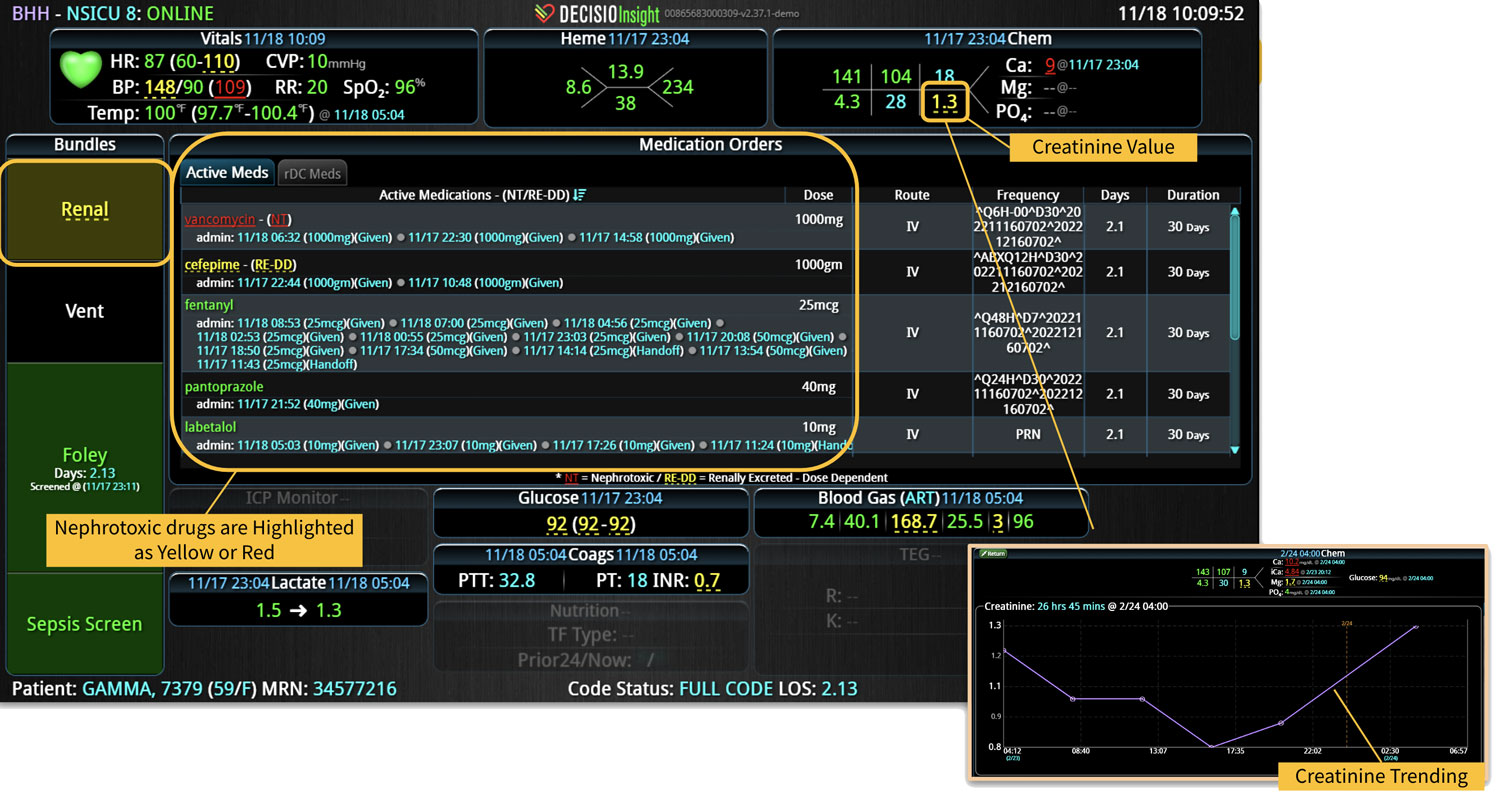
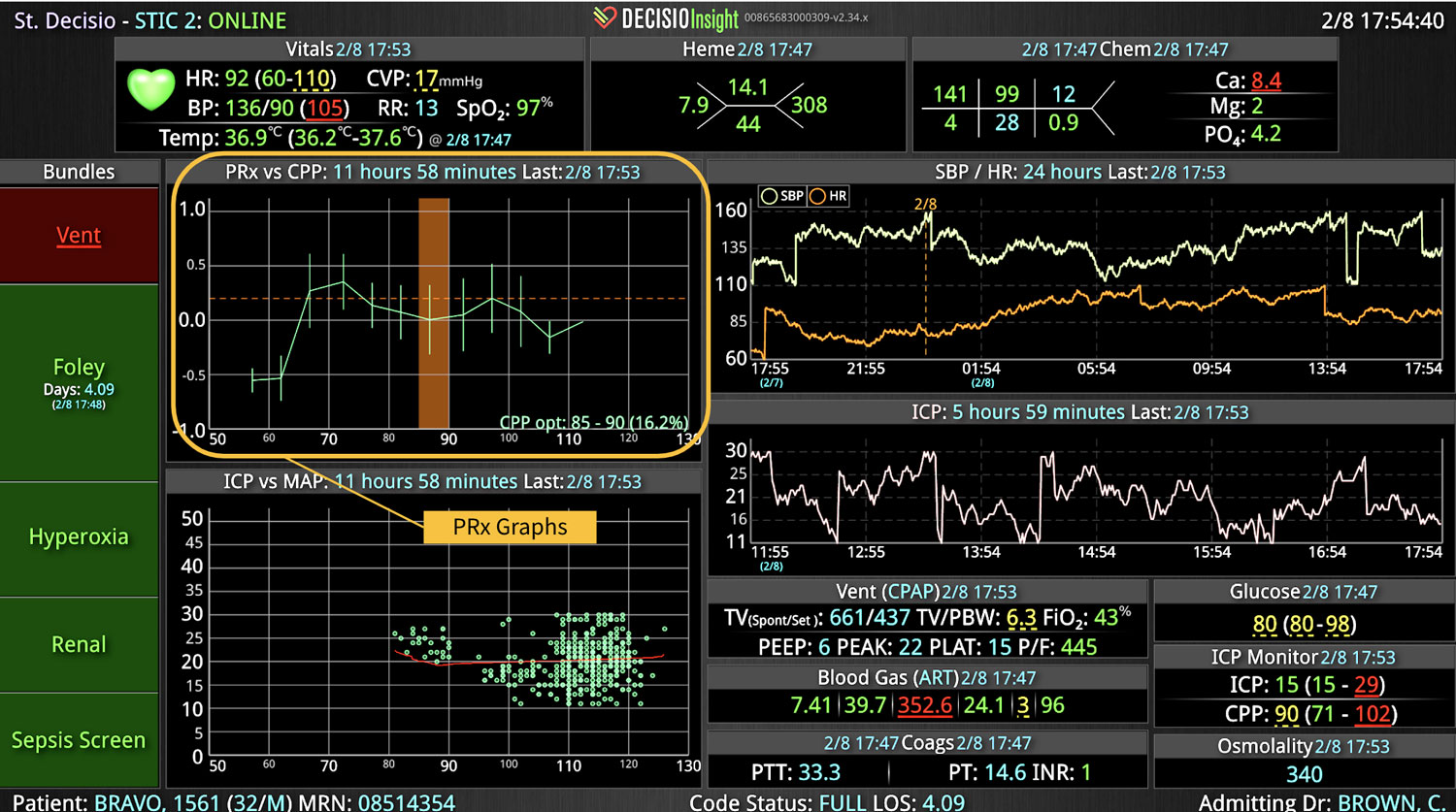
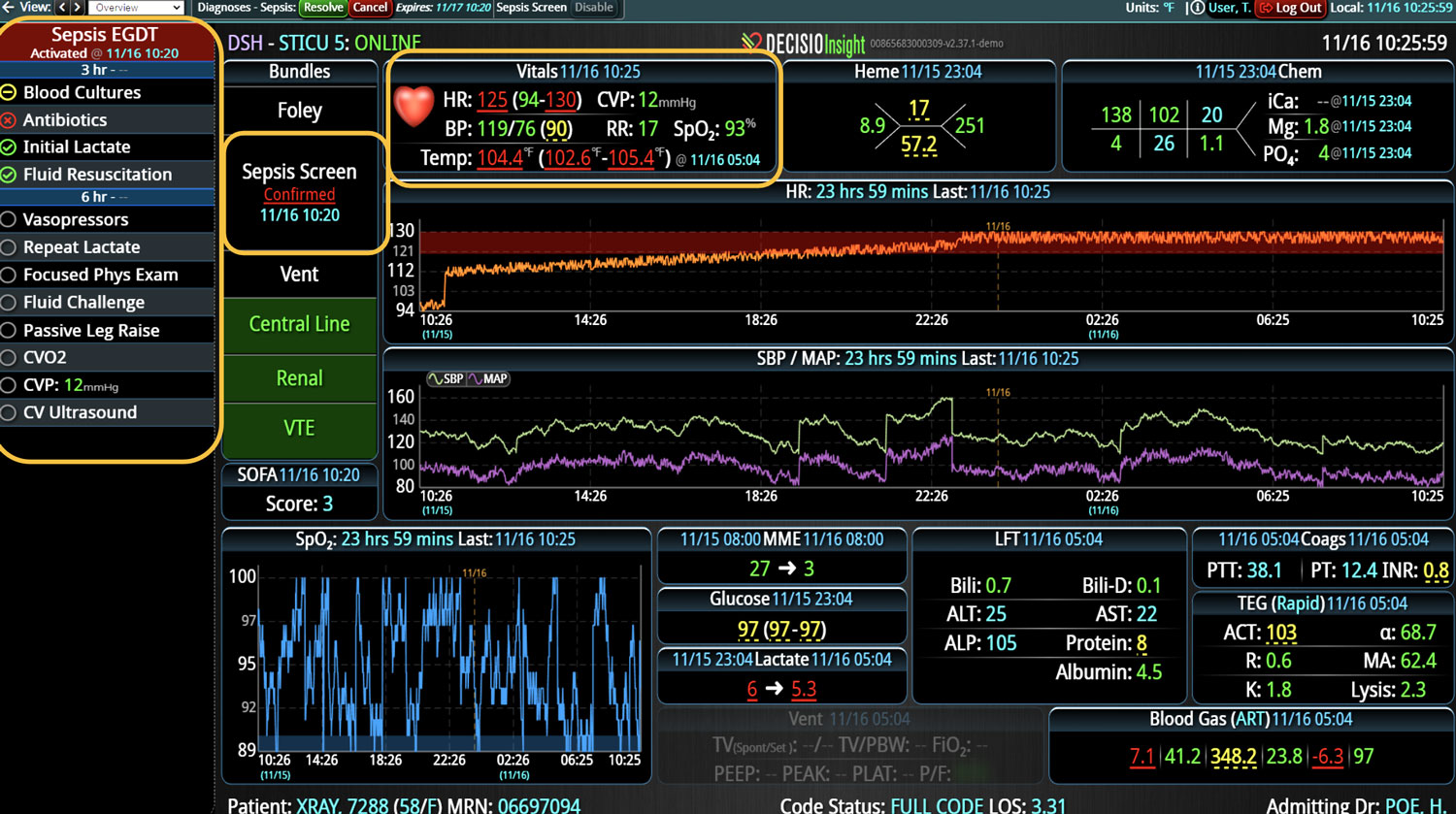
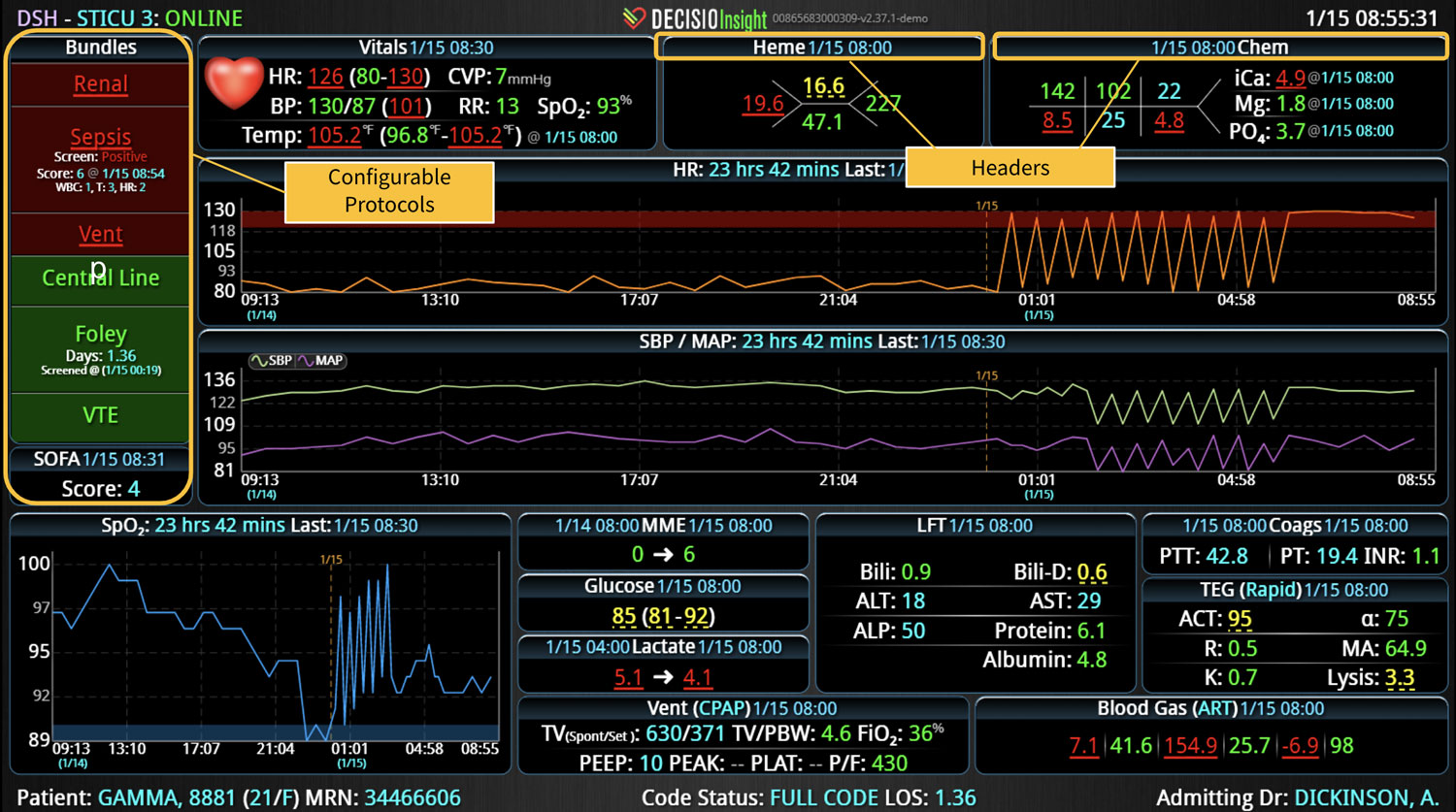
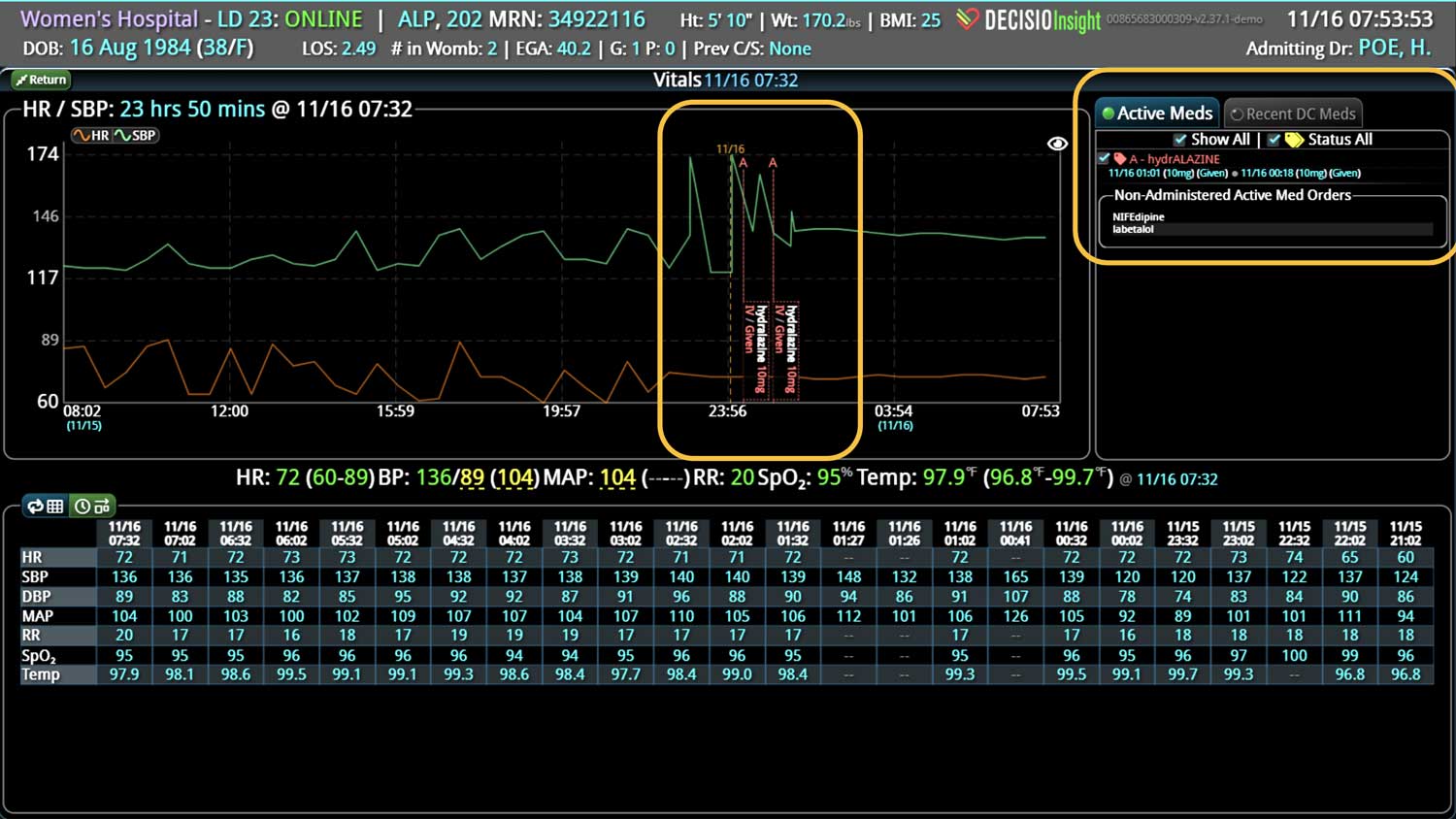
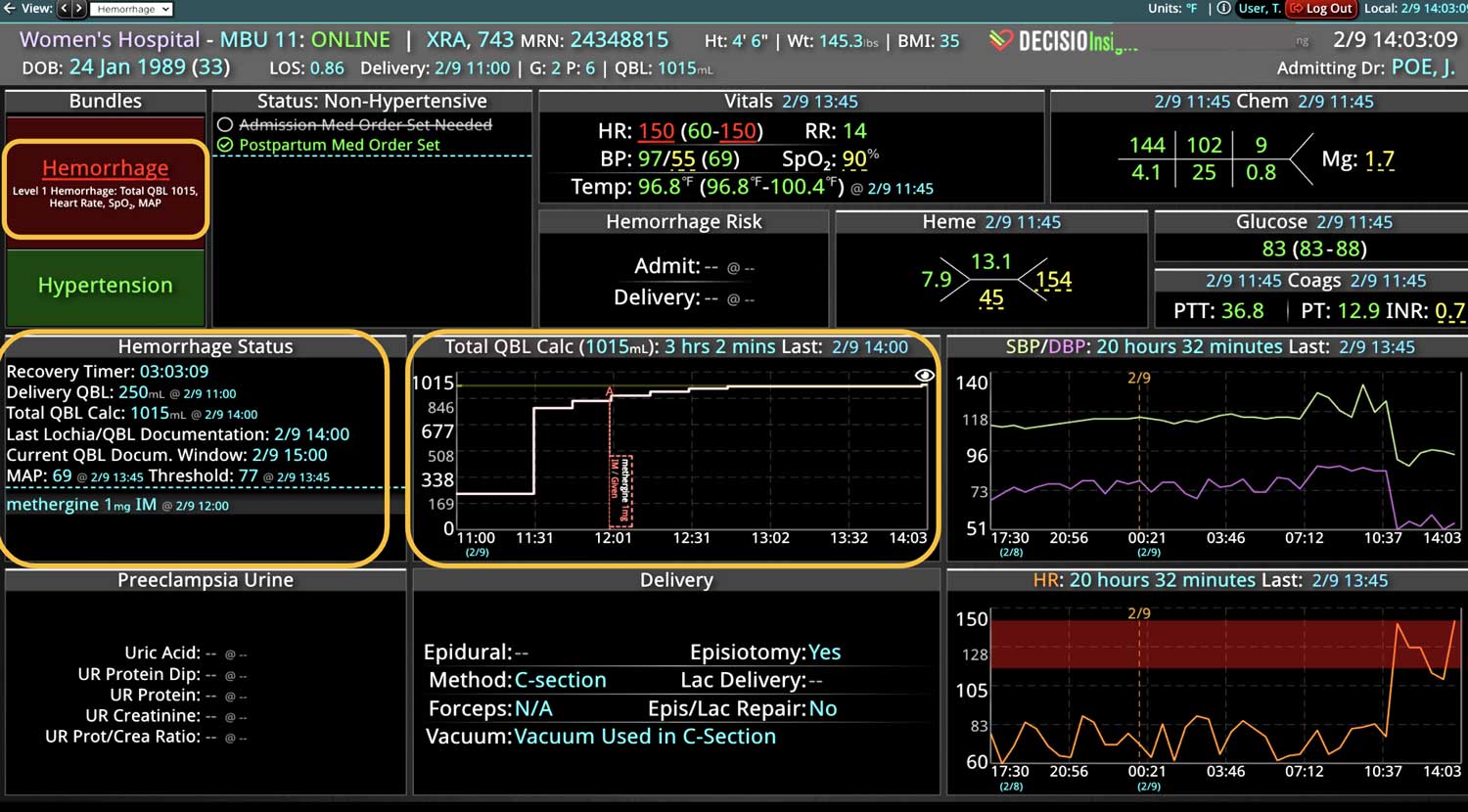
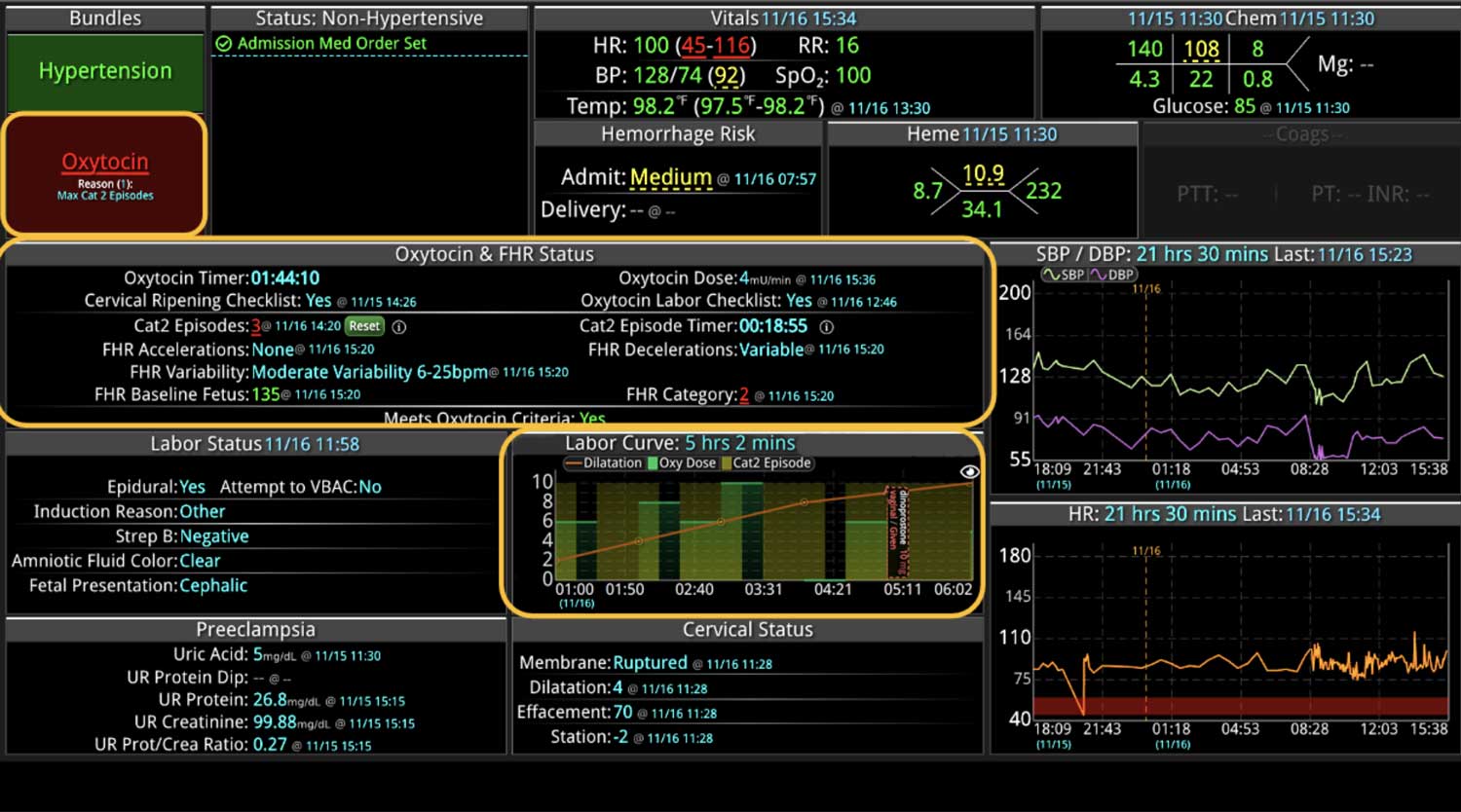
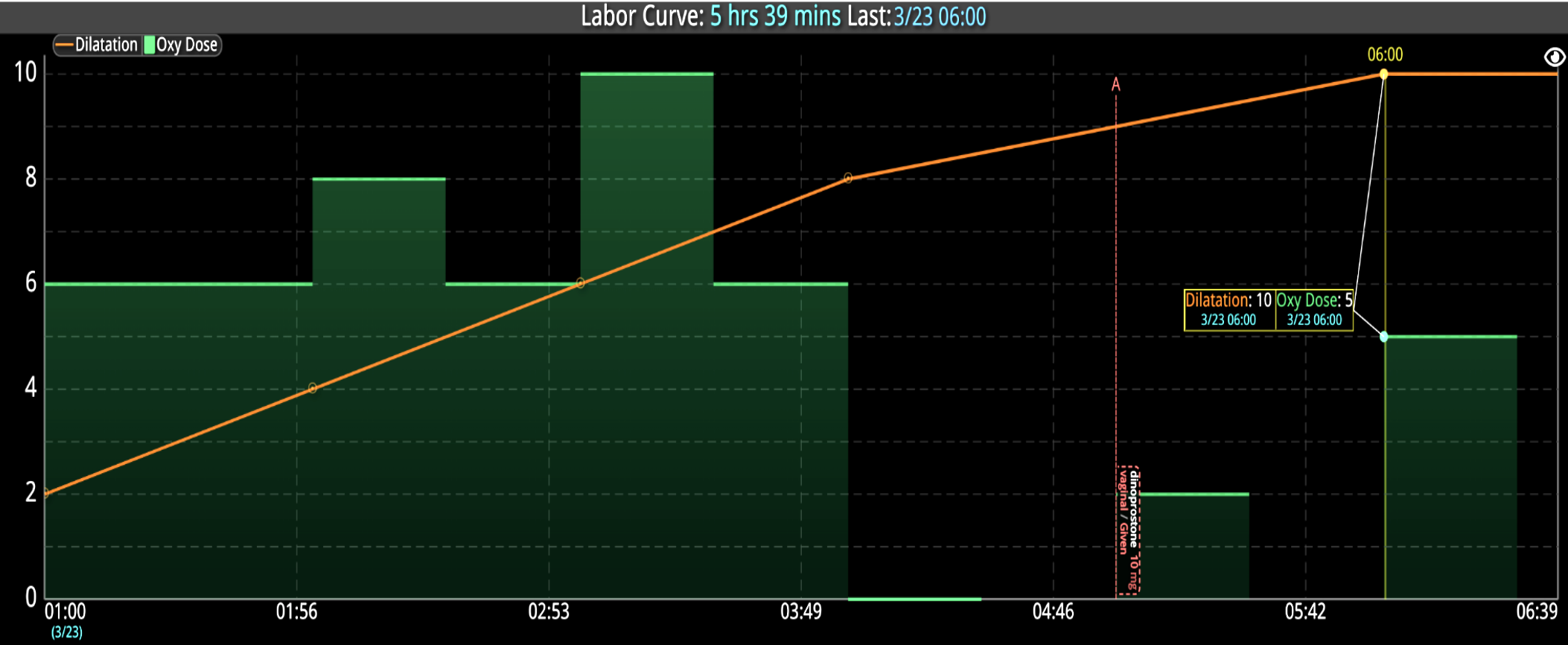
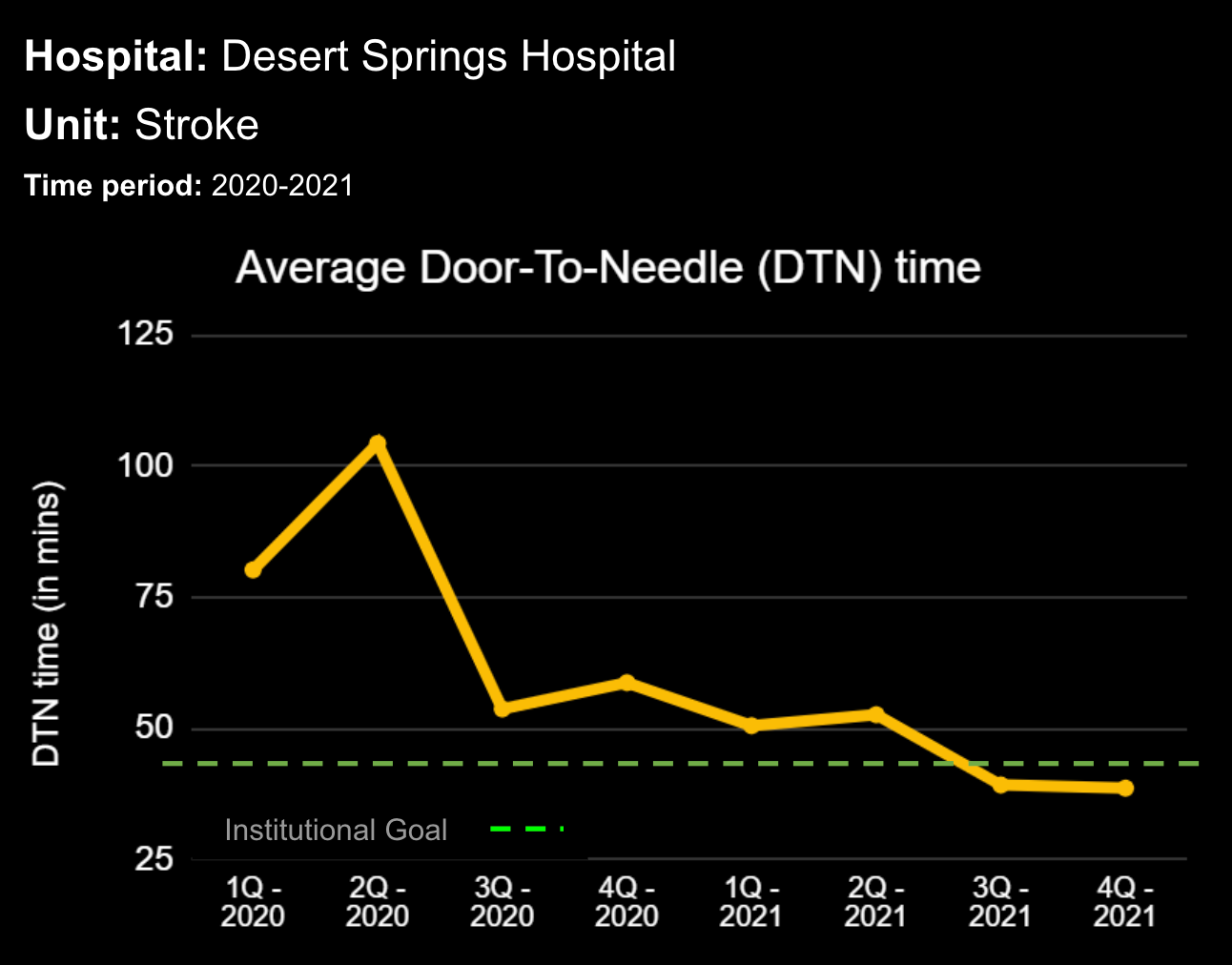
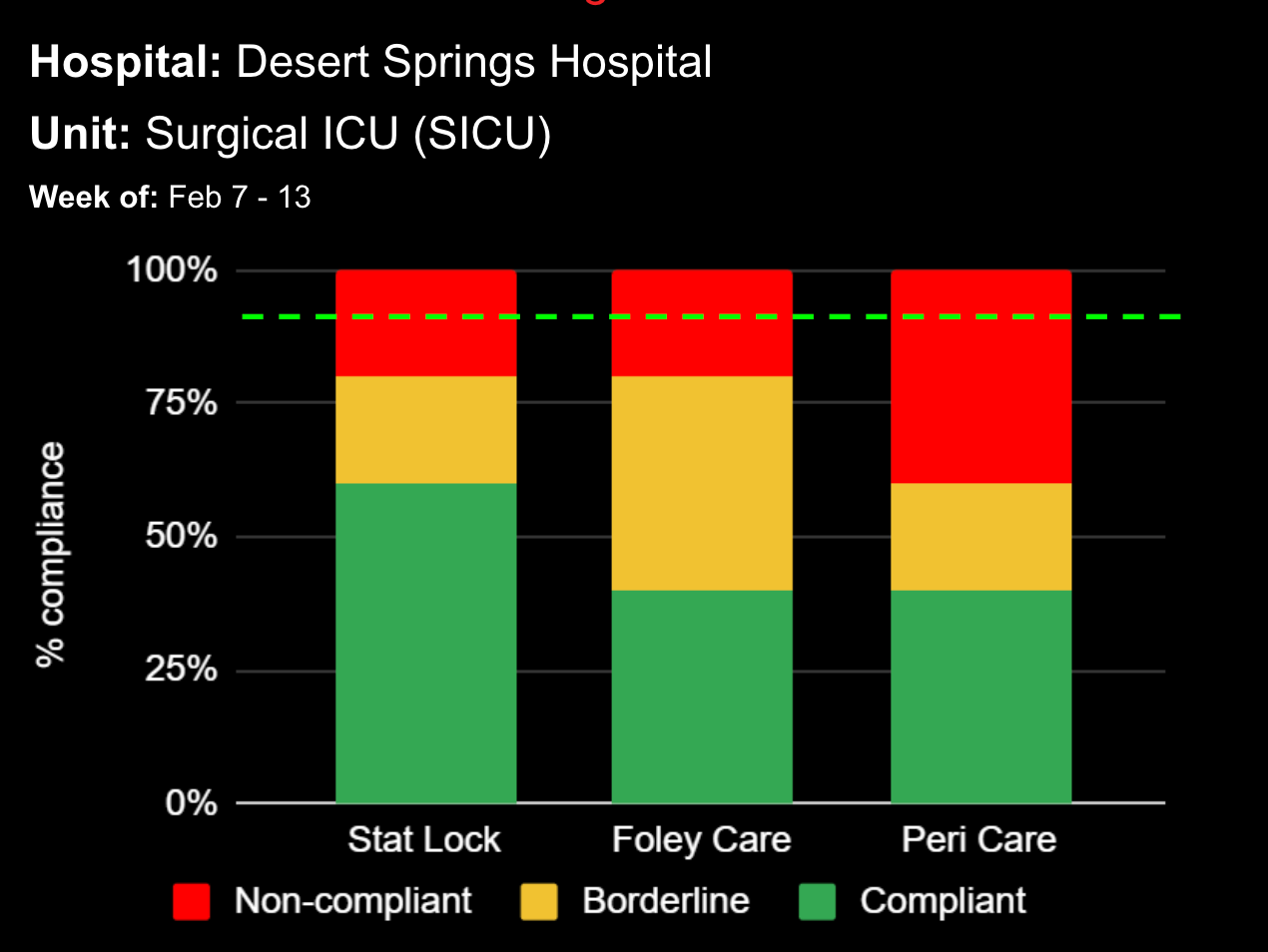
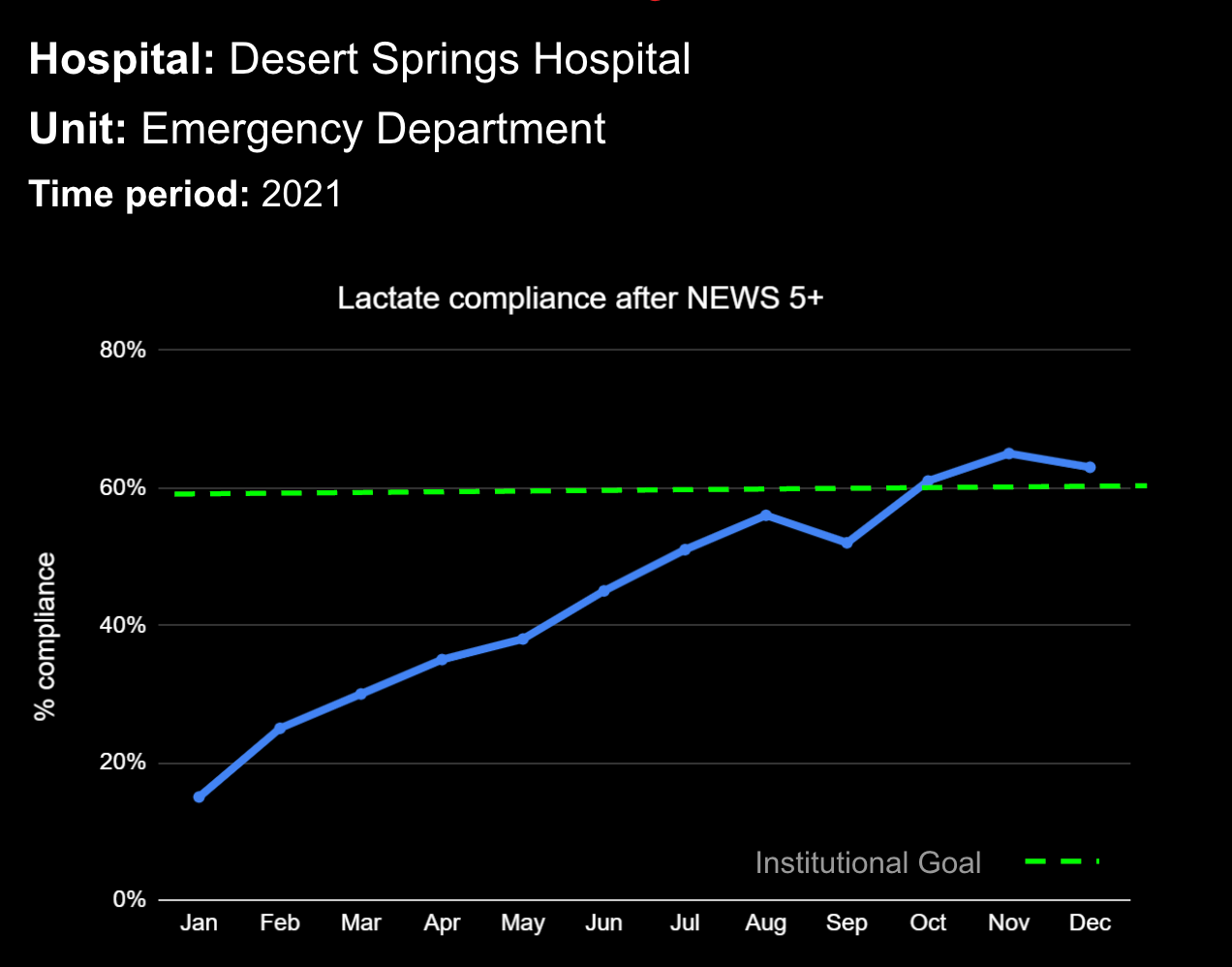
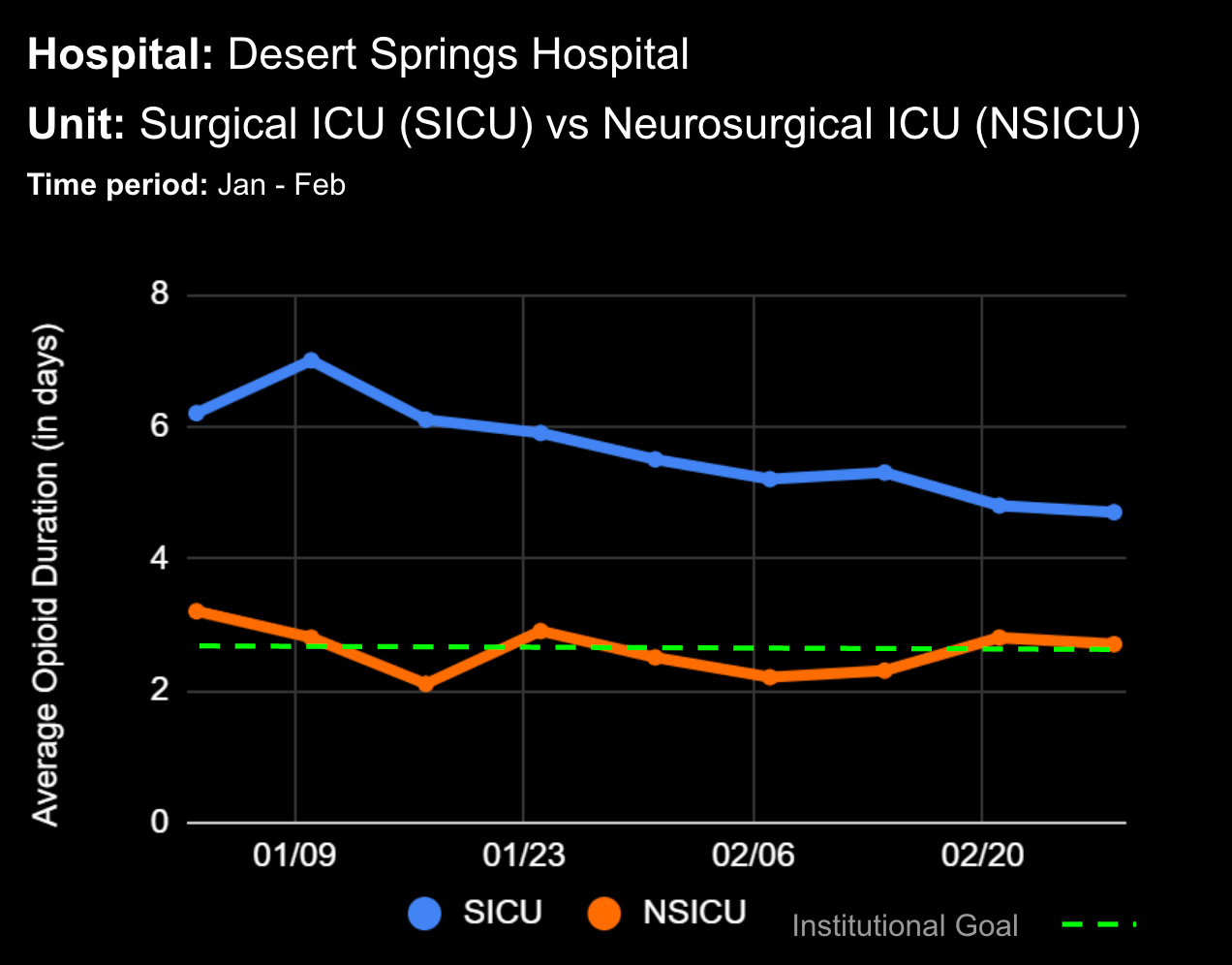
14 Jun Enhancing Hospital Operations with Rapid Response Teams and Virtual Nursing
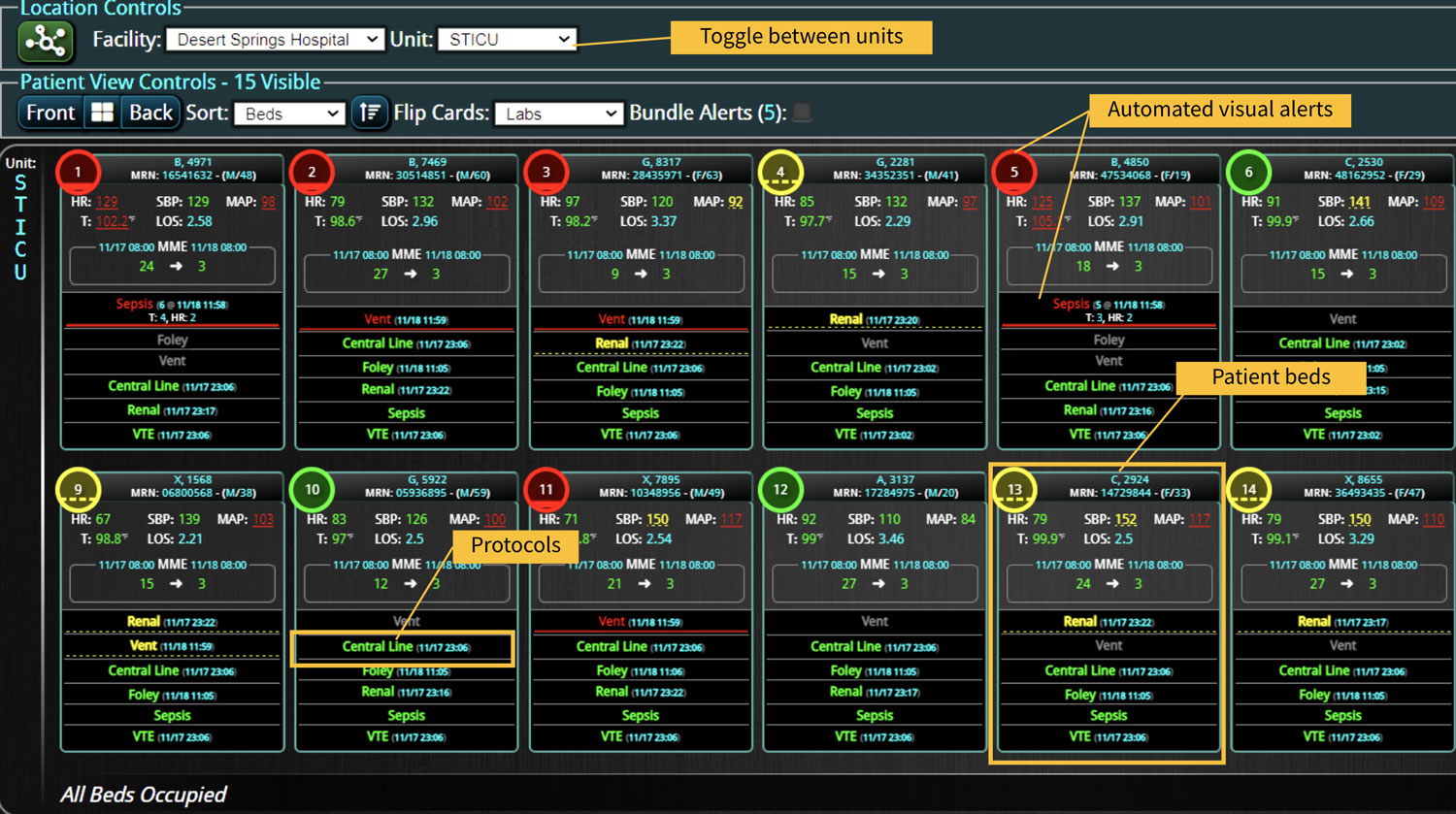
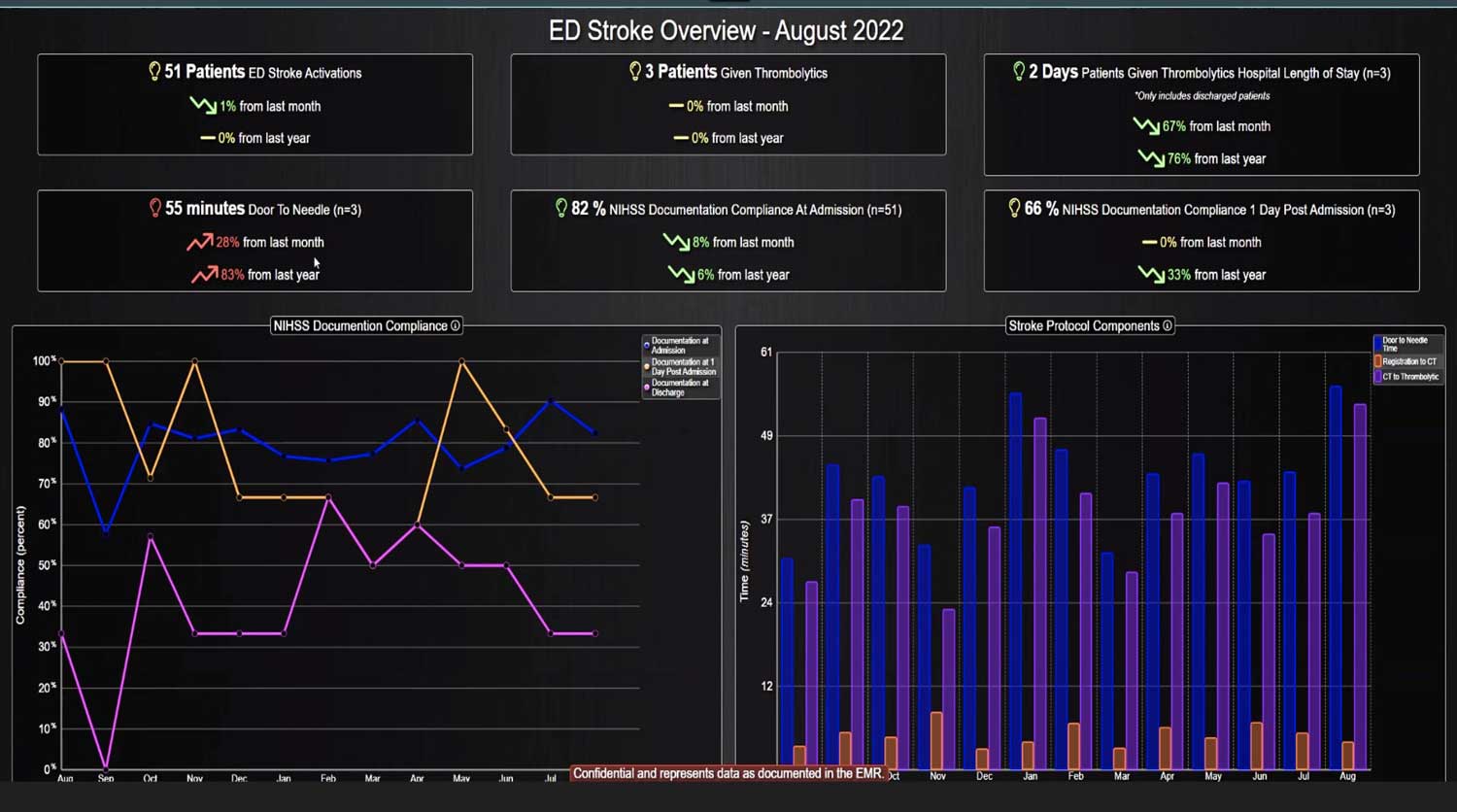
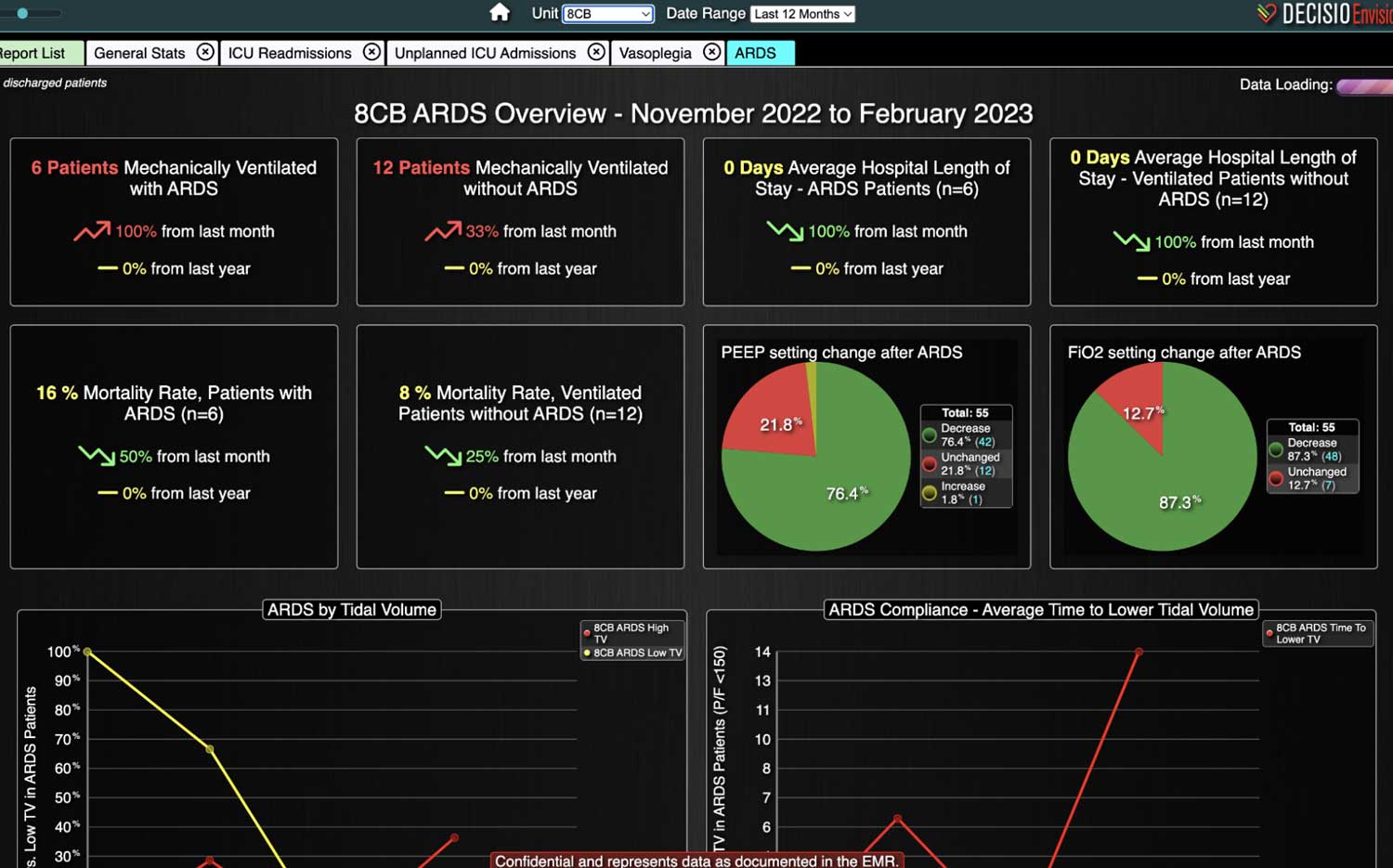
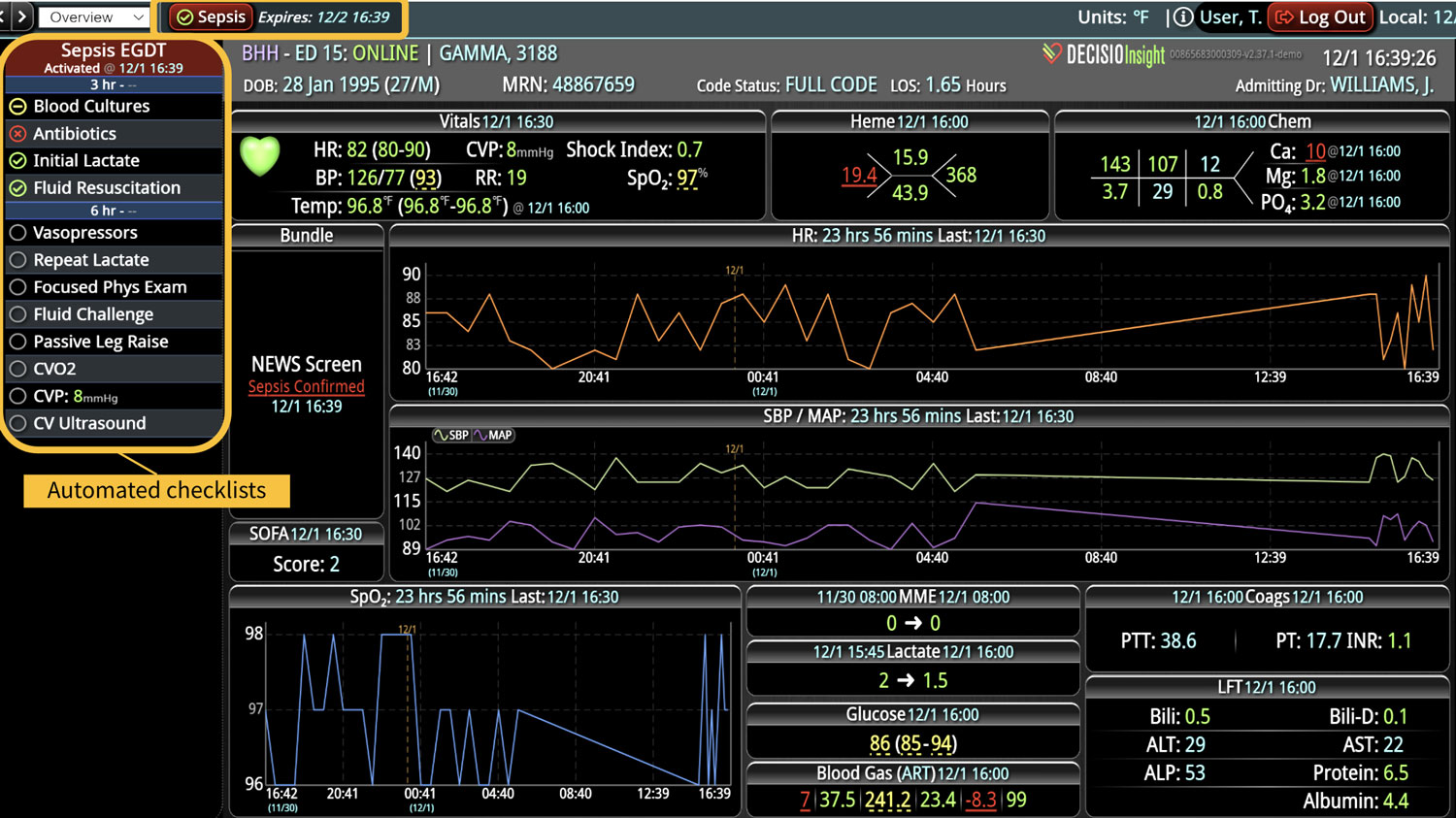
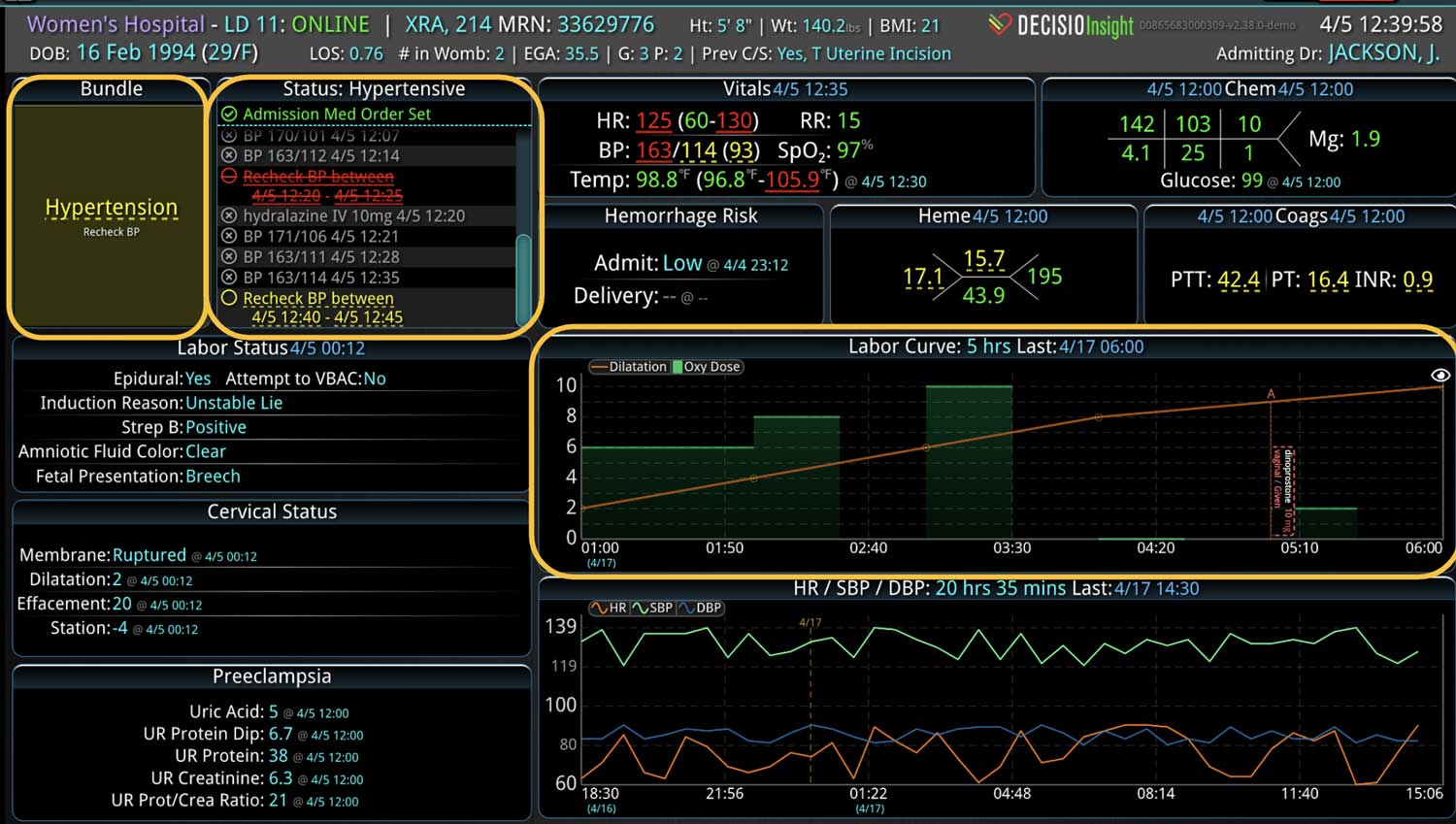
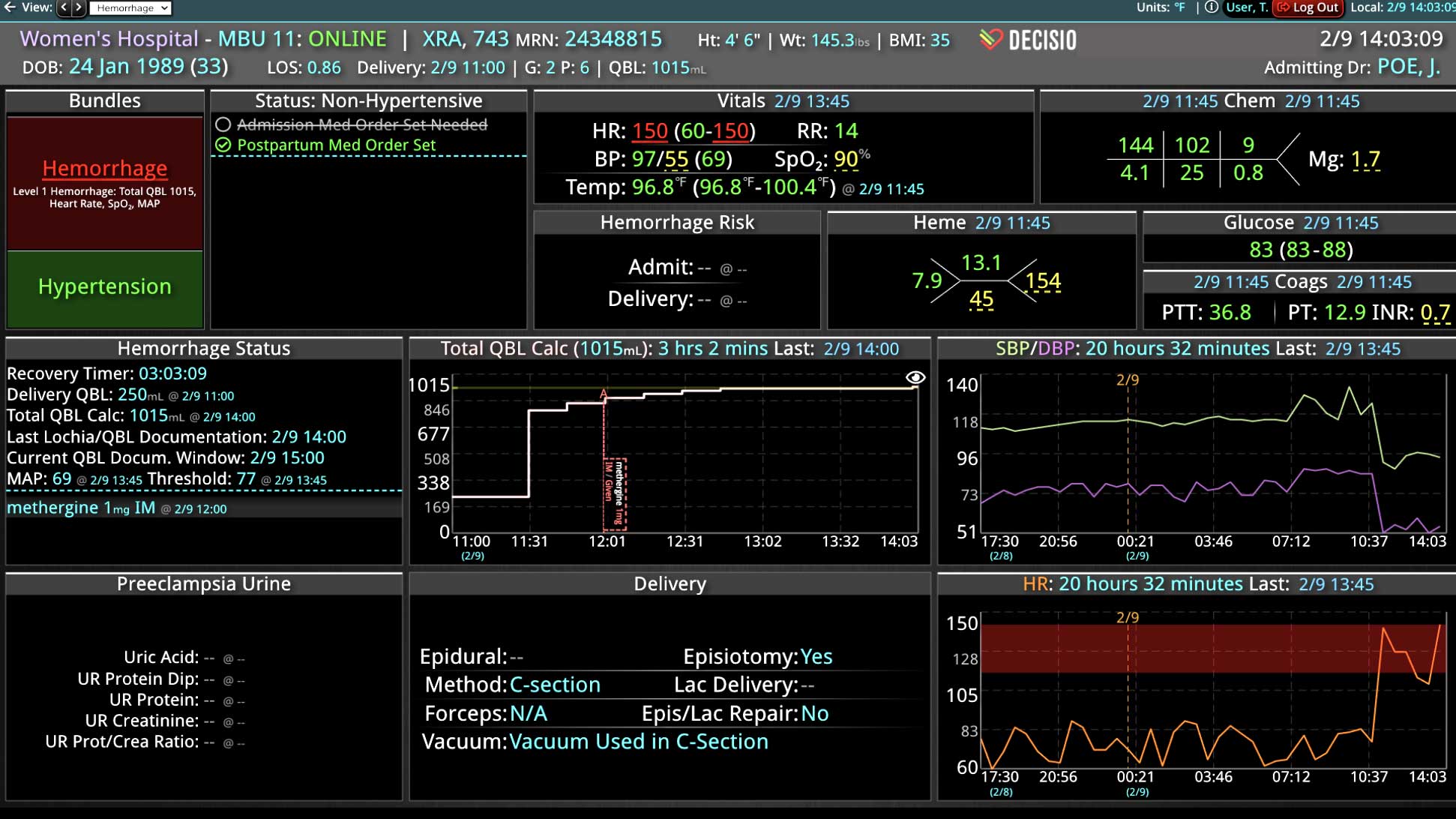
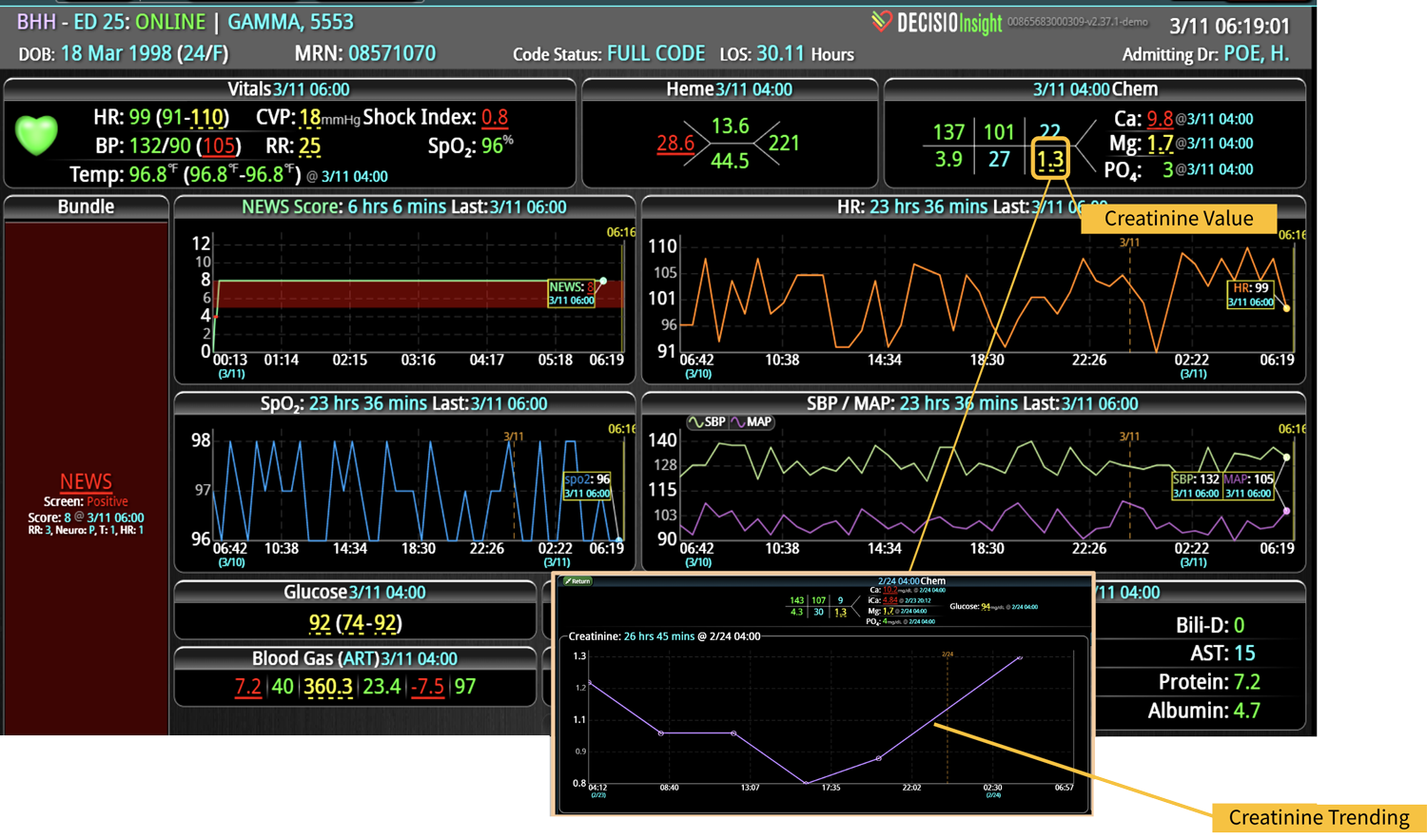
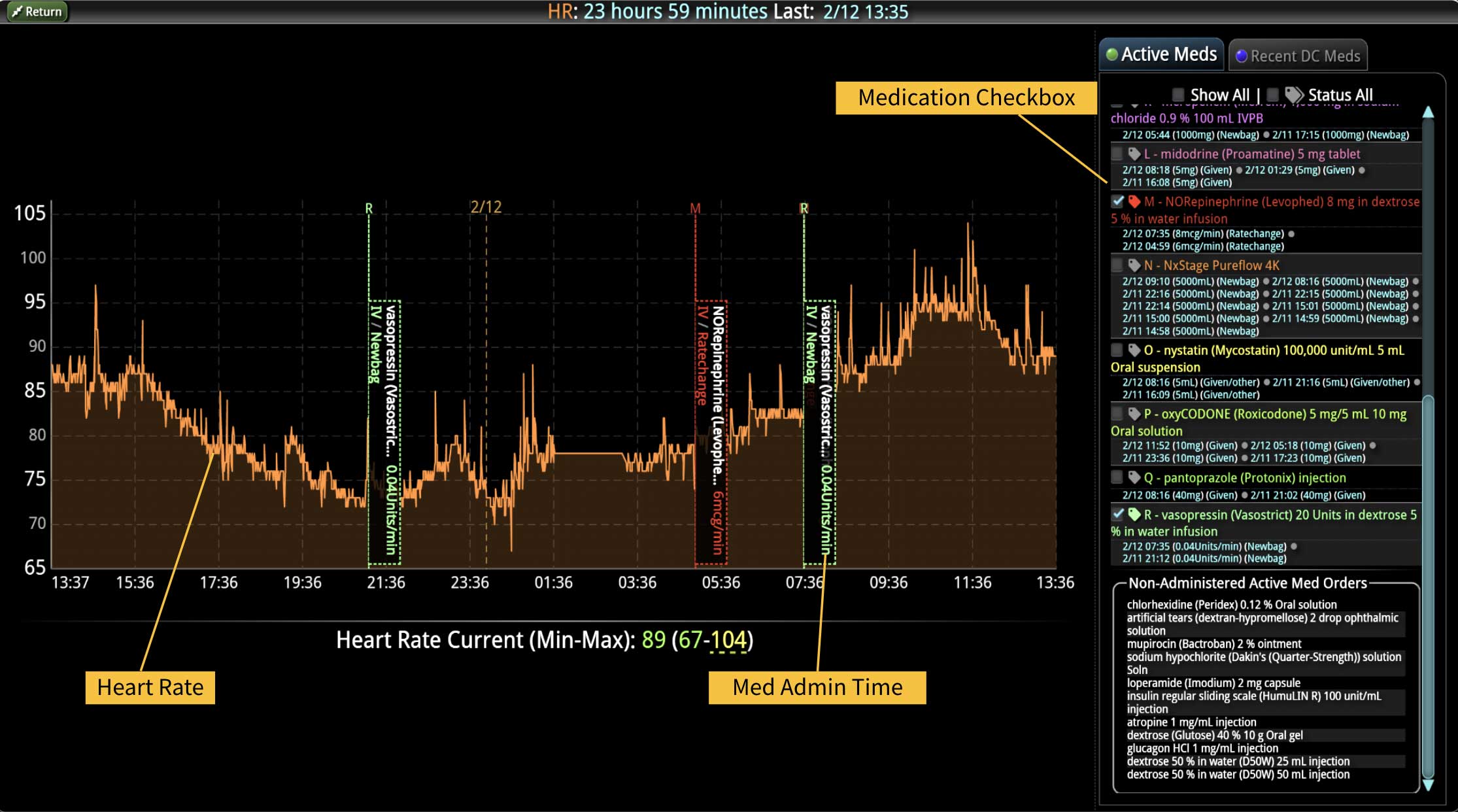
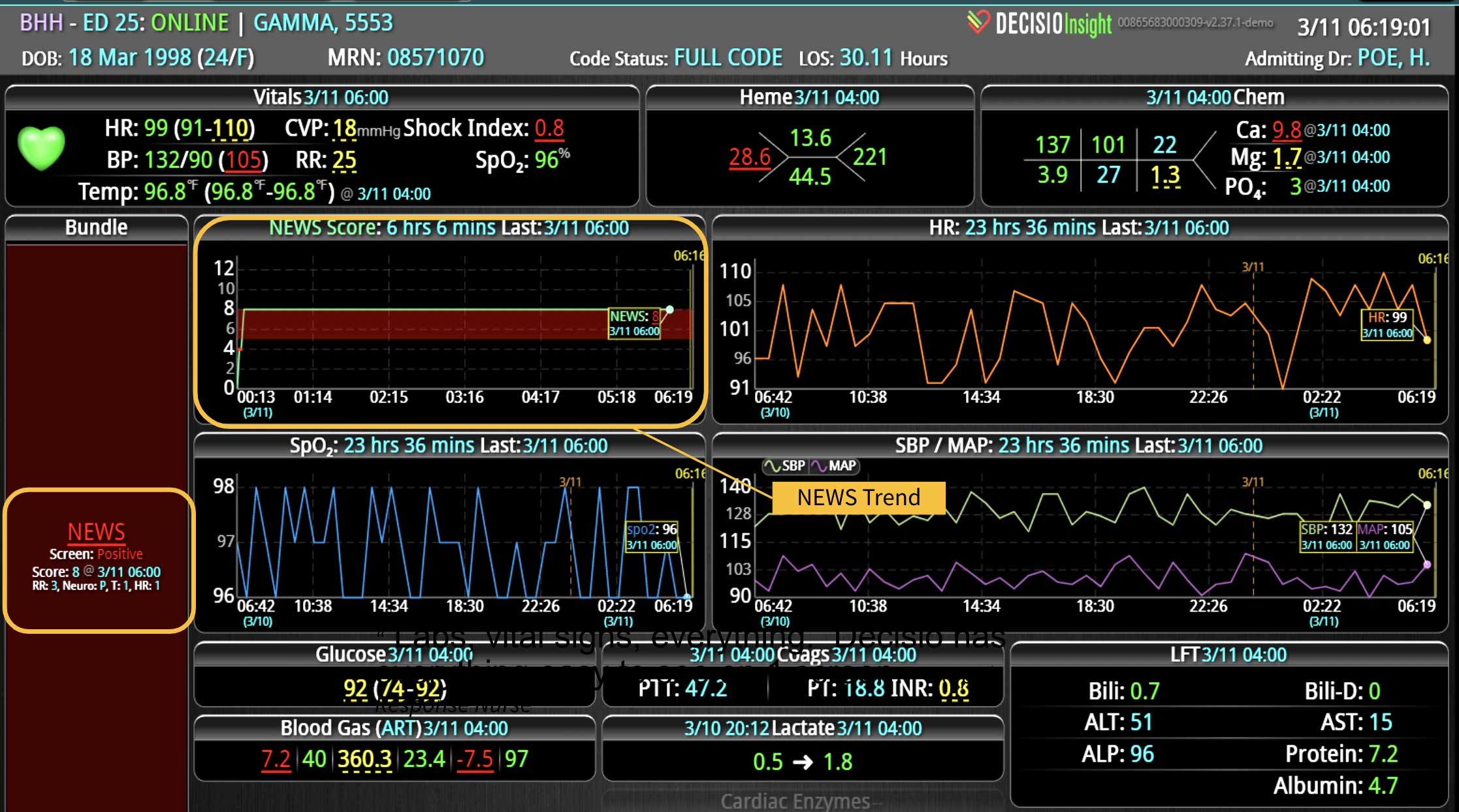
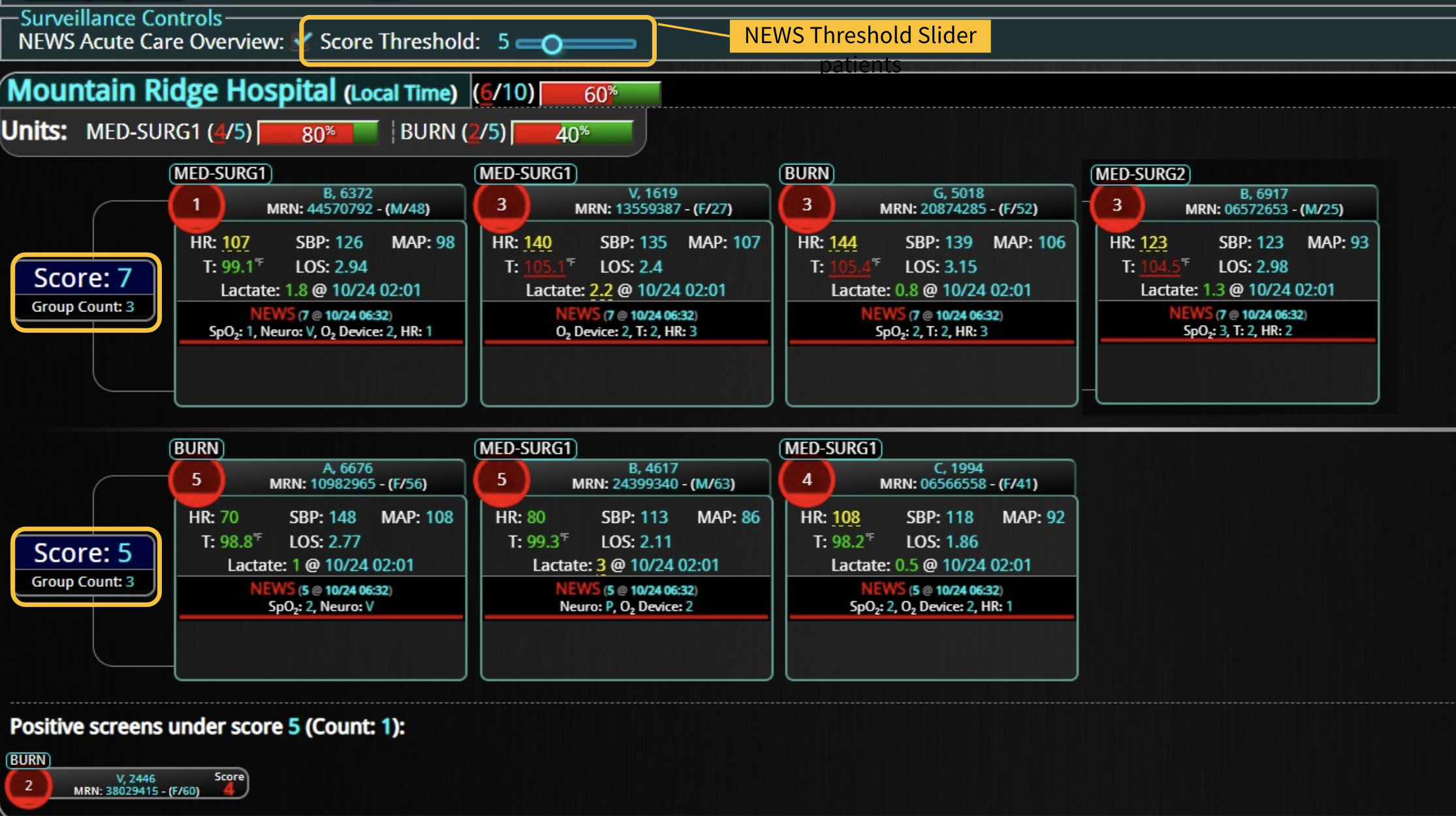
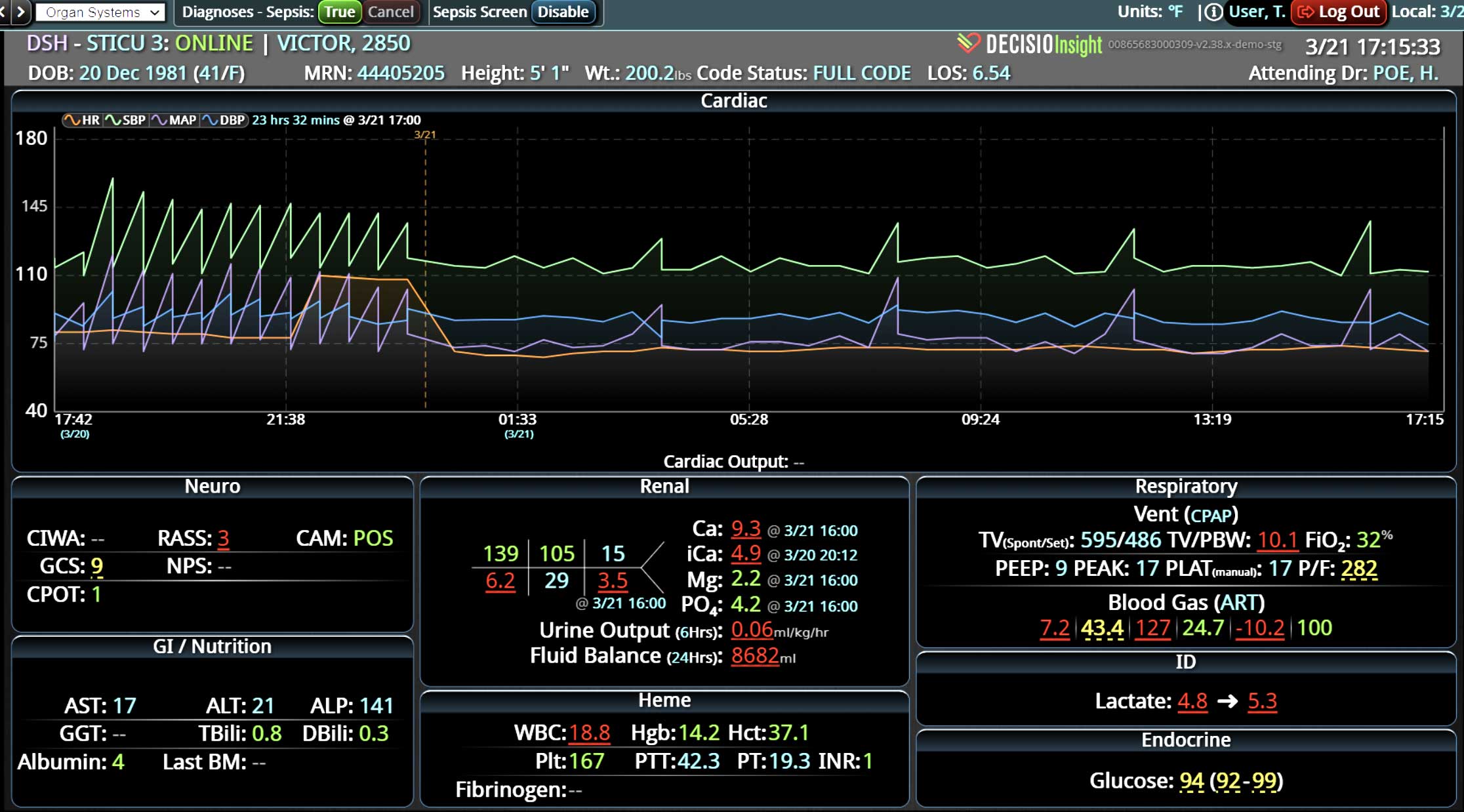
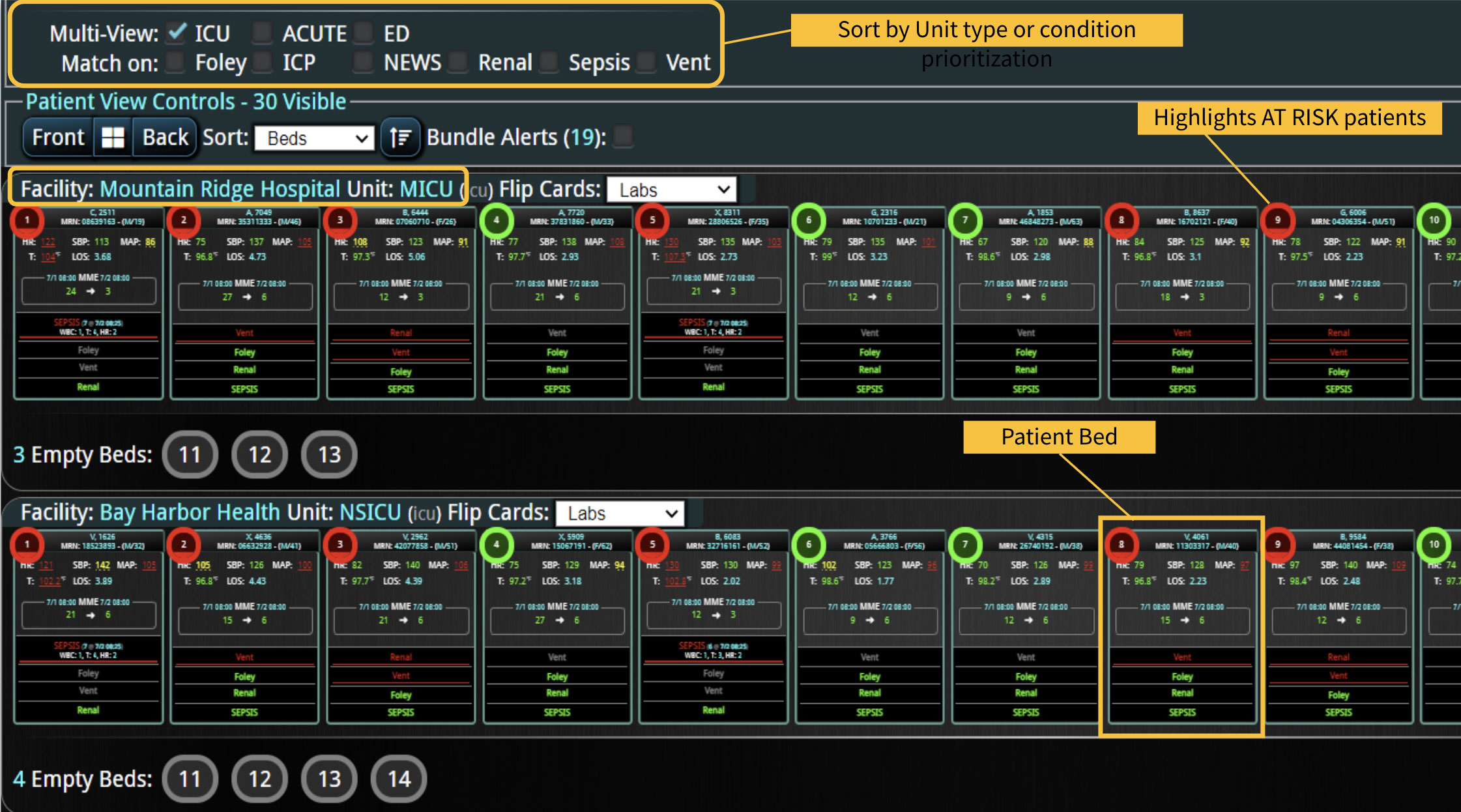
Rapid Response Teams (RRTs) do much more than just respond to emergencies; they play a multifaceted role in enhancing both patient care and hospital operations. They are not merely a safety net for the hospital; they act as the glue that holds the hospital together. Their effectiveness is significantly enhanced when supported by technology. Hospitals that have implemented an RRT and incorporated clinical software into their workflow have seen numerous benefits. We have previously discussed some of these advantages, such as improved patient outcomes, enhanced communication among clinical teams, and increased efficiency in emergency response. However, there are additional challenges, such as clinician burnout and staffing gaps, that can be addressed with the integration of virtual nursing. Virtual Nursing: A Game Changer for Hospital Efficiency Virtual nursing helps address these common challenges while offering numerous benefits to both clinicians and patients. In order to maximize these benefits and enhance the efficiency of these remote teams, it is crucial to integrate technology into clinical workflows. Let’s delve into some of these benefits in greater detail… Patient Care Enhanced Monitoring and Consultations: Further improve patient care by providing real-time remote monitoring and facilitating immediate expert consultations. Protocol Compliance: Oversee compliance with protocols such as CAUTI and CLABSI...