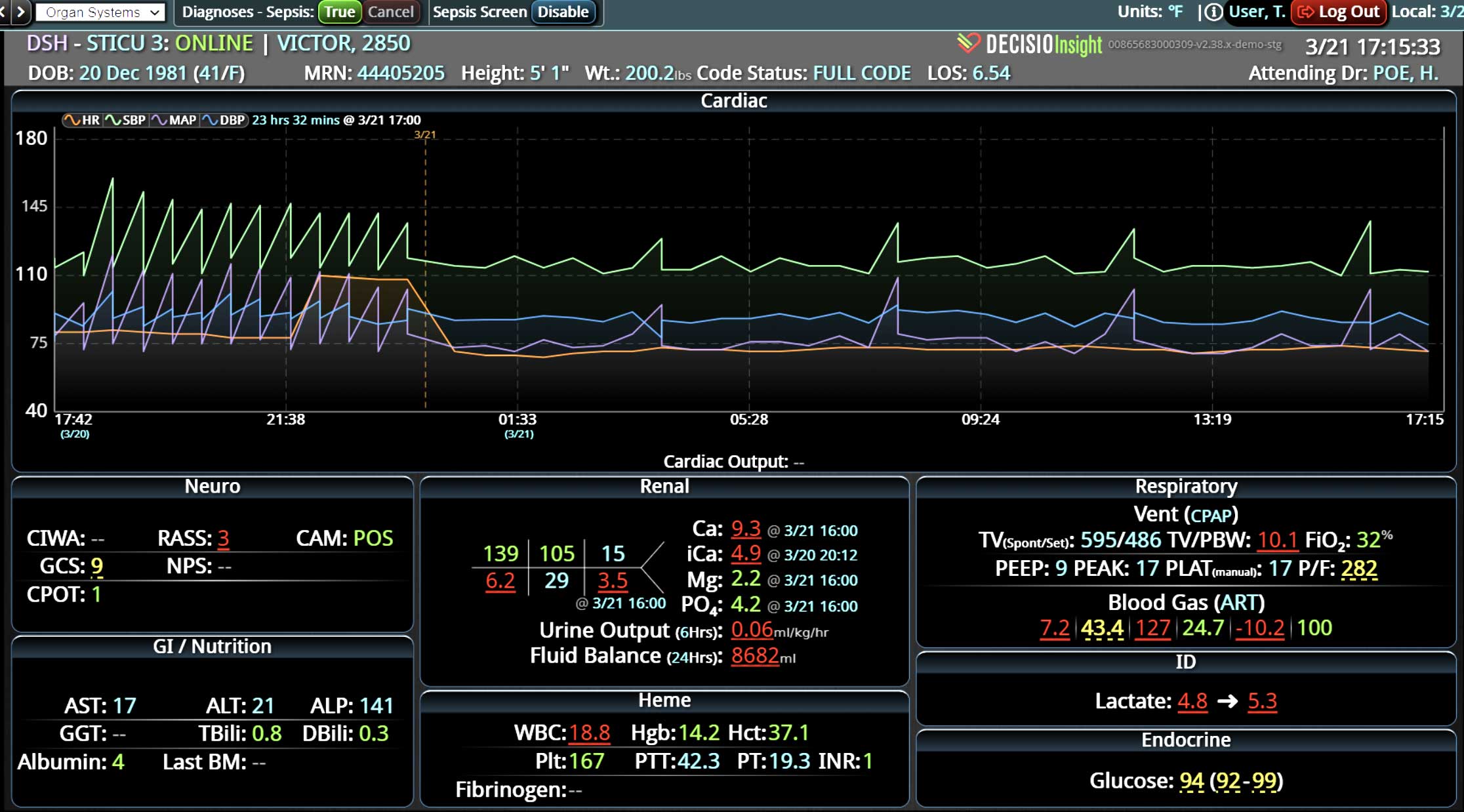
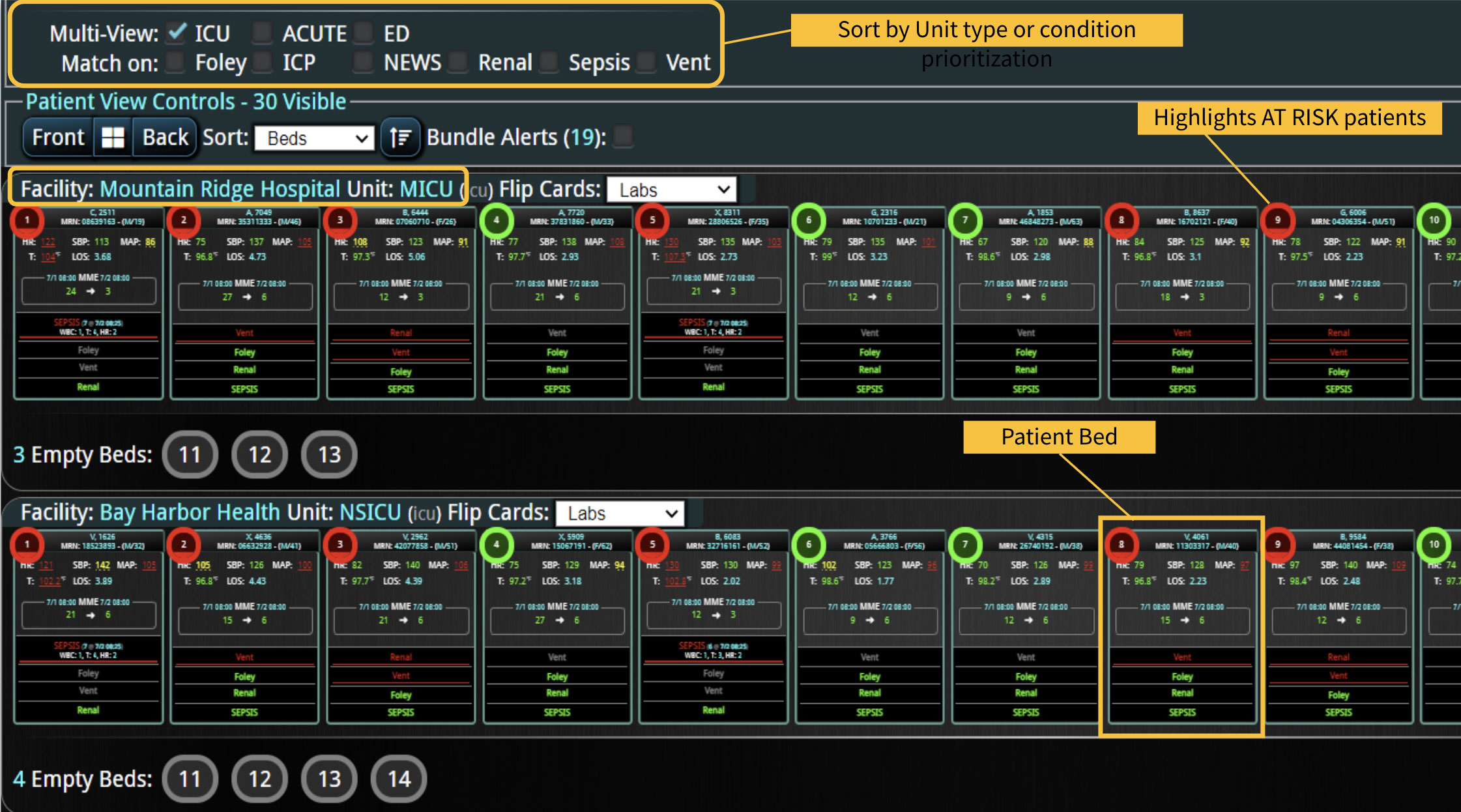
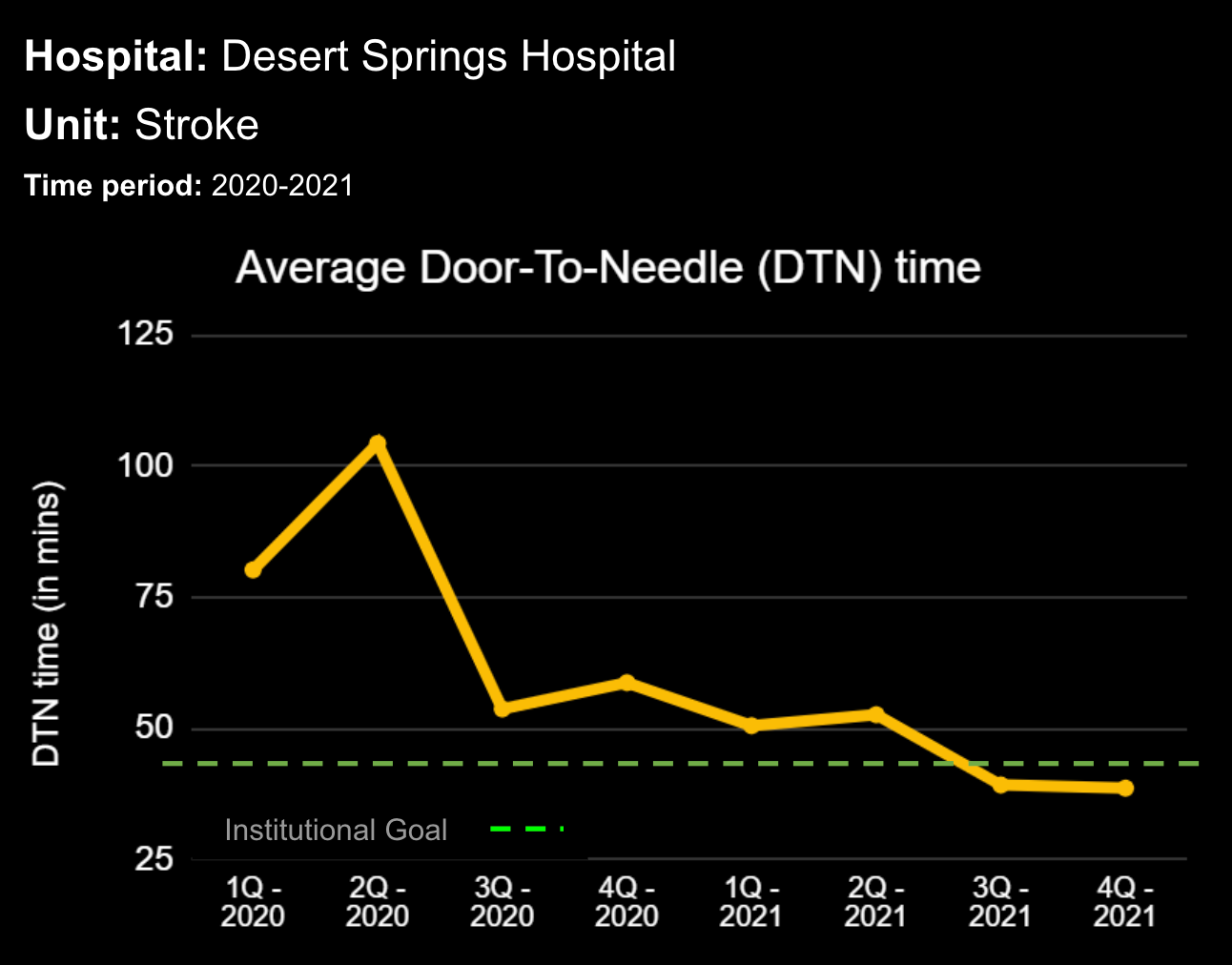
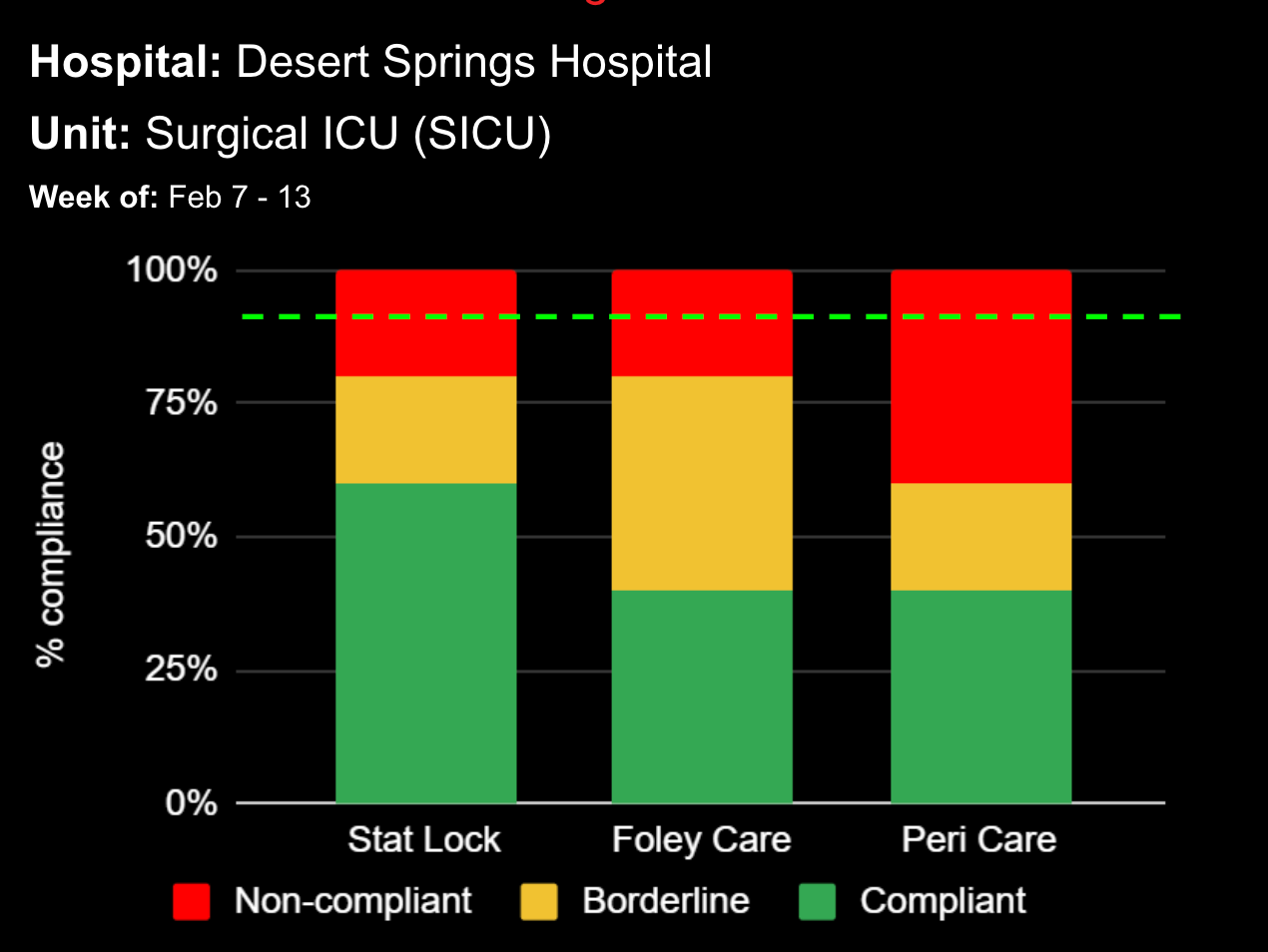
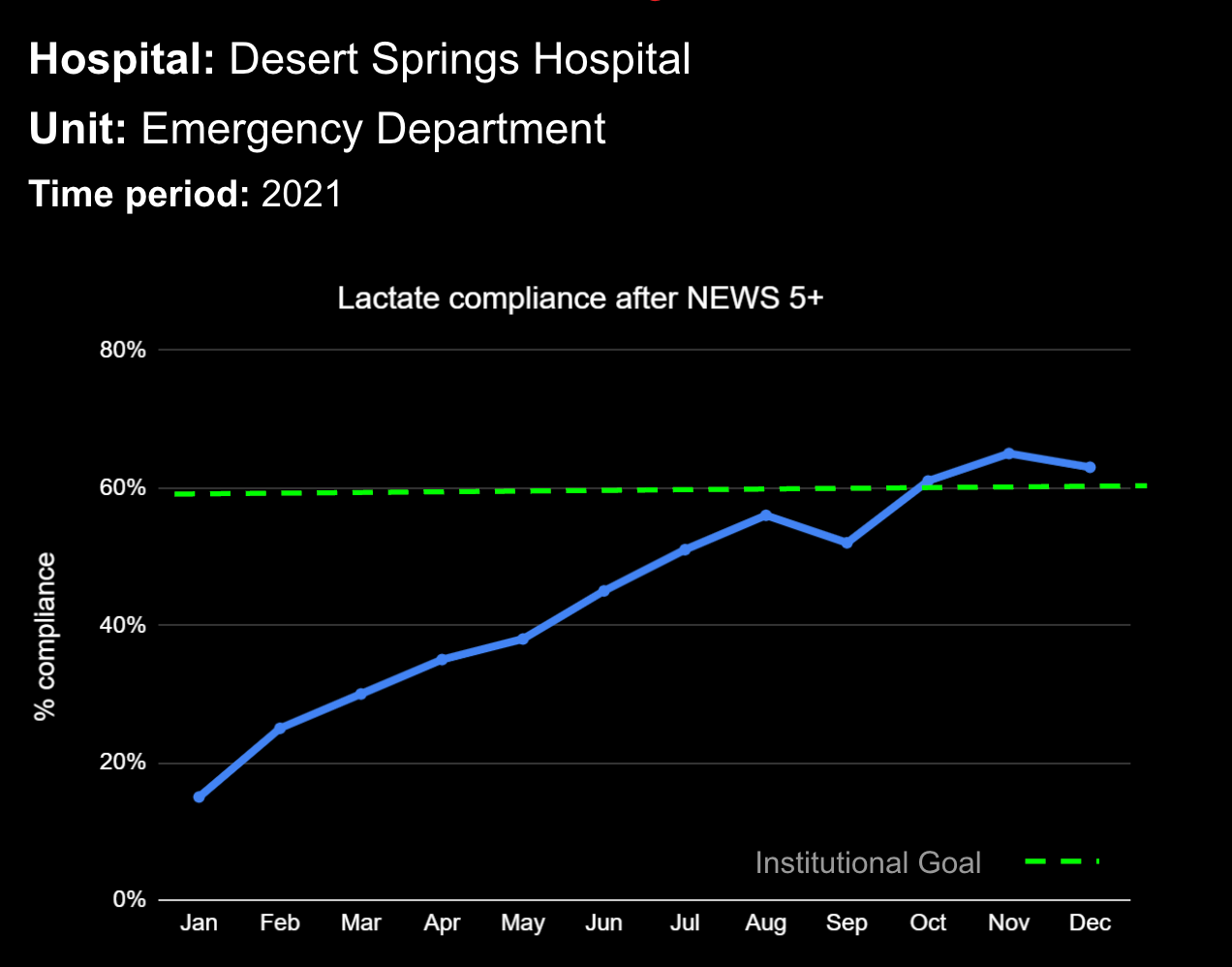
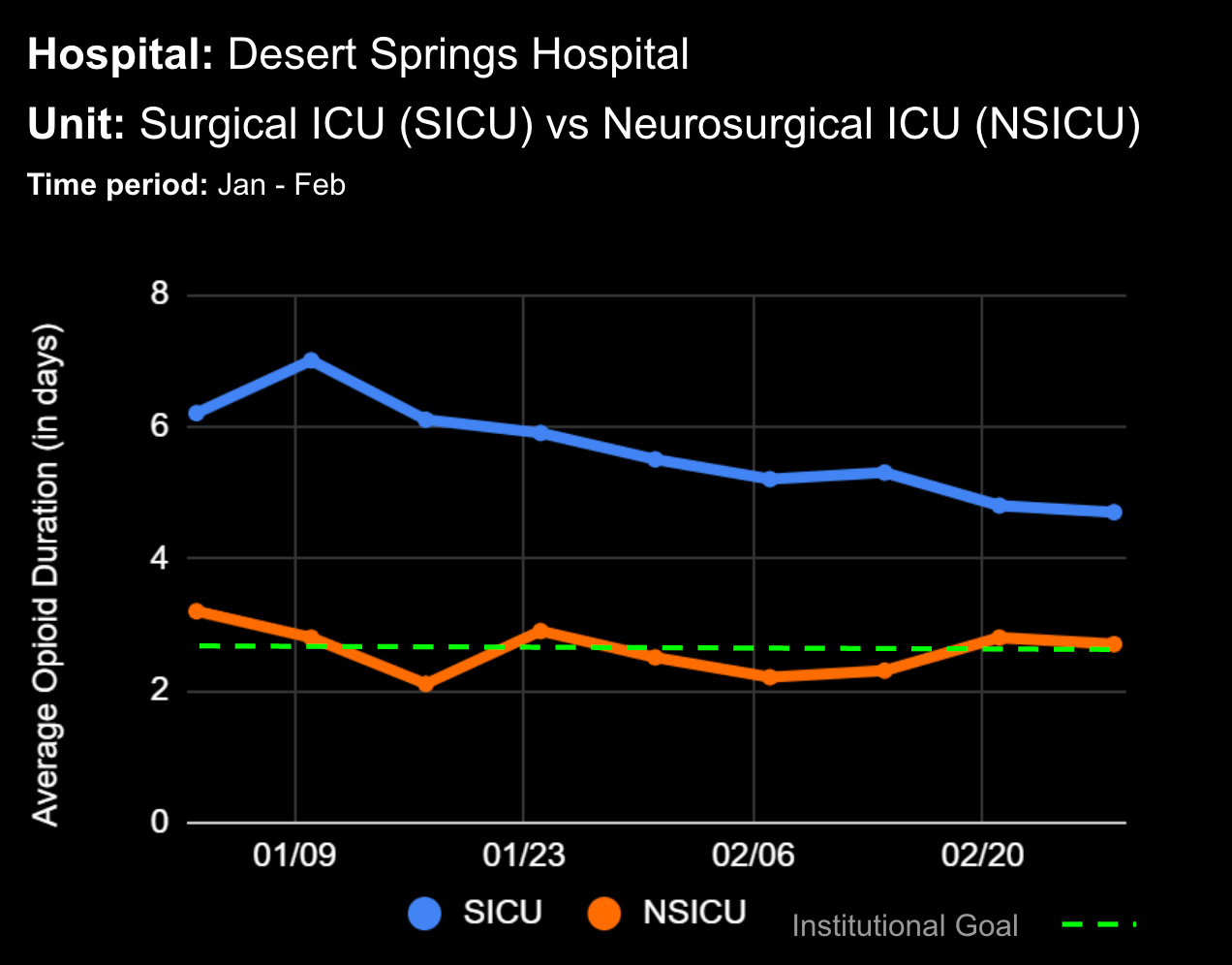
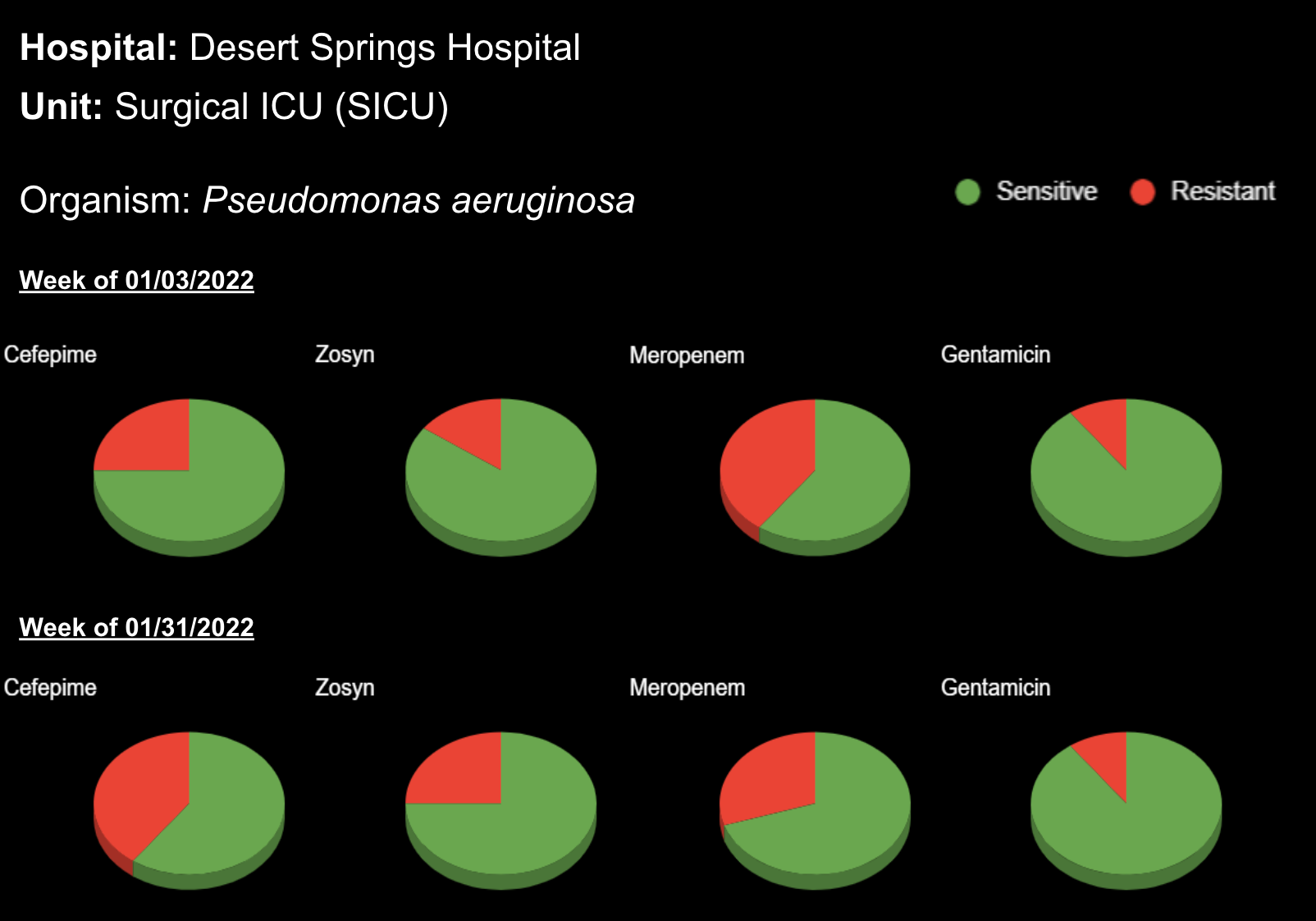
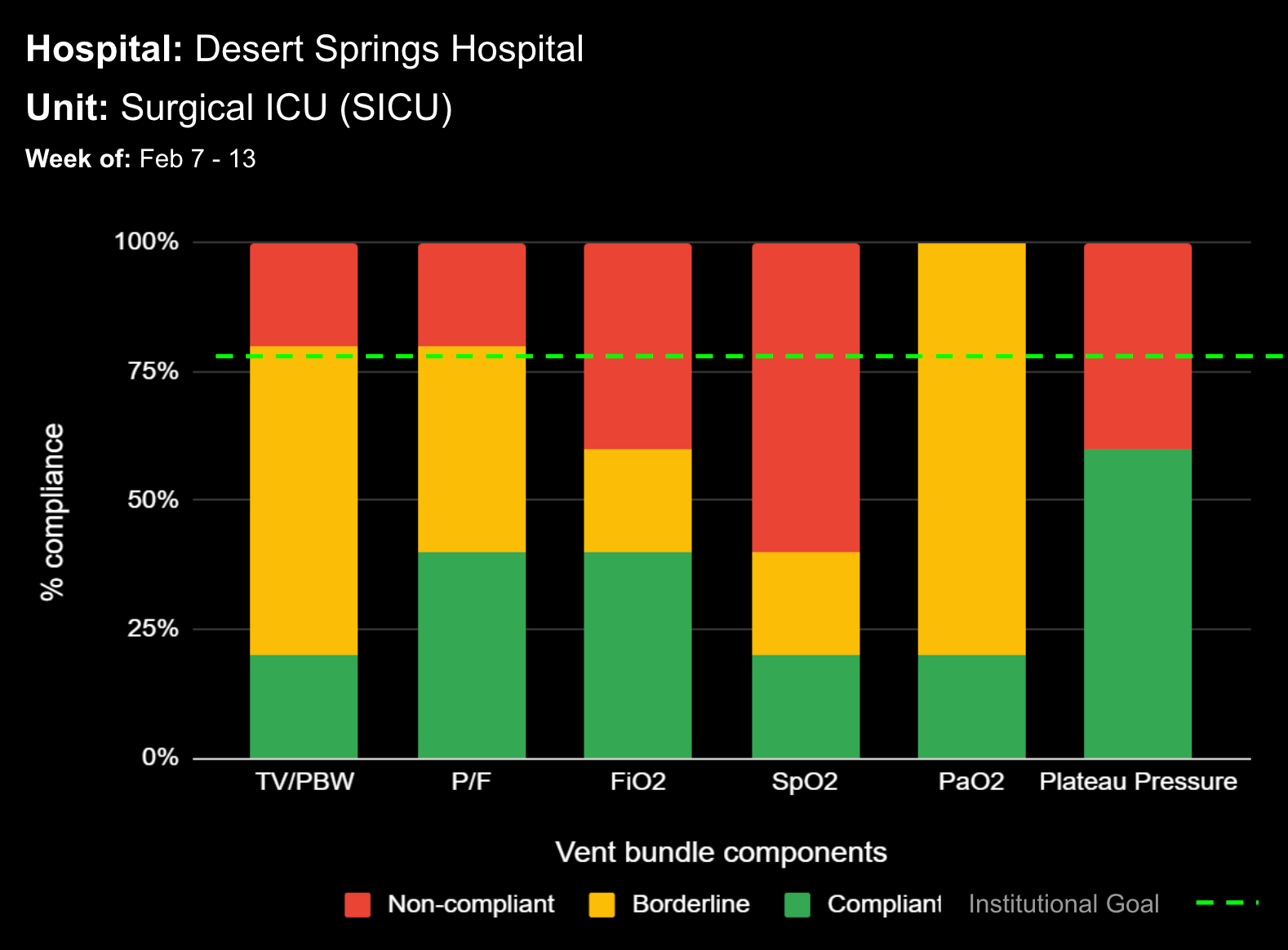
18 Jul Enhancing Family Communication at the Bedside with Clinical Decision Support Software
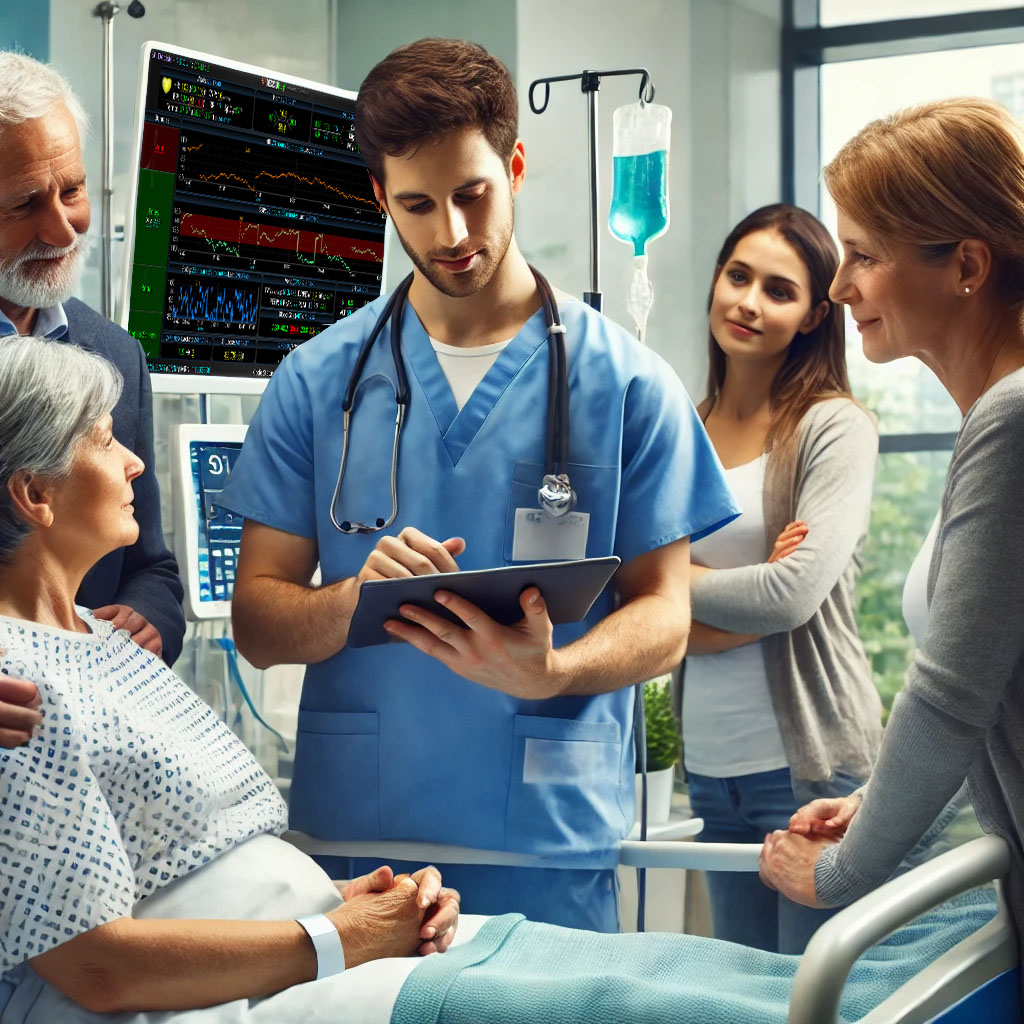
Clinical decision support (CDS) software plays a pivotal role in healthcare by providing clinical teams with evidence-based tools and information to enhance decision-making processes. It integrates clinical data from multiple sources to offer real-time guidance, improving accuracy in diagnosis, treatment plans, and overall patient care outcomes. Source: An overview of clinical decision support systems: benefits, risks, and strategies for success Effective communication between healthcare providers, patients, and their families is crucial for ensuring that patients receive the best possible care. It helps to build trust, reduce anxiety, and improve adherence to treatment plans, ultimately leading to better patient outcomes and higher satisfaction levels among family members. Challenges in Family Communication at the Bedside Family communication at the bedside often faces significant challenges that can impact patient care and satisfaction. These challenges include language barriers, varying levels of health literacy among family members, and the emotional stress and anxiety experienced by families in a hospital setting. These obstacles can lead to misunderstandings about the patient's condition and treatment plan, increased anxiety, and potential dissatisfaction with the care provided, highlighting the need for effective communication strategies and tools. [1] The Role of CDS Software in Enhancing Family Communication The integration of CDS software at the bedside can...